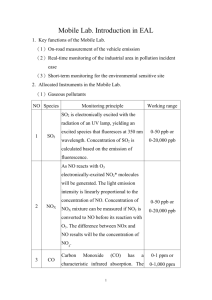
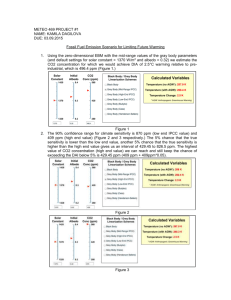
Duct Leakage
advertisement

Objectives • Summarize Electric Power Measurement • Learn about CO and CO2 measurement and instrumentation • Discuss next week field measurements Portable (Field) power meter and data logger 2 Single phase two wire 3 Single phase three wire 4 Three phase four wire 5 Electric power meters Large variety: + power meter with data logger Inexpensive power meter Power meter with power supply 6 Overview of CO2 and CO • Why make these measurements in the field? – Some background information • Types of devices for each (overview) • Pros and cons of devices (including accuracy) 7 CO2 - Standards & Guidelines • OSHA: 5,000 ppm (8-hr average) • ASHRAE (62-1999): Cindoor – Coutdoor < 700 ppm • U.S. Navy (subs) • Observations in medical literature (Clark, 1996) – – – – 8 6,000 – 10,000 ppm 1,200 ppm @ 15 min (fatigue, lack of concentration, short. breath) 1,200 ppm long-term (calcium deposition in tissues) > 2,500 ppm symptoms of oxygen deprivation in children > 60,000 ppm (6%); possible narcosis / death (within minutes) Carbon Dioxide (CO2) • Metabolic generation rate • Ventilation requirements – ASHRAE Standard 62.1 9 Metabolic Generation Rate • ASTM D6245 – Also ASHRAE Fundamentals Ch. 8 (2005) AD = 1.8 for adult, 0.8 - 1.4 for kids RQ = 0.83 when M = 1 met RQ = 1 when M = 5 met 10 10 ASHRAE Standard 62.1-2007 11 CO2: Measurement Techniques • Non-dispersive infrared (NDIR) = most common • Electrochemical (reduce CO2 / generate current) • Photoacoustic (CO2 absorbs / T up to P pulse) • Potentiometric (CO2 to solution – changes pH) • Gas chromatography w/ MS or TCD – High sensitivity – High cost 12 Non-dispersive infrared (NDIR) • Measures the infrared light absorbed by carbon dioxide as it passes through a flowthrough IR absorption cell • Possible interference from other ionic species - Interferences from other IR-absorbing gases are minimized by use of a highly wavelength-specific detector Issues: ….. CO2: NDIR Detection • See ASHRAE PDS IV • Absorption of IR light (CO2 peak absorb @ 4.3 µm) • IR light source passed through narrow band filter • Higher CO2 = greater IR absorption • Interferences: H2O, CO, CH4 (absorp 4 – 7 µm) • Accuracy = 50 to 100 ppm up to 10,000 ppm • Hold calibration a long time ??? • Cost: expensive for HVAC industry , affordable for 14 Field work Electrochemical • CO2 diffuses into the sensor through a porous membrane to the working electrode where it is case electrochemical reaction. This reaction results in an electric current that passes through the external circuit. the counter electrode is a reduction. • Advantages/disadvantages: – Can be very inexpensive – Drifting,…. Carbon Monoxide (CO) • Major sources – – – – • 16 Cigarette smoke Incomplete bringing in HVAC and Cooking systems Car exhaust …. Standards – – – – – 9 ppm (8-hour average) - NAAQS 35 ppm (1-hour average) – NAAQS 50 ppm – STEL/TWA – OSHA 400 ppm (15 minutes) - ACGIH 1,500 ppm (30 min) – IDLH (OSHA) Example: Cooking – Natural Gas 17 Measurement of Carbon Monoxide • Electrochemical (common for hand held or home) – Two electrodes – Oxidize CO to CO2 – current generated • Biomimetic (gel cell) – Synthetic hemoglobin – darkens in presence of CO • Semiconductor (wires of tin dioxide / ceramic base) – CO reduces resistance – High CO • Non-Dispersive Infrared Detection (NDIR) 18 – Used for emissions testing – Absorption band Instruments for CO andCO2 that you will use • HOBO U12 (datalogger) • Telaire 7001 CO2 analyzer (NDIR) • HOBO CO Analyzer (electrochemical) • Specs: • http://onsetcomp.com/products/sensors/tel-7001 • http://onsetcomp.com/products/data-loggers/h11-001 19 Lab exercises - next week • PRC on Tuesday – preparation • Field – Wednesday or Thursday 20 20