Alternative Mechanisms of Carbon Fixation
advertisement

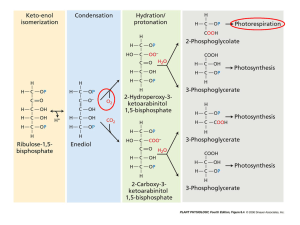
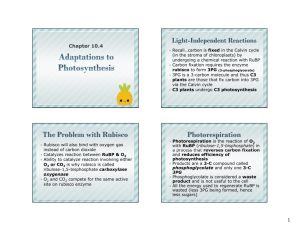
Allow for the entry of CO2 and exit of water vapor (transpiration). On sunny, hot, dry days, guard cells close to preserve water, but this poses a problem for photosynthesis. As O2 accumulates, it competes with CO2 in binding with rubisco. When oxygen more plentiful than CO2, RuBP is oxidized. Recap: in C3: In Photorespiration: 3 CO2 + 3 RuBP (5C) 6 PGA (3C) 3 O2 + 3 RuBP (5C) 3 PGA (3C) + 3 glycolate (2C) Some carbons of glycolate returned to the Calvin cycle as Glyceraldehyde 3phosphate (G3P) Some carbons converted to CO2. Decreases the production of carbs due to removal of PGA from the Calvin cycle. ¼ - ½ of carbon fixed in C3 plants are lost by photorespiration Optimal temperature for photorespiration (30-47 degrees Celsius) is much higher than photosynthesis (15 – 25 degrees Celsius) Relate back to Enzymes: O2 more likely to be the substrate of the enzyme Rubisco when temperatures are _______________. Hot, dry, bright days facilitate _____________. Global warming? Rubisco worked fine in early Earth, when oxygen levels weren’t very high and CO2 was plentiful. Photosynthesis increased amount of O2 in atmosphere. As oxygen levels increased, rubisco did not adapt to rid itself of its ability to oxidate. Solution: evolution of alternate mechanisms of carbon fixation where CO2 is concentrated at the site of Rubisco suppress rate of photorespiration. C4 photosynthesis Crussalacean Acid Metabolism (CAM) Several thousand species of plants undergo C4 Phosphenolpyruvate carboxylase (PEP carboxylase) first catalyzes addition of CO2 molecule to PEP (3C) oxaloacetate (OAA) (4C) C3 vs. C4? Leaf anatomy and function of C4 plants: two types of photosynthetic cells: Mesophyl cells located around bundle-sheath cells. IN THE CYTOPLASM, NOT THE CHLOROPLAST: PEP carboxylase: CO2 + PEP (3C) OAA (4C) OAA malate Bundle-sheath cells surrounding a vein Malate diffuses from mesophyll cells into bundle-sheath cells through cell-cell connections called plasmodesmata. CO2 removed from malate (decarboxylation) pyruvate (3C) This CO2 enters the Calvin Cycle: catalyzed by rubisco Pyruvate mesophyll cell converted to PEP Why all the hassel? Reduces the amount of photorespiration by continually pumping CO2 towards rubisco. CO2 outcompetes O2 Sugar production maximized Costs plant 2 ATP molecules per CO2 produced. C3 plants: 18 molecules of ATP used/glucose C4 plants: 30 molecules of ATP used/glucose When is it worth it? Occur in succulents: water-storing plants Cacti Pineapples Open stomata at night and close them during the day. Closing stomata during the day helps ___________________ but prevents _____ from entering the leaves. When stomata open, CO2 taken in, incorporated into C4 organic acids (using PEP carboxylase). Organic acids stored in vacuoles until morning CO2 molecules enter the C3 Calvin cycle ______________. C4: first part of carbon fixation and Calvin cycle occur in separate compartments of the leaf (spacial separation) CAM: two steps occur in the same compartments, but at different times of the day (temporal separation) Both represent evolutionary solutions to the problem of maintaining photosynthesis when stomata are closed. Initially produce organic acids that eventually transfer CO2 to the Calvin cycle. Pg. 172 #1-6