MS PowerPoint
advertisement

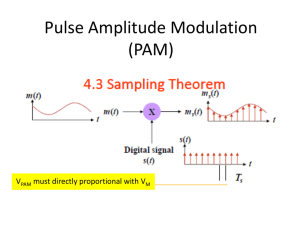
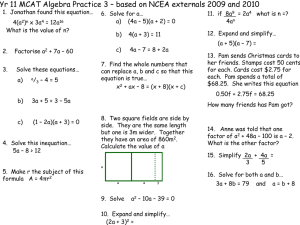
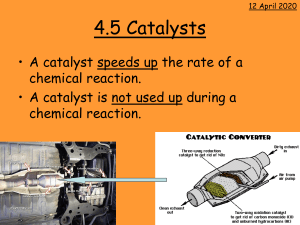
Phosphoric acid grafted MCM-41 is a novel Bronsted acid catalyst for Transesterification reaction of Diethyl oxalate with n-Butyl alcohol By D. Nedumaran and A. Pandurangan Institute of Catalysis and Petroleum Technology Anna University 00:17 Chennai-600025 Introduction 00:22 CATALYSIS •Catalysts - a chemical substance which increase the rate of chemical reaction •Catalysis - a study of catalytic activity of a chemical reaction •Homogeneous Catalyst – substrate and catalyst are in same phase •Disadvantages of Homogeneous catalyst – Homogeneous catalyst like sulfuric acid is still the catalyst of choice in the industry, together with HCl, dissolved aryl sulfonic acids and H3PO4 00:17 •But these catalysts are toxic, corrosive substances, polluting the environment and often hard to remove from the reaction mixture for recycling •Heterogeneous catalyst – substrate and catalyst are in different phase. Generally catalyst in solid phase. Substrate may be in liquid or gas phase •Advantages of heterogeneous catalyst Ecofriendly, non corrosive, non toxic, recyclable, reusable. It leads to green chemistry. 00:17 Materials Activated charcoal; Mica Hexagonal Microporous 5 00:22 10 Cubic Mesoporous 50 100 Lamellar Macroporous 50 0 1000 Salient Features of mesoporous MCM-41 High surface area (>1000m2/g) Tunable and large pore size (20 to 100 Å) Ordered pore morphology Thermal stability up to 800 °C in dry atmosphere Higher Hydrothermal stability Hydrocarbon sorption capacity > 0.7 ml/g Reusability , Recyclable 00:17 Main Objectives: To synthesis MCM-41 molecular hydrothermal crystallization procedure sieves by adopting the To characterize the catalysts by various physicochemical techniques. To test the catalytic activity of the synthesized materials over the Transesterification reaction of Diethyl oxalate with n-Butyl alcohol Optimize various reaction parameters for maximum substrate conversion. Study the reusability of the catalysts 00:17 Experimental 00:22 SYNTHESIS OF MCM-41 Silicon source 1 hour stirring Mixture 1 M H2SO4 till gel formation Gel 30 min stirring CTAB Resultant gel Autoclaved and heated for 48 hours at 145ºC in oven product Calcined at 550ºC in furnace for 6 hours MCM-41 00:17 SYNTHESIS OF ORTHO PHOSPHORIC ACID GRAFTED MCM-41 • 1 g of MCM-41 is dissolved in 10 ml deionized water and stirred for 15 minutes. • 0.2N Ortho Phosphoric acid is added drop wise and Stirred for 30 minutes followed by drying for 6 hr at 110 °C • After drying ,this material is Calcined at 300 °C for 4 hr. • This dry material is labeled as PAM 0.2. • The same method is used to synthesis PAM 0.4, PAM 0.6 and PAM 0.8 • The catalytic activity of PAM is examined with Trans esterification reaction. 00:17 GRAFTING OF PHOSPHORUS SPECIES ON MCM-41 OH OH P P HO OH Si MCM-41 00:17 OH OH O O Si MCM - 41 O Characterization The following physicochemical properties of PAM have to be done BET – surface area Pyridine FT-IR – measurement of acid sites _ FT-IR – different OH groups XPES – Binding energy of 2p e- of Phosphorus ICP – Si-P ratio NH3 – TPD – adsorption profile N2 adsorption – pore sizes P MAS NMR – Phosphorus environment TEM – morphological feature 00:17 Intensity (a.u) X-ray diffraction pattern of PAM molecular sieves obtained after calcination (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) 2 4 6 8 10 2 theta (deg) a) Si-MCM-41, b) PAM 0.2, c) PAM 0.4, d) PAM 0.6, e) PAM 0.8 00:17 NH3-TPD PAM 0.6 00:22 Reaction procedure A mixture of Diethyl oxalate (5mmol), n-Butyl alcohol (15mmol). Freshly activated catalyst (150 mg). The reactants and the catalyst were taken in 15 ml autoclave and kept it in a Hot air oven for specified temperature and time. The product thus obtained was analyzed by Gas chromatography. 00:17 Proposed Mechanism + H oo o o C2H5O-C-C-OC 2H5 H+ C2H5O-C-C-OC 2H5 DEO n-Bu H oo C2H5O-C-C-OC 2H5 H-O-C 4H9 + oo C-C-OC 2H5 + C2H5OH O-C4H9 00:17 BEO H oo C2H5O-C-C-OC 2H5 HO-C 4H9 + The effect of various catalysts on Transesterification reaction Selectivity (%) S.No. Catalyst 1 PAM 0.2 %Conver sion of DEO MONO ESTER DIESTER 82.7 56.4 43.6 90.3 49.2 50.8 96.8 40.1 59.9 92.2 32.9 67.1 PAM 0.4 2 PAM 0.6 3 4 PAM 0.8 Reaction conditions: Temp 130 °C, Mole ratio 1:3, Time 3h. Wt.of 00:17catalyst 100 mg. The effect of temperature on Transesterification reaction Selectivity (%) S.No. Temp. (°C) 1 70 2 %Conver sion of DEO MONO ESTER DIESTER 66.7 56.2 43.8 100 71.0 44.3 55.7 3 130 96.2 33.7 66.3 4 150 84.2 27.6 72.4 5 180 80.1 21.0 79.0 Reaction conditions: Catalyst PAM 0.6, Mole ratio 1:3, Time 3h, Wt.of catalyst 100 mg. 00:17 The effect of time on Transesterification reaction Selectivity (%) S.No. Time (h) 1 1 2 %Conversio n of DEO MONO ESTER DIESTER 68.2 51.7 48.3 2 83.6 48.3 51.7 3 3 94.5 41.5 58.5 4 4 94.9 33.1 66.9 5 5 95.4 23.7 76.3 Reaction conditions: Catalyst PAM 0.6, Mole ratio 1:3, Wt.of catalyst 100 mg. 00:22 Conclusion 00:22 Si-MCM-41 was synthesized by hydrothermal method. Various concentration ratio of orthophosphoric acid is loaded on Si–MCM-4. All synthesized mesoporous PAM were found to be typical mesoporous materials. XRD investigation shows that the intensity of 100 plane is well retained upto the optimum loading of PA (0.6 N). NH3-TPD of the material shows the presence of acid sites while loading PA on Si-MCM-41. PAM is the suitable solid acid catalysts for the trans esterification reaction. The product analysis shows Bronsted acid sites are the reason for absence of ether product (Butyl ethyl ether). 00:22 00:22