Chemical Incompatibilities
advertisement

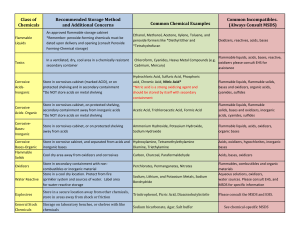
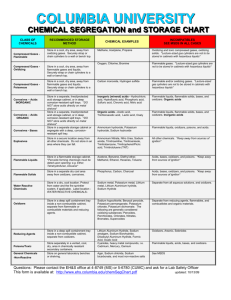
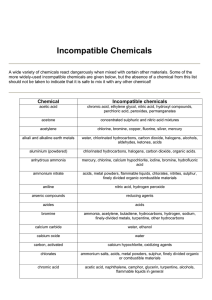
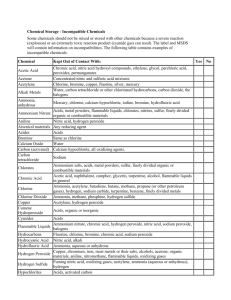
Chemical Incompatibilities Why is recognizing chemical incompatibilities so important? • Storing incompatible chemicals together can result in harmful gases/vapors, heat, fire and explosions Major groups of incompatibles • Acids and bases • Oxidizers and flammable liquids • Water reactive and aqueous/corrosive materials Acids and Bases Acids • Nitric acid • Sulfuric acid • Phosphoric acid • Hydrochloric acid Bases • Sodium hydroxide • Potassium hydroxide • Ammonium hydroxide • Imidazole Oxidizers and Flammables Oxidizers • 30% (or greater) hydrogen peroxide • Silver nitrate • Ammonium persulfate • Potassium permanganate • Nitric acid Flammables • Ethanol • Glacial acetic acid • Propanol • Acetone • Xylene • Methanol Water Reactive and Aqueous/Corrosive Water Reactive • Sodium • Lithium • Lithium borohydride • Sodium hydride Aqueous • Fuming nitric acid • Concentrated sulfuric acid • Concentrated phosphoric acid Incompatible Chemical Storage • Best option is in separate storage cabinets or shelves • Secondary containment is the next best option Incompatible Chemical Storage • Includes refrigerators and other storage locations for chemicals Chemical Storage Reminder • Chemicals can expire (e.g. ethyl ether) • Important to keep an eye on container • Make note of date received • Observe expiration dates Can you spot the mistake? Can you spot the mistake? Glacial Acetic Acid: flammable! Flammable liquid can’t be stored with acids (HCl) unless it’s in a secondary container Can you spot the mistake? Can you spot the mistake? Hydrogen Peroxide: oxidizer! Oxidizers and flammables stored in fridges/freezers must be in secondary containers