Acids, Bases, and pH

Chapter 9
Section 1
Explain the chemical composition of acids and bases, and explain the change of pH in neutralization reactions.
I can differentiate between acids and bases.
When dissolved in water, they ionize (form ions)
Form H + (Hydrogen) ions, which attach to water molecules to form hydronium ions, H
3
O +
Properties:
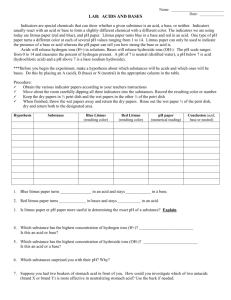
Taste sour
Blue litmus paper turns red
Conduct electric current
Corrosive
Complete ionization in water
High concentration of hydronium ions in the liquid
Strong acid
Conducts electricity
Strong electrolyte
Weak acids
Low concentration of hydronium ions in the liquid
Do not conduct electricity well
Weak electrolyte
Double headed arrow
Corrosive
Can damage living tissues
Vapors can be harmful to eyes, mouth and lungs
Wear safety goggles, gloves, lab apron
When dissolved in water form OH (hydroxide ions)
Properties
Tastes bitter
Solution feels slippery
Turn red litmus paper blue
Like acids, bases can also damage the skin
When bases dissolve in water, they ionize.
NaOH Na + + OH -
Not all bases contain OH -
Some will react with water to form hydroxide ion
NH
3
+ H
2
O NH
4
+ + OH -
High concentration of OH in the solution
Ba(OH)
2
Ba 2+
Complete ionization in water
Good conductor of electricity
Strong electrolyte
+ 2OH -
Low concentration of OH in solution
NH
3
+ H
2
O NH
4
+ + OH -
Do not ionize completely
Not a good conductor of electricity
Weak electrolyte
Bases are corrosive and can damage living tissue
Wear safety goggles, gloves and a lab apron!!
What ions do acids produce?
What ions do bases produce?
What is the difference between a strong acid and a weak acid?
Why should we observe lab safety rules when working with acids and bases?
I can explain pH.
You can determine if a substance is an acid or a base by using an indicator.
An indicator is a substance that changes color in the presence of an acid or base.
Indicators measure the level of hydronium ions. The level determines if a substance is acidic or basic.
Cabbage juice can be used as an indicator
Litmus paper is a common indicator
Acids turn blue litmus paper red
Bases turn red litmus paper blue
Only indicates if a substance is an acid or a base
To determine strength or weakness, pH values are used catalog.flatworldknowledge.com
profmarsolais.com
A measure of the concentration of H
3
O + ions in solution
Acidity or basicity of a solution can be critical
Enzymes in your body will not function properly if your blood is too basic or acidic
Fish cannot survive in waters that are too acidic or basic ck12.org
hapnotes.wikidot.com
Acid: substance that produces H + ions in aqueous solution
Base: substance that produces OH ions in aqueous solution
[H + ]
[OH ]
Stronger Weaker Weaker Stronger
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
Acids pH Scale
Bases
• Small differences in pH mean large differences in acidity
• Example: pH of coke = 3 pH of coffee = 5
Coke is 10 2 , or 100, times more acidic than coffee.
ch302.cm.utexas.edu
gizmodo.com
Lemon juice has a pH of 2.2. Is it an acid or a base?
Detergents such as Tide have a pH of about 10.
Is Tide an acid or a base?
Seawater has a pH of 8.2. Is seawater an acid or a base?
The inside of your mouth has a pH of 7. Is it an acid or a base?
409 cleaner contains ammonia that has a pH of 12.
What will 409 do to red litmus paper?
A soft drink has a pH of 3.2.
What will it do to a piece of red litmus paper?
You can find pH from the concentration of a strong acid.
pH is the negative power of 10 that is used to describe the concentration of H
3
O + ions.
The concentration of H
3
O + in pure water is 1 x 10 -7 .
The pH of pure water = 7
The concentration of H
3
O + ions in a solution of a strong acid is the same as the concentration of the acid.
Determine the pH of a 0.0001 M (Molar) solution of the strong acid HCl.
concentration of H
3
O + ions = concentration of HCl concentration of H
3
O + ions = 0.0001 M = 1 x 10 -4 M pH = -(-4) = 4