Class 22 - Department of Chemistry
advertisement

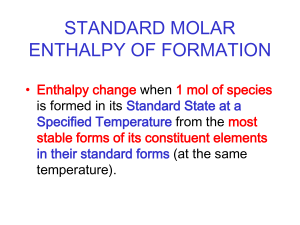
CHEMISTRY 161 Chapter 6 www.chem.hawaii.edu/Bil301/welcome.html THERMODYNAMICS HEAT CHANGE quantitative study of heat and energy changes of a system CH4(g) + 2 O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2 H2O(l) the state (condition) of a system is defined by T, p, n, V, E the state (condition) of a system is defined by T, p, n, V, E STATE FUNCTIONS properties which depend only on the initial and final state, but not on the way how this condition was achieved ΔV = Vfinal – Vinitial Δp = pfinal – pinitial ΔT = Tfinal – Tinitial ΔE = Efinal – Einitial Energy is a STATE FUNCTION ΔE = m g Δh IT DOES NOT MATTER WHICH PATH YOU TAKE Hess Law ENTHALPY, H CH4(g) + 2O2(g) - 802 kJ Reactants - 890 kJ CO2(g) + 2H2O(g) - 88 kJ CO2(g) + 2H2O(l) Products Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics a system at thermodynamical equilibrium has a constant temperature heat is spontaneous transfer of thermal energy two bodies at different temperatures T1 > T2 spontaneous T1 T2 First Law of Thermodynamics energy can be converted from one form to another, but cannot be created or destroyed CONSERVATION OF ENERGY SURROUNDINGS + - SYSTEM THE TOTAL ENERGY OF THE UNIVERSE IS CONSTANT ΔE = ΔEsystem + ΔEsurrounding = 0 First Law of Thermodynamics ΔEsystem = ΔQ + ΔW ΔQ heat change ΔW work done DQ > 0 ENDOTHERMIC DQ < 0 EXOTHERMIC ? mechanical work ΔW = - p ΔV M ΔV < 0 the energy of gas goes up M ΔV > 0 the energy of gas goes down First Law and Enthalpy ΔEsystem = ΔQ - pΔV 1.constant pressure 2. ideal gas law → enthalpy change Δ H → pV=nRT p ΔV = Δn R T ΔEsystem = ΔQ – R T Δn ΔQ = ΔEsystem + R T Δn = ΔH ΔQ = ΔEsystem + R T Δn = ΔH Δ n = nfinal – ninitial Calculate the energy change of a system for the reaction process at 1 atm and 25C 2 CO(g) + O2(g) → 2 CO2(g) ΔHo = -566.0 kJ ΔEsystem = ΔH0 - R T Δn ΔEsystem = -563.5 kJ A gas is compressed in a cylinder from a volume of 20 L to 2.0 L by a constant pressure of 10 atm. Calculate the amount of work done on the system. Calculate the amount of work done against an atmospheric pressure of 1.00 atm when 500.0 g of zinc dissolves in excess acid at 30.0°C. Zn(s) + 2H+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + H2 (g) The heat of solution of KCl is +17.2 kJ/mol and the lattice energy of KCl(s) is 701.2 kJ/mol. Calculate the total heat of hydration of 1 mol of gas phase K+ ions and Cl– ions. Homework Chapter 6, problems