All prefixes & suffixes. (1st Quiz on Jan 25th)
advertisement

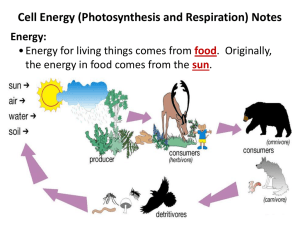
1 2 • Living things need energy to survive and function. • You get the energy you need from the food you eat. • Where does that energy come from? • Sun Plants You !!! • You must eat food to get energy (you are a heterotroph). – When you breakdown your food you store the energy in the bonds of ATP. • Plants can make their own food (they are autotrophs). – Plants store sunlight energy in the chemical bonds of glucose (a carbohydrate). ATP 3 glucose ATP: Energy Storage WHAT IS ATP? • Universal Energy Molecule • The cell’s “Energy Bank” • Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) • Consist of – a sugar called ribose – N containing Adenine – Three phosphate groups 4 5 ATP Adenine Ribose 3 Phosphate groups 6 When the energy is used the ATP is converted into ADP P P ADP ATP Partially charged battery Fully charged battery The Bonds between the phosphate groups in ATP are VERY HIGH ENERGY. When a phosphate group is removed-energy is released CLIP 7 Using ATP in Active Transport Animation ATP 8 • Cell can make ATP from ADP by using the energy from carbohydrates. • This means that ADP the energy in ATP carbohydrates is then stored in Energy from the Carbohydrates is stored in ATP until needed by cells. ATP!!! Breaking down Carbohydrates releases energy . ATP is the major energy link between energy-9 using and energy releasing reactions. CLIP Trapping Energy glucose Clip 10 hotosynthesis is the process by which plants: • Use – sunlight, carbon dioxide & water • Produce – high energy carbohydrates such as sugars (glucose) &starches. Plants store sunlight energy in Glucose! 11 Where does photosynthesis take place? 12 Leaf Structure Photosynthesis Location: The leaves of plants: a.stomata b.cells Chloroplast Cell Goes in CO2 Stomata 13 14 The Internal Structure of a Leaf Section 23-4 CO2 enters through the stomata Epidermis Chloroplasts Stomata Guard cells Goes in CO2 Let’s go look at leaves…… Chloroplast Structure Chloroplasts are only found in photosynthetic, eukaryotic cells. Using the energy from the sunlight, chloroplasts are able to form ATP as well as synthesizing sugars from H20 & CO2. 15 Chloroplast Structure Chloroplast 16 Organelle where photosynthesis takes place. Outer Membrane Inner Membrane Stroma Thylakoid Chloroplast Structure Chloroplast Picture 17 Things to know about Chloroplasts 1. Have a double membrane the inner membrane the outer membrane 2. Have their own DNA this carries the information to make the enzymes 18.1 1. 2. Things to know about Chloroplasts Have a double membrane the inner membrane the outer membrane Have their own DNA this carries the information to make the enzymes 3. Have their own ribosomes more like the ribosomes of prokaryotes than eukaryotes make their own enzymes required for photosynthesis require carbon dioxide and water produce glucose 4. Contain chlorophyll this green chemical Pigments (pigment) "traps" sunlight energy are molecules that absorb 18.2 • Plants absorb certain wavelengths of light. • Blue and Red. • Pigments are molecules that absorb light. b a • Main pigment is Chlorophyll. • When they absorb light, they are absorbing Energy. 19 20 Photosynthesis: Products &Reactants SUN CO2 + H2O Light Energy SUN Chloroplast Glucose & O2 Formula For Photosynthesis • 6 _____ + 6 ______ +__________ Reactants ______ + ______ Products 21 Photosynthesis Takes Place in 2 Steps. 22 The light reaction is the photo part of photosynthesis. Step 1: Light Dependent Reaction. – Energy captured from Sunlight. – H2O is split into H+, electrons, & Oxygen (O2). – The O2 diffuses out of the Chloroplasts. – MADE: O2 , ATP & NADPH. – Takes place: Thylakoid 23 The Calvin cycle is the synthesis part of photosynthesis. Step 2: Light Independent Reaction (CALVIN CYCLE). –The Chemical Energy Sunlight Stored in ATP and NADPH is used to make Glucose using CO2. –This is a light independent reaction. –MADE: Glucose –Takes place: Stroma This process is known as carbon fixation. Water ATP NADPH Oxygen Step 1: Light Dependent Reaction 24 Photosynthesis: An Overview LIGHT REACTION Section 8-3 DARK REACTION-Light Independent Thylakoid Membrane SUNLIGHT Stroma Water CO2 Chloroplast Chloroplast NADP+ ADP + P LightDependent Reactions Calvin Cycle ATP NADPH O2 Go to Section: Sugars 25 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy from sunlight → C6H12O6 + 6O2 Photosynthesis Occurs in two Steps Light dependent Reaction Produces Oxygen ATP NADPH Occurs (location) Thylakoid Membrane Dark Reaction/ Calvin Cycle Produces Glucose Occurs (location) Stroma 26 PLANTS STORE ENERGY FROM THE SUN IN THE BONDS OF GLUCOSE !!!! 27 Where does each reactant enter the plant??? 28 • Once plants use light energy to form carbohydrates, other organisms, called Heterotrophs, can then use this carbohydrate energy for their own life processes. • One way carbohydrate energy is used by organisms is through the process of cellular respiration. Sun Plants You!! 29 Major Conce pt How it’s all connect ed. Cellular Respiration 30 Cellular Respiration • Process that occurs in cells in which cells break down Glucose for ENERGY! • Occurs in cytoplasm and Mitochondria. Breaking down food for energy. 31 Cellular Respiration Overview: • Plants are producers and make glucose by the process of photosynthesis. • Heterotrophs breakdown glucose for energy. • There are two important ways a cell can harvest energy from food: fermentation and cellular respiration. 36 Breaking down food for energy. 32 Cellular Respiration Takes Place in 3 Steps. Step 1: Glycolysis Step 2: Krebs Cycle Step 3: Electron Transport 33 Step 1: Glycolysis 34 • Means “Splitting Glucose” • Glycolysis starts with Glucose. –Glucose is broken down into 2 molecules called Pyruvate (aka pyruvic acid ). –Happens in the Cytoplasm. –Clip •Glycolysis does not need oxygen! Steps 2 & 3 Occur in the Mitochondria Mitochondria Anatomy 2 membranes Own ribosomes Own DNA 35 In the presence of Oxygen: Step 2: Krebs Cycle Step 3: Electron Transport • Happens in the Mitochondria • Starts with Pyruvate. • Pyruvate moves into the mitochondria and is broken down into CO2,H2O & ATP. 36 37 Cellular Respiration Review With oxygen Glucose Glycolysis Krebs cycle Fermentation (without oxygen) Go to Section: Electron transport Alcohol or lactic acid 36 38 Breaking down glucose without oxygen 39 Glucose Glycolysis With out oxygen Go to Section: Krebs cycle Fermentation (without oxygen) Electron transport Alcohol or lactic acid Ethanol and Carbon Dioxide Pyruvic Acid Lactic Acid Fermentation • Without oxygen: Pyruvate is converted into Lactic Acid or Alcohol during Fermentation. • Lactic Acid- Muscle cells • Alcohol- Yeast 40 41 • In the presence of oxygen: 1 Glucose is converted into 36 ATP. C6H12O6 + 6 O2 => 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + 36 ATP • Without oxygen: 1 Glucose is converted into 2 ATP. 42 Photosynthesis vs. Respiration Photosynthesis •produces food •stores energy •Uses H2O •uses CO2 •releases O2 •occurs in sunlight 43 Respiration •uses food •releases energy •Produces H2O •produces CO2 •uses O2 •occurs in the dark as well as light Energy Converters video. Click picture. 44 • Photosynthesis “they might be giants”