The Respiratory System - Mrs. Grigar

The Respiratory System http://137.222.110.150/calnet/irish_cal/exotics/respiratory%20system.jpg
The system of the body that deals with breathing
The body takes in the oxygen that it needs and removes the carbon dioxide that it doesn’t
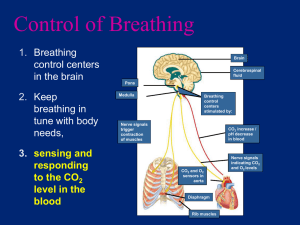
The Oxygen Delivery System
• Main function - to supply the blood with oxygen
• Does this through breathing
Function
- to bring oxygen into the body
- to remove carbon dioxide and water from the body
O
2
CO
2
Breathing and Respiration are NOT the same thing!
Breathing
Moving air in and out of the lungs
• Breathing is partly a result of changes in air pressure-gases move from an area of high pressure to an area of low pressure.
• Lungs are considered an excretory organexcrete(get rid of) carbon dioxide
Respiration
Chemical reaction that releases energy
What’s the Difference
Between Breathing, Circulation, and Respiration?
Breathing is simply inhaling and exhaling air.
Circulation is the transport of O
2 from the lungs to the body’s cells, and the transport of CO
2 from the body’s cells back to the lungs.
It involves the heart, blood vessels, and blood.
Carbon dioxide is carried from all cells back to lungs
Oxygen is carried from lungs to all cells
Respiration is a chemical reaction that makes energy from glucose
(sugar)
and oxygen.
C
6
H
12
O
6
+ 6O
2
ENERGY +
6CO
2
+ 6H
2
O glucose + oxygen ENERGY + carbon dioxide + water
Respiration takes place in cells.
Inhalation
• Breathing in
• Body gets oxygen from the air
• Rib muscles contract to pull ribs up and out
• Diaphragm muscle contracts to pull down the lungs
• Tissue expands to force (pull) in air.
• Less air pressure in lungs
Exhalation
• Breathing out
• Get rid of carbon dioxide
• Rib muscles relax
• Diaphragm muscle relaxes
• Tissue returns to resting position and forces (pushes) air out
• Increased air pressure in lungs
http://mhln.com
Parts of the System
• Mouth
• Nose
• Trachea
– splits into bronchi
– bronchioles
• Lungs
– Bronchioles
– Alveoli
• Diaphragm
• Bronchial tubes
Lungs
• Many smaller tubes
• Alveoli (alveolus) – surrounded by capillaries
• Average adult's lungs contain about 600 million of these air-filled sacs
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/
The main body organs or parts of the respiratory system are:
• Nose
(mouth sometimes)
• trachea
(windpipe)
• bronchi tubes
• lungs
(main organ)
• bronchioles
(smaller tubes)
• alveoli
(tiny air sacs)
• diaphragm
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/
http://biology.clc.uc.edu/courses/bio105/respirat.htm
Structure
Nose or
Mouth or bronchial tubes
Function of Organs
1) nose : moistens, warms and filters air septum nasal cavity
1930’s “nose job”
2) mouth : takes in and breathes out air
3) pharynx : top of throat pharynx epiglottis pharynx esophagu s trachea
4) epiglottis : flap that closes off trachea when you swallow
5) larynx : vocal cords; vibrate to produce sound vocal cords
Cancer of the larynx
Artificial Larynx, 1933
6) trachea : windpipe; connects nose and mouth to lungs trachea bronchus
7) bronchus or bronchial tubes : where trachea splits and enters both lungs
8) lungs : main organs of respiratory system; full of alveoli
The right lung is slightly larger than the left. It has 3 lobes or areas; the left lung has 2 lobes.
Each lung weighs about one pound.
9) alveoli : tiny sacs in lungs that are covered with capillaries;
CO
2 they exchange for O
2
10) diaphragm: a strong muscle that fills lungs with air when it contracts downward, and empties lungs when it relaxes
http://users.tpg.com.au/users/amcgann/body/respiratory.html
Pathway of Oxygen
Body breathes in the air which is pulled through the nose or mouth and down through the trachea
http://webschoolsolutions.com/patts/systems/lungs.htm
Pathway of Oxygen
The trachea is a pipe shaped by rings of cartilage.
It divides into two tubes called bronchi.
Bronchi carry air into each lung.
Pathway of Oxygen
Inside the lung, the tubes divide into smaller and smaller tubes called bronchioles.
At the end of each of these tubes are small air sacs called alveoli.
Capillaries, which are small blood vessels with thin walls, are wrapped around these alveoli.
http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/
Pathway of Oxygen
Capillary walls are so thin and close to each other that the air easily diffuses through.
http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/
Pathway of Oxygen
Oxygen diffuses through the capillaries into the bloodstream.
Carbon dioxide in the bloodstream, diffuses through into the alveoli, and is then removed from the body when we breathe out.
http://users.tpg.com.au/users/amcgann/body/respiratory.html
http://www.mtsinai.org/
http://mhln.com
http://www.borg.com/~lubehawk/hrespsys.htm
In the lungs, the exchange of gases (oxygen & carbon dioxide) occurs in tiny air sacs called the alveoli.
How does oxygen move to the circulatory system from the alveoli?
Capillaries wrap around each air sac. The air sacs have thin walls that let gases move through them.
Pleura
• Membrane lining the lungs and chest cavity
The Diaphragm
The muscle that controls the breathing process.
The Diaphragm
The diaphragm contracts; flattens and pulls down to cause the chest to expand and air is pulled into the lungs (inhale)
The Diaphragm
When the diaphragm relaxes, the chest collapses and the air in the lungs is forced out (exhale)
http://users.tpg.com.au/users/amcgann/body/respiratory.html
How is air brought into your lungs?
The diaphragm, a muscle just below your lungs & near the bottom of the ribcage, helps pull in air into the body (as well as force it out).
This is how it does it
• Epiglottis-
– A flap of tissue at the lower end of the pharynx; when you swallow your epiglottis fold down to prevent food or liquid from entering your airway.
• Diseases and Disorders
– Things that can harm your respiratory system
• Smoking-first and second hand smoke
– Nicotine
– Tar
– Carbon monoxide
• Polluted air
• Coal
• Dust
• asbestos
Diseases of the
Respiratory System
Asthma-shortness of breath wheezing or coughing
•Caused often by an allergic reaction
•Causes the bronchial tubes to contract quickly http://kidshealth.org/kid/closet/movies/asth ma_movie.html
Asthma
• Bronchitis-infection of the bronchial tubes
– Too much mucus is produced
– Causes coughing which harms cilia and bronchial tubes
Bronchitis
inflammation of bronchial tubes
• Emphysema-a disease in which the alveoli in the lungs enlarge
– Main cause is smoking
– Alveoli in the lungs lose their ability to expand and contractcan’t push air out of lungs so less oxygen moves into the bloodstream
– People w/emphysema need extra oxygen(from oxygen tanks)
Emphysema
oxygen-dependent
• Lung Cancer-main cause is smoking
– Leading type of cancer deaths
– Caused by inhaling the tar in cigarette smoke
– Carcinogens-tar and other ingredients found in smoke that lead to uncontrolled growth of cells(cancer)
Lung Cancer
Pneumonia: lungs are swollen and filled with pus or liquid
How does the respiratory system work with the circulatory system?
• The respiratory & circulatory systems work together to get oxygen to cells (and to help them get rid of carbon dioxide).
• The respiratory system brings oxygen into the lungs and gets it into the blood.
• The circulatory system takes that oxygen and transports it through the blood to your body cells.
• Also, carbon dioxide is removed from your cells by the circulatory system and brought to your lungs, which exhale it back out of your body and into the air outside.
When the body needs more oxygen, it will breathe rapidly to get the oxygen it needs to meet its energy needs.
.
As the body gets more active , it needs more oxygen .
My lungs are working extra hard! Can we slow down?.
Q: What two things happen at the same time in the alveoli (air sacs)?
Blood picks up oxygen from the lungs at the alveoli and blood releases carbon dioxide into the alveoli.
Your body is so complex that it takes two systems working together as a team to get oxygen to your body cells.
Air enters the body
Nasal or Oral Cavity
Pharynx
Larynx
Trachea
Bronchi
Bronchioles
Alveoli
Oxygen diffuses into capillaries and into the bloodstream
Mouth/Nasal Cavity
Pharynx
Trachea
Bronchi
Alveoli
Diaphragm
Larynx
Lungs
2
7 the area ringed in purple
1
4
3
5
QUIZ
6
Relationship to digestive system
• Cellular respiration requires glucose and oxygen to release energy to the body
• C
6
H
12
O
6
+ 6O
2
6CO
2
+ 6 H
2
O + Energy
• Oxygen is provided by the respiratory system
• Glucose is provided by the digestive system
• (glucose is made during photosynthesis)
“Respirate”
A respiratory System Song by. Mr. Rojas www.rrojas.com/home/rojassongs/respiratesong
• http://science.nationalgeographic.com/scie nce/health-and-human-body/humanbody/lungs-article.html
Test what you know with an online practice quiz on the
Respiratory System: www.quia.com/quiz/796944.html