物質的基本單元: 分子
『從原子到宇宙』課程第五週
胡維平
國立中正大學化學暨生物化學系
10/31/2013
I. Chemical Bonding
Model of a Buckyball with Potassium Ion
Interaction of H Atoms
Pauling Electronegativity Values
Dipolar HF Showing Dipole Moment
Electrostatic Potential Map of HF
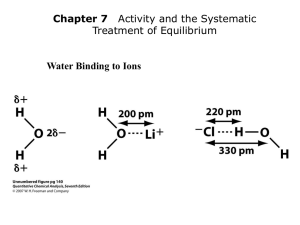
Charge Distribution in Water Molecule; Electrostatic
Potential Diagram of Water
Structure and Charge Distribution of NH3; Electrostatic
Potential Diagram of NH3
Cancellation of Bond Polarities in CO2; Electrostatic
Potential Diagram for CO2
Ionic Compound in Solid State
Gas Phase of Ionic Substance
Structure of LiF
Chemical Bonds
•
Covalent Bonds
Bonds form between atoms by sharing electrons.
Resulting collection of atoms is called a molecule.
Copyright © Cengage Learning.
All rights reserved
14
Covalent Bonding
Copyright © Cengage Learning.
All rights reserved
15
Chemical Bonds
•
Ionic Bonds
Bonds form due to force of attraction between
oppositely charged ions.
Ion – atom or group of atoms that has a net
positive or negative charge.
Cation – positive ion; lost electron(s).
Anion – negative ion; gained electron(s).
Copyright © Cengage Learning.
All rights reserved
16
Molecular vs. Ionic Compounds
Copyright © Cengage Learning.
All rights reserved
17
Crystals of Sodium Chloride
Charles D. Winters #C5090D
Crystals of Copper II Sulfate (CuSO4)
Structure of Quartz
Structure of Ice (Hydrogen Bond)
Electrostatic Diagram Showing
Three Possible Types of Bonds
Structures of Ethane and Ethanol
Molecular Structures of Vitamins A and C
Molecular Structure of Vitamin A
Frank Cox
Molecular Structure of Vitamin C
Frank Cox
Graphite and Diamond
#200457884-001 Credit: Photodisc Red
Structures of Diamond, Graphite, and Buckyball (C60)
1996 Nobel Prize
Graphene (石墨烯)
2010 Nobel Prize
Combination of H 1s Atomic Orbitals
to Form MOs.
MO Energy-Level Diagram for H2
FIGURE 14.27: Bonding and Antibonding
MOs
MO Energy-Level Diagram for H2
Correct MO Energy-Level Diagram
for B2 (:B:B:)
Apparatus Used to Measure
Paramagnetism of a Sample
Diagrams, Bond Orders, Bond Energies,
and Bond Lengths for Diatomic Molecules B2 to F2
Partial MO Energy-Level Diagram for HF
Electron Probability Distribution in the
Bonding MO of HF
Sigma Bonding
System in Benzene
FIGURE 14.50: (a) Pi MO System in Benzene, (b)
Delocalized Pi MO Over Entire Ring of C Atoms
Structure of Benzoic Acid
Members of Halogen Family (X2)
Tom Pantages
Sulfur Crystals (S8)
Ken O'Donoghue
Acids and Bases
Dissociation of Acid in Water
強酸及弱酸
Acid Molecules
Organic Acids: Acetic Acid and
Benzoic Acid
強酸: HX, X = Cl, Br, NO3, HSO4, ClO4
HX H+ + X- 水中完全解離
弱酸:R-COOH (有機酸), HF, H2CO3
R-COOH H+ + R-COO- 水中部分解離
強鹼: MOH, M = Na, K; Na2CO3
MOH M+ + OH- 水中完全解離
Na2CO3 + H2O ↔ 2Na+ + HCO3- + OH-
弱鹼:R-NH2 (有機胺), NaHCO3
R-NH2 + H2O ↔ R-NH3+ + OH- 水中部分解離
NaHCO3 + H2O ↔ Na+ + H2CO3 + OH-
pH 值
• 25° C 純水中 H2O ↔ H+ + OH[H+] = [OH-] = 0.0000001 mole/liter = 10-7 M
• 酸性: [H+] > [OH-] ;鹼性: [H+] < [OH-]
• 25° C 任何水溶液中 (不管酸性鹼性)
[H+] × [OH-] = 10-14 M2
• pH = -log [H+], pOH = -log [OH-],
[H+] = 0.1, pH = 1; [H+] = 10-7, pH = 7
pH + pOH = 14
pH 值愈小溶液愈酸, pH 值愈大溶液愈鹼,pH = 7
時為中性
How Do We Measure pH?
• For less accurate measurements, one can use
– Litmus paper (石蕊試紙)
• “Red” paper turns blue above ~pH = 8
• “Blue” paper turns red below ~pH = 5
– Or an indicator.
2009, Prentice-Hall,
How Do We Measure pH?
For more accurate
measurements, one
uses a pH meter,
which measures the
voltage in the solution.
2009, Prentice-Hall,
Measuring the pH of Vinegar and Aqueous
Ammonia
pH Scale