Document
advertisement

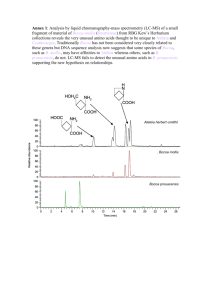
Ecotoxicology Toxicology Uptake and distribution of xenobiotics Functions of the biological membrane Maintain homeostasis Selective uptake and excretion Excitability Ca ++ pH=7.4 [conc. 2] pH = 6.4 [conc. 4] ++++++ -------- The biological membrane The lipophilic route Phospholipid Passage of chemicals through the membrane depends on: Size Fat solubility Resemblance with endogenous molecules The passage takes place through: Passive diffusion through the phospholipids Through water and ion channels Active transport through channels Endocytosis Passive diffusion most important toxicologically The diffusion rate increases with the water-octanol distribution coefficient (Kow) Kow <1 1 >1 >>1 Kow = n-octanol Water 1:5 1:1 5:1 21:1 [conc] octanol [conc] water n-octanol:water Distribution coefficient 7 10 2,2',4,4',5,5'-PCB 2,2',4,5,5'-PCB 6 DDT 10 DDE 4,4'-PCB 5 10 4 10 Parathion Naphtalen p-dichlorbenzen Chlorbenzen 3 10 Toluen 2 Chloroform Benzen 10 Benzoic acid 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 Solubility in water (nM) 7 10 8 10 9 10 Diffusion rate Kow O and N increase hydrophilic characteristics Alkyl groups increase lipophilic characteristics mnemonic rule: compound lipophilic if C 4 > N +O Ionization AH A- + H + BOH B+ + OHpH dependent Water + - The diffusion follows the concentration gradient given by Fick’s law dn = -P A D C dt P = Permeability constant (mol/cm2) A = Area ΔC = Concentration difference Uptake of Benzoic acid og Aniline Plasma pH 7.4 Stomach pH 2 COOH COO- 100 + H+ 1 NH2 NH3+ H++ 1000 Intestine pH 6 COO100 + H+ 1 2512 NH2 COOH COOH + H+ NH3+ + H+ 251 1 Plasma pH 7.4 NH2 H++ 1 1 1 NH3+ COO- COOH 10 COO- 1 2512 NH3+ NH2 251 + H+ 1 + H+ The hydrophilic route Channel for divalent cation 2+ 2+ 2+ 2+ 2+ 2+ 2+ Pyrethroides’ effect on excitable membranes Cadmium passes the Ca++ channel Cd++ [0,97 Å] Ca++ [0,99 Å] Endocytosis Endocytosis of iron iron - transferrin complex receptor coated vesikel H+ H+ lysosome Uptake, distribution and excretion of xenobiotics Alimentary canal Respiratory surfaces Skin Liver Bile Kidney Bladder Faeces Urine Blood and lymph Lungs/gills Organs Secretory structures Alveoli Air/water Fat Extra-cellular fluid Secretions Soft Hard tissue tissue Enterohepatic circulation Mercury uptake in maggots 120 10 ppm Weight (mg) Ppm Hg (Hg++) 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 1.0 ppm 0.1 ppm 0.5 1 2 3 Day no 40 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 6 Day no 7 8 1 2 3 4 5 6 Day no 7 8 120 Weight (mg) 90 Ppm Hg (MeHg) 60 60 30 60 40 1 2 3 4 5 6 Day no 7 8 Air route Blood / haemolymphe Nose and pharynx Bronchi / Trachea Bronchioler / Tracheoles Alimentary channel The skin Hydrofile Wet skin: Soap and other detergents: Organic solvents: Lipofile Increases penetration by a factor 3 Increased penetration of hydrophilic compounds Irreversible degradation of corneum Xenobiotics are distributed in tissue fluids Plasma Extracellular fluid Plasma: Extracell. fluid: Intracell. fluid: Intracellular fluid 4% of body weight 13% 41% - Lipophilic compounds Hydrophilic compounds Plasma - protein linkage K1 The organism’s other compartments K2 K1 = K dissociation K2 High Kdiss Low Kdiss loosely bound tightly bound Low affinity and high capacity toxicological most important Compartment of distribution Dose Blood sample ”Apparent compartment of distribution” VD Dose (mg) VD = Plasma concentrat ion (mg/l) VD low: high depositing in organs VD high: low depositing in organs Depositing to organs Conc. 1. order Time Conc. 0. order Time Brodie-Gillette’s box model Absorption Target site Bound Bound Free Metabolism Metabolites Bound Free Free Depot Excretion Excretory organs Vertebrate kidney Nephridia in earthworm Nephridium of an invertebrate Excretion CKonc. 1. order Tid Conc. 0. order Tid % dioxin remaining In body dC = -ke C dt 100 T½ = 30,5 days 50 30 0 10 20 30 Time (days) 40 50 lnC0 - lnCt ln2 0,693 = = T½ = ke ke ke