EHSO online WHMIS Training Presentation

University of Manitoba
WHMIS
Revised November 2011
1
WHMIS Stands for…
W
orkplace
H
azardous
M
aterials
I
nformation
S
ystem
2
WHMIS is…
The Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System is a
Canada-wide system designed to give employers and workers information about hazardous materials used in the workplace.
WHMIS standards are coordinated between both Federal and
Provincial governments.
Manitoba Workplace Safety and Health Act and Regulations sets the WHMIS requirements.
3
WHMIS has 3 Main Parts
Labels – provide information about the hazards of the product
Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) – provide further detailed information
Education – how to use the information provided
4
The GOAL is…
Identify 6 Classes of Controlled Products
Understand the Main Hazards associated with each class
Recognize and understand the two types of WHMIS labels
Understand how to use Material Safety Data Sheets
A Controlled Product is…
A Controlled Product is any substance or material which meets any of the criteria for inclusion in one or more of the six WHMIS Hazard Classes as defined in the Federal
Controlled Product Regulation.
Under WHMIS , there is no comprehensive list of controlled products but only a list of hazard criteria.
6
WHMIS Does Not Apply
When WHMIS does not apply there may be another Act or regulation that does.
WHMIS does not apply to controlled products that are:
Wood or a product made of wood
Tobacco or a product made of tobacco
A manufactured item that will not release chemicals
Products transported under the Transportation of
Dangerous Goods Act – for more information regarding TDG: http://umanitoba.ca/admin/human_resources/ehso/emanagement/tdg.html
WHMIS Does Not Apply
WHMIS does not apply to products covered by:
Explosives Act
Food and Drugs Act
Pest Control Products Act
Certain products in the Hazardous Products Act
Nuclear Safety and Control Act
WHMIS Applies for
WHMIS labels and MSDS are still required for:
Mixtures of radioactive nuclide(s) and a non-radioactive carrier material where:
The carrier material is greater than 1.0 ml / 1 g
The carrier material poses a carcinogenic, toxic, reactive, or infectious hazard
For more information regarding Radiation Safety: http://umanitoba.ca/admin/human_resources/ehso/rad_safety/index.html
Hazard Classes & Symbols
There are 6 Hazard Classes
Hazard Classes & Symbols
Class A : Compressed Gases
Risks
Physical hazard (120kg)
Explosive hazard
Content hazard
Examples
CO
2 cylinders
N
2 cylinders
O
2 cylinders
acetylene
Hazard Classes & Symbols
Class A : Compressed Gases
Handling and Use
Secure cylinder upright with valve cap on when not in use
Use gas specific regulator
Test connections for leaks
Avoid heat & ignition sources
Transport using specialized cart
Store in cool ventilated area
Hazard Classes & Symbols
Class A : Liquid N
2
& Dry Ice
Risks
Frostbite
Samples may explode
Asphyxiation
Handling and Use
Avoid skin contact
Wear insulated gloves and eye protection
Store in a well ventilated room
Transport securely to prevent accidental spillage
Store Liquid N
2 in a vented dewar
Hazard Classes & Symbols
Class B : Flammable & Combustible
Six Subdivisions
1. Flammable gas
2. Flammable liquid
3. Combustible liquid
4. Flammable solid
5. Flammable aerosol
6. Reactive flammable material
Hazard Classes & Symbols
Class B : Flammable & Combustible
Risks
Fire hazard – will burn if ignited
Could ignite spontaneously
Could ignite upon mixing with water or other chemicals
Many are poisonous
Hazard Classes & Symbols
Class B : Flammable & Combustible
Examples
1. Flammable gas – hydrogen, methane
2. Flammable liquid [flash pt <37.8C] – gasoline, ether
3. Combustible liquid [flash pt >37.8C] – kerosene, varsol
4. Flammable solid – magnesium metal, aluminum dust
5. Flammable aerosol – propane, butane, isobutane
6. Reactive flammable material – phosphorus, sodium metal
Hazard Classes & Symbols
Class B : Flammable & Combustible
Handling and Use
Avoid contact with flames, heat, & ignition sources
Cap tightly for storage, vapours are flammable
Avoid inhalation and skin contact
Ground and bond when dispensing from 25L container
Store in flammable storage cabinets if in excess of 50L
Transport separate from oxidizing materials
Transport securely using secondary containment
Hazard Classes & Symbols
Class C : Oxidizing Material
Risks
Increase fire and explosion hazard
May cause combustibles to explode or react violently
May burn skin and eyes on contact
Most are corrosive and poisonous
Examples
Peroxides
Nitrates
Persulfates
Hypochlorites
(bleach)
Hazard Classes & Symbols
Class C : Oxidizing Material
Handling and Use
Wear the recommended protective equipment and clothing
Store away from sources of heat and ignition
Many oxidizers are shock sensitive, handle carefully
Store and transport separately from flammables and organics
Store in non-corroding containers
Transport securely
Hazard Classes & Symbols
Class D : Poisonous and Infectious
Division 1 – Materials Causing Immediate and Serious Toxic Effects (acute)
Division 2 – Materials Causing Other Toxic
Effects (chronic, delayed)
Division 3 – Biohazardous Infectious Material
20
Hazard Classes & Symbols
Class D : Poisonous and Infectious
Division 1
Risks
Small quantities may be harmful or lethal
May be toxic not only if ingested but also if inhaled or absorbed through skin or eyes
Many acute toxic compounds act as carcinogens at lower levels
Examples
Carbon monoxide
All halogens
Cyanides
Hazard Classes & Symbols
Class D : Poisonous and Infectious
Division 2
Risks
Materials which have harmful effects after repeated exposures or over long periods of time
Damage could include:
Permanent injury or death
Birth defects
Cancer
Organ damage
Sensitization and allergies
Examples
Asbestos
Formaldehyde, benzene
Ammonia
Hazard Classes & Symbols
Class D : Poisonous and Infectious
Division 3
Risks
Infectious materials which may cause disease resulting in illness or death
Examples
Blood, tissue, and body fluids
Tissue culture
Experimental cultures
Hazard Classes & Symbols
Class D : Poisonous and Infectious
Handling and Use
Wear protective clothing to avoid all exposures: skin, inhalation, ingestion, and injection
Work in a fume hood or BSC
Avoid creating dust, vapours, and aerosols
Obtain appropriate immunizations
Handle exterior containers as though it is contaminated
Store and transport securely to prevent accidental spillage
Hazard Classes & Symbols
Class E : Corrosive Material
Risks
Will burn human tissue including skin, eyes, nose mouth, throat & lungs
Will corrode many lab related materials particularly metals
Fumes may damage the environment
Examples
Strong acids & bases
Hydrogen fluoride
Hydrogen chloride
Hazard Classes & Symbols
Class E : Corrosive Material
Handling and Use
Wear appropriate protective clothing
When possible work in the fume hood
Open containers slowly
When diluting acids, always add acid to water
Store in non-corroding containers, on non-corroding trays
(secondary containers )
Store away from combustibles, organics, and sources of heat and ignition
Transport separate from flammables
Transport securely using secondary containment
Hazard Classes & Symbols
Class F : Dangerously Reactive
Risks
May be unstable or vigorously polymerize
May react with water to release a toxic or flammable gas
May self-react when shocked or heated
Highly reactive with incompatible materials
May burn eyes and skin on contact
Examples
Ether
Acrylates
1,3-butadiene
Metal azides
Hazard Classes & Symbols
Class F : Dangerously Reactive
Handling and Use
Follow MSDS recommendations for use and storage
Wear protective clothing, especially eye protection
Open slowly and carefully & use in fume hood
Ensure lab equipment is clean and free of impurities
Store away from incompatible chemicals
Keep away from heat and ignition sources; avoid sudden temperature changes
May require inhibitors to prevent reaction during storage
Examine storage containers frequently
Store & transport securely
Label Types
Supplier Labels
Workplace Labels
U of M Waste Tag
29
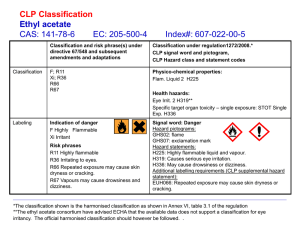
Labels
Supplier Labels
The following must be included on a supplier label:
Product Name
WHMIS Symbols
Risk Phrases
Precautionary Measures
First Aid Measures
MSDS Reference
Supplier Name
All information must be within a hatched border
Labels
Laboratory Supply House - Supplier Label
3) Symbol
31
Labels
Workplace Labels
The following must be included on a workplace label:
Product Name
Safe Handling Instructions
MSDS Reference
Methanol
Flammable, poisonous, harmful vapor
Keep away from heat, sparks, flames
Avoid contact with eyes and skin
Labels
Workplace Labels
x x x x x
Methanol
Must be present on:
Products decanted or transferred from an original container
Product where original label is lost or becomes illegible
Products produced and used at the workplace
You can print your own WHMIS workplace labels
Labels
Workplace Labels – Hazardous Waste
The following must be included on a hazardous waste label:
Product Name
Concentration
Hazard
Labels
Workplace Labels – Hazardous Waste
Waste Tags must:
Be present on containers that do not have a correct supplier label
Must list any chemical over 1% or any quantity if it poses a significant hazard
Use only chemical names (no trade names, abbreviations, or formulas)
Print your own hazardous waste labels
Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS)
Provides detailed information on the hazards of a controlled product
An important element for developing safe work procedures and control measures
Must be provided by the supplier, or If you have created a product, you must prepare a MSDS
Risk Group 2 and higher biological agents also require a MSDS or a Pathogen Safety Data Sheet (PSDS)
Must be replaced every 3 years
All MSDS must be kept for 30 years
36
MSDS
Information Provided
Product Information
This section identifies product name, manufacturer and suppliers names, addresses, and emergency phone numbers, and the intended use of the product.
Hazardous Ingredients
This section lists All potentially hazardous ingredients, with the approximate amount (percent), and toxicity data for the individual ingredients. Information regarding the LD50 and LC50 (the amount of a chemical that is expected to kill 50% of a test animal population within a specified time) will also be given. The lower the value the greater the poisoning potential.
MSDS
Information Provided
Physical Data
Provides information on the physical and chemical properties such as odour, boiling point, and vapour density.
Fire or Explosion Hazard Data
Provides the conditions under which the product may catch fire or explode, as well as information for developing strategies and procedures to deal with fire and explosion hazards.
First Aid Measures
Lists the procedures for emergency first aid.
MSDS
Information Provided
Reactivity Data
Provides information regarding stability, self-reactivity, hazardous decomposition products, and conditions to avoid when using the product.
Toxicological Properties
Identifies how the substance can enter the body and the possible health effects from short term (acute) exposures such as irritation, sensitization; and long-term (chronic) such as liver or kidney damage, sensitization, cancer, or reproductive effects. Known exposure limits will also be given.
MSDS
Information Provided
Preventative Measures
Provides preventive measures you can take to protect yourself from exposure including: extra ventilation, personal protective equipment
(PPE), safe use, handling, storage, disposal, transport, and spill control.
Preparation information
Indicated who was responsible for preparation and date of preparation of MSDS. It is 3 years from this date when the MSDS needs to be renewed.
Information may be labeled as Trade Secret if a claim has been filed.
The information is released to medical professionals in case of emergency.
MSDS
Example
MSDS
Location, Location, Location
Hazardous Waste Disposal Procedures
The University has well established guidelines and procedures to deal with hazardous waste disposal
EHSO provides hazardous waste disposal services at no charge to the University faculties and departments
Incorporate waste disposal into lab procedures or experiments
NO disposal of Hazardous Waste is permitted down the drain or regular trash can
Remember that your end point is someone’s starting point
Refer to the EHSO webpage for details
Spill Clean-up
Chemical, Radiological, or Biological
If a spill occurs that poses an immediate risk to people, or if someone is injured – it is an EMERGENCY – call 555
Minor spills should be cleaned up by trained staff
Spills must never be cleaned up by untrained staff
Under no circumstance shall caretakers be instructed to clean up any lab spills
The best time to learn about and practice cleaning up a spill is before it happens – read the MSDS
EHSO is also available to assist with the cleanup of “non-emergency” spills beyond the capabilities of available staff
Information on spills cleanup can be found on the EHSO website
Chemical Storage
General Chemical Organization
Organize by compatibility not alphabetically
Separate each compatible group
In separate cabinets or on separate shelves
Or in secondary containers in same cabinet or shelf
Make sure all containers are properly closed
Containers must be labeled and tightly capped
Chemical Storage
General Chemical Organization
Flammables
Bases
Oxidizers
Acids
Store in flammable storage cabinets
Store separately
Store separately
Store in corrosive resistant acid cabinet
EXCEPT: chromic, nitric, and perchloric acids which should be stored separately
Glacial acetic acid should be stored as a flammable
Chemical Storage
Potentially Explosive Chemicals
Picric Acid and Nitro Compounds
Dry picric acid may explode if subjected to heat, shock, or friction
(opening the lid)
Picric acid must be stored under wet.
Some nitro compounds may have similar requirements
Peroxide Forming Compounds
Example ethers, dioxanes, sodium amide
Peroxide formation may be initiated by light or air
Peroxides are prone to explosive decomposition when subjected to heat, shock, or friction (opening the lid)
Evaluate the conditions of these chemicals regularly
Refer to MSDS for storage and handling requirements
Chemical Storage
General Chemical Segregation
Do Not Store:
Oxidizers
Alkali metals
Acetic Acid
Acetone
Hypochlorites
Chlorine
Cyanides (Alkaline)
Potassium chlorate
Chlorates (ClO
3
)
Hydrogen Sulphide
H
2
O
2
Chromic Acid
With:
Flammables
Water, CO
2
, CO, or CCl
4
Chromic, nitric or perchloric acid, peroxides, permanganates, or hydroxides i.e. KOH
Concentrated sulphuric or nitric acids
Acids
Ammonia, acetylene, butadiene, benzene, petroleum derivatives, or sodium carbides
Acids
Acids
Ammonium salts, acids, metal powders, sulphur, or carbon
Nitric acid
Flammables, Cu, Cr, Fe, or respective salts
Acetic acid, alcohol, naphthalene, glycerine, or other flammable liquids
Annhydrous Ammonia Halogens, Hg, HF, or CaClO
4
Acids (conc.) Bases (conc.)
Chemical Storage
General Chemical Organization & Segregation
Do Not:
Do not place heavy materials, liquid chemicals, and large containers above eye level
Do not store chemicals on the floor
Do not store items in fume hoods
Do not expose stored chemicals to direct heat or sunlight
Chemical Inventory
U of M Chemical Inventory Database
As part of the Manitoba
Workplace Safety and Health Act and Regulations, an inventory of chemicals is required at the
University.
The University provides the EHS
Assistant database. It can be accessed from the EHSO website.
53
Your supervisor or a designate is responsible for work‐site‐specific education that includes:
Hazard information for the controlled products used at your work site
Safe use, storage and handling of specific controlled products used at your work site
Dealing with fugitive emissions and emergencies at your work site
MSDS location