PowerPoint Title
advertisement

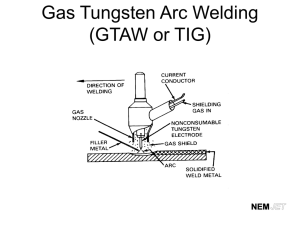
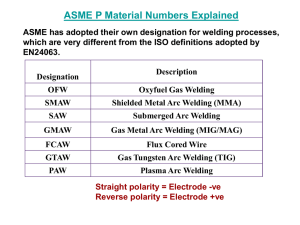
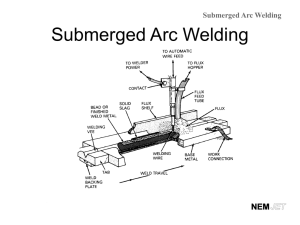
Welding Processes, Metallurgy and Defects Summer 2010 Mikal Balmforth, P.E., CWEng, CWI MIT Research Associate MIT Welding Laboratory Overview • • • • Major welding processes Some welding metallurgy topics Common weld defects Other welding related issues Arc Welding Processes • Shielded metal arc welding (SMAW) – Also stick or MMA welding – Simple, common process – Consumable, flux coated electrode • Gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW) – – – – – Also TIG welding Non-consumable tungsten Inert gas shielding Clean, precision work Filler added externally electrode Arc Welding Processes • Gas metal arc welding (GMAW) – – – – Also MIG or MAG welding Consumable wire electrode Gas shielding Often automated • Flux cored arc welding (FCAW) – Similar to GMAW – Hollow electrode wire filled with flux – Often no shielding gas Arc Welding Processes • Others – Submerged arc welding (SAW) – Plasma arc welding (PAW) – Underwater welding Resistance Welding Processes • Spot welding – – – – Sheet metal Two copper electrodes Heat from resistance at interface Autos have thousands of spot welds • Seam welding – Wheel shaped electrodes • Projection welding – Dimples or projections in sheet or components concentrates heat • Upset welding – Components forged at elevated temperature Solid State Welding Processes • Friction welding (FRW) • Inertia welding (IFW) • Friction stir welding (FSW) Solid State Welding Processes • Diffusion welding (DFW) – Often used in aircraft and aerospace • Ultrasonic welding (USW) – Used for plastics and electronic components • Explosion welding (EXW) – Often dissimilar metals or cladding High Energy Density Welding Processes • Narrow, deep welds are produced – Lower heat input and narrower HAZ • High speeds are possible • Laser beam welding (LBW) – Solid state or gas lasers – Usually done in air High Energy Density Welding Processes • Electron beam welding (EBW) – Concentrated stream of high-velocity electrons – Usually done in vacuum – Can be high power Allied Processes • Brazing and soldering (450°C, 840°F) • Oxyfuel gas welding • Thermal cutting – Oxygen, plasma arc, other – Gouging Regions of a Fusion Weld • • • • Fusion zone (FZ) – weld metal Fusion boundary (FB) Heat affected zone (HAZ) Unaffected base metal (BM) FB FZ HAZ BM Fusion Zone • Autogenous, homogeneous or heterogeneous • Molten to solid Heat Affected Zone • Grain growth, recovery and recrystallization, precipitates, stresses Welding Metallurgy Issues • How does the heat from welding affect the material and its properties? • Control microstructures and prevent defects • What filler metals, processing conditions, and welding techniques to use – Chemistry – Heat input – Welds often require pre- and/or post-heating Classification of Weld Defects • Fabrication • Delayed (hydrogen-induced) • Service Fabrication Defects • Porosity • Incomplete fusion • Incomplete penetration • Undercut Fabrication Defects Cont. • Solidification cracking – Also called hot or centerline cracking • HAZ hot cracking • Inclusions – slag or tungsten Fabrication Defects Cont. • Reheat cracking • Liquid metal embrittlement (LME) Fabrication Defects Cont. • Lamellar tearing • Incorrect weld shape or size • Spatter Delayed (H-induced) Defects • Usually initiates in course grained HAZ, but can occur in weld metal • Four requirements: – Susceptible microstructure – Source of hydrogen – Low temperature – Tensile stress Service Defects • Fatigue failures – Cyclic loading conditions – Cracks propagate from weld defects • Mechanical overload – Ductile rupture can initiate at defects Service Defects • Corrosion – Intergranular corrosion (IGC) • Localized grain boundary attack • Sensitization in austenitic stainless steels – Stress corrosion cracking (SCC) • Tensile stress combined with corrosive media • Transgranular or intergranular crack propagation Significance of Weld Defects • Failure initiation sites • Reduced tensile and other mechanical properties • Reduced fatigue life • Toughness / Fracture mechanics – Allowable defect size Other Welding Related Issues • Codes and Standards / Certification – WPS, PQR, WPQR – AWS, ASME, API, etc. • Testing / Inspection – Metallography, SEM, mechanical testing – NDE • Visual, dye penetrant, ultrasonics, x-ray, magnetic particle, eddy current • Safety – Worker, workplace, fumes, fire prevention • Weld repair • Stresses and distortion