Chapter 03 - Yale Chemistry
advertisement
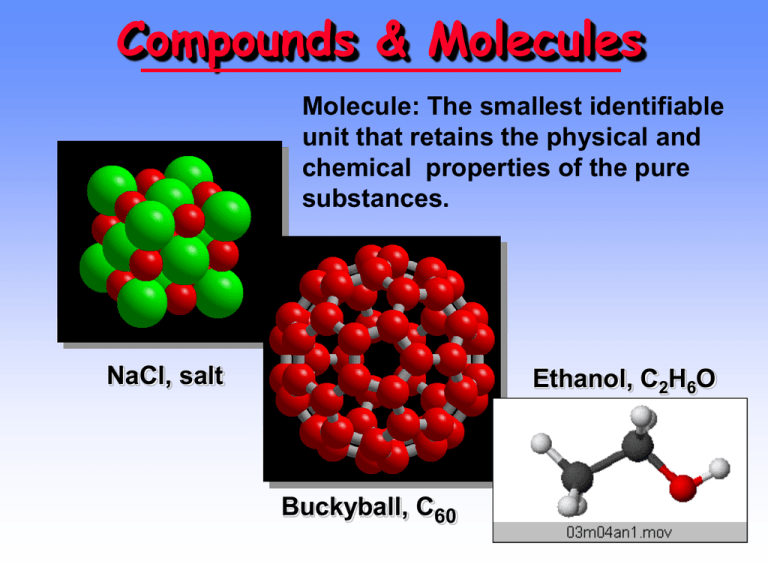
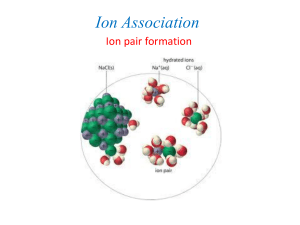
Compounds & Molecules Molecule: The smallest identifiable unit that retains the physical and chemical properties of the pure substances. NaCl, salt Ethanol, C2H6O Buckyball, C60 Compounds & Molecules • COMPOUND is a combination of 2 or more elements in definite ratios by mass. • The character of each element is lost when forming a compound (e.g., think of NaCl). • MOLECULES are the smallest units of a compound that retains the characteristics of the compound. MOLECULAR FORMULAS • Formula for glycine is C2H5NO2 (description of the composition) • In one molecule there are – 2 C atoms – 5 H atoms – 1 N atom – 2 O atoms CONDENSED FORMULAS • Formula for glycine is NH2CH2CO2H (composition and functional groups) • In one molecule there are – 1 NH2 (amine group) – 1 CH2 group – 1 CO2H group STRUCTURAL FORMULAS • Show how the atoms are attached within a molecule • The lines between atoms represent chemical bonds that hold the atoms together. WRITING FORMULAS • Can also write glycine as the condensed formula H2NCH2COOH showing functional groups (atom ordering and connectivity) • or in the form of a structural formula H H O H N C C O H H showing how atoms are attached to each other (bond orders) MOLECULAR MODELING An even higher level of structural detail H H O H N C C O H H Ball & stick Drawing of glycine Space-filling Resources for Molecular Modeling • Modeling software –CAChe (General Chemistry Interactive CD-ROM) –Rasmol –Molden –Gaussview –Maestro MOLECULAR WEIGHT AND MOLAR MASS Molecular weight = sum of the atomic weights of all atoms in the molecule. Molar mass = molecular weight in grams per mol. What is the molar mass of ethanol, C2H6O? 1 mol contains 2 moles of C (12.01 g C/1 mol) = 24.02 g C 6 moles of H (1.01 g H/1 mol) = 6.06 g H 1 mol of O (16.00 g O/1 mol) = 16.00 g O TOTAL = molar mass = 46.08 g/mol Tylenol • Formula = C8H9NO2 • Molar mass = 151.2 g/mol Molar Mass How many moles of alcohol (C2H6O) are there in a “standard” can of beer if there are 21.3 g of C2H6O? (a) Molar mass of C2H6O = 46.08 g/mol (b) Calc. moles of alcohol 1 mol 21.3 g • = 0.462 mol 46.08 g How many molecules of alcohol are there in a “standard” can of beer if there are 21.3 g of C2H6O? We know there are 0.462 mol of C2H6O. 6.022 x 1023 molecules 0.462 mol • 1 mol = 2.78 x 1023 molecules How many atoms of C are there in a “standard” can of beer if there are 21.3 g of C2H6O? There are 2.78 x 1023 molecules. Each molecule contains 2 C atoms. Therefore, the number of C atoms is 2 C atoms 23 2.78 x 10 molecules • 1 molecule = 5.57 x 1023 C atoms Molecular & Ionic Compounds Heme NaCl Molecular compounds consist of discrete molecules Ionic compounds consist of discrete ions IONS AND IONIC COMPOUNDS • IONS are atoms or groups of atoms with a positive or negative charge. • Taking away an electron from an atom gives a CATION with a positive charge • Adding an electron to an atom gives an ANION with a negative charge. Forming Cations & Anions A CATION forms when an atom loses one or more electrons. Mg --> Mg2+ oxidation + 2 e- An ANION forms when an atom gains one or more electrons F + e- --> Freduction oxidation reduction PREDICTING ION CHARGES In general • metals (Mg) lose electrons ---> cations • nonmetals (F) gain electrons ---> anions Charges on Common Ions Cation charge=group # +1 Anion charge=group #-8 -4 -3 -2 -1 +2 +3 By losing or gaining e-, atom has same number of electrons as nearest Group 8A atom. Predicting Charges on Monatomic Ions METALS M ---> n e- + Mn+ where n = periodic group Na+ sodium ion Mg2+ magnesium ion Al3+ aluminum ion Transition metals --> M2+ or M3+ are common Fe2+ iron(II) ion Fe3+ iron(III) ion NONMETALS NONMETAL + n e- ------> Xnwhere n = 8 - Group no. Group 4A Group 5A Group 6A Group 7A C4-,carbide N3-, nitride O2-, oxide F-, fluoride S2-, sulfide Cl-, chloride Br-, bromide I-, iodide Ion Formation Reaction of aluminum and bromine POLYATOMIC IONS CD Screen 3.6 Groups of atoms with a charge. MEMORIZE the names and formulas of common polyatomic ions listed in Table 3.1, page 107 (next slide) Polyatomic Ions NH4+ ammonium ion One of the few common polyatomic cations Polyatomic Ions (oxoanions) HNO3 nitric acid NO3nitrate ion Prefix per- and suffix –ate: largest # Suffix -ate : greater # of oxygen atoms Suffix -ite : smaller # of oxygen atoms Prefix hypo- and suffix –ite: smallest # Polyatomic Ions SO42sulfate ion SO32sulfite ion Polyatomic Ions NO3nitrate ion NO2nitrite ion Polyatomic Ions CO32carbonate ion HCO3bicarbonate ion hydrogen carbonate Polyatomic Ions PO43phosphate ion CH3CO2acetate ion COMPOUNDS FORMED FROM IONS CATION + ANION ---> COMPOUND Na+ + Cl- --> NaCl A neutral compd. requires equal number of + and - charges. IONIC COMPOUNDS NH4 + Cl ammonium chloride, NH4Cl Some Ionic Compounds Ca2+ + 2 F- ---> CaF2 Mg2+ + NO3- ----> Mg(NO3)2 magnesium nitrate calcium fluoride Fe2+ + PO43- ----> Fe3(PO4)2 iron(II) phosphate Properties of Ionic Compounds Forming NaCl from Na and Cl2 • A metal atom can transfer an electron to a nonmetal. • The resulting cation and anion are attracted to each other by electrostatic forces. Electrostatic Forces The oppositely charged ions in ionic compounds are attracted to one another by ELECTROSTATIC FORCES. These forces are governed by COULOMB’S LAW. Electrostatic Forces COULOMB’S LAW (charge on +)(charge on -) Force of attraction = 2 (distance between ions) As ion charge increases, the attractive force _______________. As the distance between ions increases, the attractive force ________________. This idea is important and will come up many times in future discussions! Importance of Coulomb’s Law NaCl, Na+ and Cl-, m.p. 804 oC MgO, Mg2+ and O2m.p. 2800 oC ELEMENTS THAT EXIST AS MOLECULES Allotropes of C See SCREEN 3.2 on the CD-ROM Screen 3.2 ELEMENTS THAT EXIST AS DIATOMIC MOLECULES (gases) ELEMENTS THAT EXIST AS POLYATOMIC MOLECULES S8 sulfur molecules White P4 and polymeric red phosphorus Molecular Compounds Compounds without Ions CO2 Carbon dioxide CH4 methane BCl3 boron trichloride Naming Molecular Compounds CO2 Carbon dioxide CH4 methane BCl3 boron trichloride All are formed from two or more nonmetals. Ionic compounds generally involve a metal and nonmetal (NaCl) Empirical & Molecular Formulas A pure compound always consists of the same elements combined in the same proportions by weight. Therefore, we can express molecular composition as PERCENT BY WEIGHT Ethanol, C2H6O 52.13% C 13.15% H 34.72% O Percent Composition Consider some of the family of nitrogenoxygen compounds: NO2, nitrogen dioxide and closely related, NO, nitrogen monoxide (or nitric oxide) Chemistry of NO, nitrogen monoxide Structure of NO2 Percent Composition Consider NO2, Molar mass = ? What is the weight percent of N and of O? Wt. % N = 14.0 g N • 100% = 30.4 % 46.0 g NO2 Wt. % O 2 (16 .0 g O per mole ) x 100 % 69 .6% 46 .0 g What are the weight percentages of N and O in NO? Determining Formulas In chemical analysis we determine the % by weight of each element in a given amount of pure compound and derive the EMPIRICAL or SIMPLEST formula. PROBLEM: A compound of B and H is 81.10% B. What is its empirical formula? A compound of B and H is 81.10% B. What is its empirical formula? • Because it contains only B and H, it must contain 18.90% H. • In 100.0 g of the compound there are 81.10 g of B and 18.90 g of H. • Calculate the number of moles of each constitutent. A compound of B and H is 81.10% B. What is its empirical formula? Calculate the number of moles of each element in 100.0 g of sample. 1 mol 81.10 g B • = 7.502 mol B 10.81 g 1 mol 18.90 g H • = 18.75 mol H 1.008 g A compound of B and H is 81.10% B. What is its empirical formula? Now, recognize that atoms combine in the ratio of small whole numbers Find the ratio of moles of elements in the compound. A compound of B and H is 81.10% B. What is its empirical formula? Take the ratio of moles of B and H. Always divide by the smaller number. 18.75 mol H 2.499 mol H 2.5 mol H = = 7.502 mol B 1.000 mol B 1.0 mol B But we need a whole number ratio. 2.5 mol H/1.0 mol B = 5 mol H to 2 mol B EMPIRICAL FORMULA = B2H5 A compound of B and H is 81.10% B. Its empirical formula is B2H5. What is its molecular formula ? Is the molecular formula B2H5, B4H10, B6H15, B8H20, etc.? B 2H 6 B2H6 is one example of this class of compounds. A compound of B and H is 81.10% B. Its empirical formula is B2H5. What is its molecular formula? We need to do an EXPERIMENT to find the MOLAR MASS. Here experiment gives 53.3 g/mol Compare with the mass of B2H5 = 26.66 g/unit Find the ratio of these masses. 53.3 g/mol 2 units of B2H5 = 26.66 g/unit of B2H5 1 mol Molecular formula = B4H10 How to Determine the molar mass? Mass spectrometer Mass Spectrum of Ethanol Mass Spectrum of Ethanol (from the NIST site) CH2O+ 31 CH3CH2O+ 45 CH3CH2OH+ 46 Determine the formula of a compound of Sn and I using the following data. • • • • Reaction of Sn and I2 is done using excess Sn. Mass of Sn in the beginning = 1.056 g Mass of iodine (I2) used = 1.947 g Mass of Sn remaining = 0.601 g Tin and Iodine Compound Find the mass of Sn that combined with 1.947 g I2. Mass of Sn initially = 1.056 g Mass of Sn recovered = 0.601 g Mass of Sn used = 0.455 g Find moles of Sn used: 1 mol 0.455 g Sn • = 3.83 x 10-3 mol Sn 118.7 g Tin and Iodine Compound Now find the number of moles of I2 that combined with 3.83 x 10-3 mol Sn. Mass of I2 used was 1.947 g. 1 mol 1.947 g I2 • = 7.671 x 10-3 mol I2 253.81 g How many moles of iodine atoms? -3 7.671 x 10 2 mol I atoms mol I2 1 mol I2 = 1.534 x 10-2 mol I atoms Tin and Iodine Compound Now find the ratio of number of moles of moles of I and Sn that combined. 1.534 x 10-2 mol I 4.01 mol I = 1.00 mol Sn 3.83 x 10-3 mol Sn Empirical formula is SnI4