Inert Gas Purification Systems
advertisement

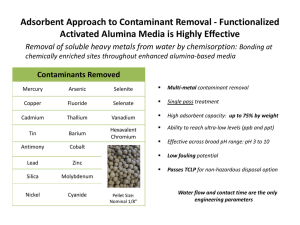
Inert Gas Purification Systems Why do we need them??? • Many of the materials used in research and development today are extremely air sensitive, and can be dangerous in the presence of air. • Purifiers are designed to remove oxygen, moisture and nitrogen from an inert gas to one part per million. • Safety is also a critical issue in experiments and research today. Purifier Components • • • • • • • • Circulation blower Copper catalyst Molecular Sieve Vacuum pump Solenoid Assembly Pressure control Regeneration control Manual footswitch • Isolation valves (automatic or manual) • Solvent removal systems • Titanium reactor (in the case of N2 removal) • Exhaust traps Purifier theory The purpose of a purifier is to remove oxygen and moisture from an inert gas flowing through a controlled atmosphere system such as a glovebox. The typical purifier contains two purification agents. One agent is a molecular sieve which removes H2O by process of molecular adsorption.The other agent is called Q5 and is an O2 absorbent material. Oxygen removal • Oxygen removal from Argon, Helium, or Nitrogen is accomplished with a reactant/catalyst known as Q5, a material consisting of finely divided copper on an Alumina Matrix. The copper reacts with oxygen to form cupric oxide. Moisture removal • Moisture is removed by a molecular sieve enclosed in the same container as the Oxygen reactant. Also removed by the molecular sieve at ambient temperatures are carbon dioxide, nitrogen dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, carbon monoxide and many organic compounds including: Alcohol's, aromatics, amines, halogenated compounds, oxygenated compounds, hydrocarbons and organic acids. Regeneration Theory • To restore the purification capability of the material two reactions must take place. • The H2O trapped by the sieve must be removed completely. • The O2 must be removed from the Cu and returned to essentially pure form. Regeneration theory (cont.) • The restoration of the sieve is accomplished by heating the material which vaporizes the water. A dry gas is passed over the sieve which carries the H2O off and out of the column. The restoration of the the Q5 is accomplished by passing a H2 rich gas through the reactant. The H2 reacts with the O2 and the reactant is reduced to pure Cu with H20 as the by product which is then pumped off. Materials that can damage the purifier • Sulfur and Sulfur compounds such as H2S, COS, SO2, SO3, These materials will poison the reactant material in the purifier. • Also, large quantities of Halides, Chlorides, Halogens (Freon), Alchohols, Hydrazine, Phosphene, Arsine, Arsinate, Mercury and saturation with water may also deactivate the Oxygen reactant. If any of these materials are to be used, a suitable trap should be installed. Selecting a purifier • Consider ! • The size of the Glove-box • Determine the leak rates if applicable • Calculate the frequency of ante chamber operation • Determine the desired purity level Circulating Vs Purging • When purging a glove-box the atmosphere in the box can only achieve an O2 and H2O level that is present in the source gas. • Purging a box can be very expensive depending on the gas and the volume of the box to be purged. • When using a closed loop circulation purifier the supply gas does not need be pure, it is the purifiers job to remove H2O and O2 in the gas to the 1ppm level. • The system only uses gas when transferring in and out of the box. Purifier options • Purifiers can be configured with dual columns for continuous operation. • They can be configured for different flow rates. • In addition to standard configurations custom solvent traps can be supplied for removal of harmful materials that can damage catalyst. • Nitrogen removal systems are also available. Utilities required • Two separate gases are required for standard purifiers. • One is your choice of inert gas. Argon, Nitrogen or Helium with a delivery pressure of approx. 35psi • The other is your choice of inert gas with a 4-5% mixture of H2.(Regeneration gas) • Electrical service. (varies depending on configuration) typically 115vac/20 amps. • Venting (application specific) Instrumentation • In order to determine the conditions of the atmosphere in the glove-box the following analyzers are available. • Moisture • Oxygen • Nitrogen • Other custom systems are available I.e. GC/MS