GASES
advertisement

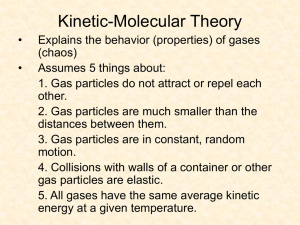
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF GASES Or GAS LAWS KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY • • • • 1. Ideal gases vs. Real gases 2. Perfect elasticity 3. Average kinetic energy KE= ½ mv2 Properties of gases • • • • • • 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Expansion Fluidity Low density Compressibility Diffusion Effusion Pressure What is it??? • • • • • • Barometer/Manometer Millimeters/Torrs Atmospheres kiloPascals 1 atm. = 101.3 kPa = 760 mm 7.5 mm = 1 kPa Conversions • Change 800 mm to atm. and to kPa. • Change 108 kPa’s to mm and atm. Practice: • Convert 699 mm to kPa and atm. • Convert 1.05 atm to kPa and mm. • Convert 101.9 kPa to mm and atm Gases and Temperature • • • • • • • Kelvin scale 0o Celsius = 273K Conversion: Add 273 to Celsius temperature Change 25oC to Kelvin Change 287K to Celsius Convert 45oC to Kelvin Convert 30 K to Celsius Boyle’s Law • Robert Boyle theorized that the pressure and volume of a gas were indirectly proportional. What does this mean?? • PV = k Problems • A gas is collected at a constant temperature of 25o with a pressure of 689 mm and volume of 32 mL. Find the pressure if the volume goes to 55 mL? • V1 P1 = V 2 P2 One more: • 45 mL of a gas is collected at 102.7 kPa. Find the volume if the pressure goes to 705 mm. Charles’ Law • Charles worked with temperature and volume of gases. • Temperature and volume are directly proportional. • V/T = k Problems: V1/ T1 = V2/ T2 • If 28 mL of H2 are collected at 28oC. What is the volume at 36oC at constant pressure? • Kelvin!!! • If 35 mL of N2 are collected at 31oC,what is the temperature in oC if the volume rises to 45mL? Gay –Lussac’s Law • Gay- Lussac worked with pressure and temperature of gases. • He said that pressure and temperature were directly proportional. • P/T =k Problems: • A gas is collected at 43oC and a pressure of 1.2 atm. Find the new pressure if the temperature drops to 21oC. Kelvin!!! • P1/T1 =P2 /T2 Another problem: • At constant volume,CO2 is collected at 768mm with a temperature of 23oC. Find the new temperature in oC of 99.1 kPa’s of pressure. COMBINED GAS LAW • PUT THE THREE EQUATINS TOGETHER AND MAKE INTO ONE. • WRITE THIS EQUATION. • V1P1/ T1 = V 2P2/ T2 PROBLEMS • 25 CM3 OF HYDROGEN IS COLLECTED AT 260C WITH A PRESSURE OF 1.2 ATM. FIND THE NEW VOLUME IF THE PRESSURE DROPS TO .98 ATM AND THE TEMPERATURE DROPS TO 220C. ANOTHER PROBLEM • 78 cm3 OF OXYGEN IS COLLECTED AT 42OC WITH A PRESSURE OF 767mm. FIND THE NEW VOLUME AT STP. Combined: • 35 cm3 of N2 is collected at .98 atm of pressure with a temperature of 210C. What is the new temperature in 0C if the volume rises to 45 cm3 and pressure rises to 788 mm? Over water problems • 15 liters of Chlorine is collected over water at 718 mm of pressure at a temperature of 60oC. Find the new volume at 766 mm. This is Dalton’s Law of partial pressure. The total pressure of a container with many gases is the sum of the partial pressures. ANOTHER PROBLEM: • 25 mL of Fluorine gas is collected over water at 25 oC with a pressure of 102 kPa’s. Find the new pressure of 32 mL. REVIEW • 33 mL of O2 is collected over water at 40oC at a pressure of 697 mm. Find the new volume at 300C with a new pressure of 1.01 atm. Another one: • 65 mL of F2 are collected over water at 280C with a pressure of 101.8 kPa. Find the new temperature of the gas at standard pressure. For the quiz: • 50.0 mL of a gas is collected over water at STP. Find the new volume if the new pressure is .97 atm and new temperature is • 180C. Ideal gas law • This is the last gas law and it involves all variables PLUS the mass of the gas. • Variables: • P= atmospheres • R=.0821 L. Atm / K. mole • V=liters n= moles • T = Kelvin THE FORMULA • PV = n RT • YOU MUST HAVE THE RIGHT UNITS TO USE THE CONSTANT!! EXAMPLES • What is the volume of H2 gas if 15 grams is collected at 25oC with a pressure of .89 atm.? PROBLEM #2 • What is the pressure of 3.5 grams of CO2 that is collected at 24oC with a volume of 550 mL? PROBLEM #3 • What is the mass of chlorine gas,Cl2, if 4.8 liters are collected over water at 102.7 kPa’s with a temperature of 28oC? Problem #4 •Find the volume of O2 that is collected over water at 25oC with a pressure of 736 mm and mass of 16 grams. Molar mass problems • What is the molar mass of 5.7 grams of a gas at 230C with a volume of 4.1 liters at 1.1 atm of pressure? • Formula: •M = mRT/PV •M = molar mass •m= mass A problem: • What is the molar mass of 4 grams of a gas with a pressure of 791 mm at 42oC with a volume of 450 mL? Molar mass: • What is the molar mass of a sample of Ar with .0045 moles that has a pressure of 725 mm at 210C and a volume of 55 mL. Molar mass • What is the molar mass of CO if 6.5 grams occupies 2.5 liters at 21oC with a pressure of 737 mm? MOLAR VOLUME PROBLEMS • To calculate molar volume and molar mass, you need to know that: • 1 mole of any gas occupies 22.4 liters of volume at STP. PRACTICE: • What is the molar volume of 35 grams of CO2 at STP? More molar volume • What is the number of moles of H2 at STP if you collect 350 mL? Molar volume with a twist: • How many grams of SO2 gas at STP occupies 450 millilters of volume? Graham’s Law • The rate of the movement of a gas is dependent on its mass. • Which gas will diffuse or effuse faster? • N2 or F2 ?? Ideal gas law review • What is the mass of 68 mL of Ne with a pressure of 99.7 kPa’s that is collect OVER WATER at 26oC? Molar volume review • How many liters does 18 grams of Cl2 occupy at STP?