Synthetic Base stocks
advertisement

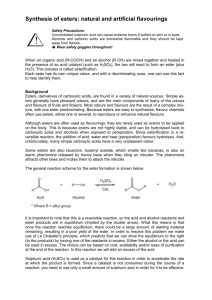
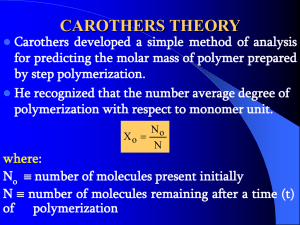
Mineral Oils - Nature’s Synthesis Paraffinic Cyclic/Aromatic Low cost Big mixture Mineral Oil Mineral oil refining removes many of the least desirable components (e.g. aromatics, waxes) and modifies the rest (e.g. hyrofinishing, hydrodewaxing and/or hydroprocessing) Base Stock Component Properties Paraffins Iso-Paraffins Naphthenes Aromatics VI very high high medium/low lowest high low lower lowest Traction lowest low Volatility low low higher highest Solvency poor fair good excellent Oxidation Resistance good good lower resistance easily oxidized Pour point medium/high medium/high Synthetic Base stocks • Synthesized hydrocarbons • Synthesized non-hydrocarbons (typically containing oxygen atoms) Synthesized hydrocarbons • • • • Polyalphaolefins Polybutenes Alkylated aromatics Cycloaliphatics Polyalphaolefins (PAO) • Chain molecular structures synthesized from ethylene polymerization • High VI and high oxidation stability • Low pour point, low traction and volatility • Best as engine oil basestock. Most popular PAO is polydecenes, which is the basestock of Mobil 1 Polymerization of ethylene PAO Manufacture R - CH = CH2 Polymerization Hydrogenation 3 Hydrogenated trimers, tetramers, etc. Alpha-olefins 1-Decene R - CH CH2 - CH H CH R x Polydecene “Ideal” Actual Synthetic Polyalphaolefin (PAO) Hydrogenated Polydecene From Crude Oil to Synthetic Lubricants Synthetics are usually sourced from crude oil Many manufacturing steps result in high cost Crude Oil Atmospheric 1-Decene Distillation Catalytic Polymerization Distillation Distillation Synthetic Lubricants Sales & Marketing Cracker Feed Alphaolefins Catalytic Catalytic Cracking Polymerization Hydrogenation Blending Polydecene Formulation Light Olefins Separation Ethylene Additives On sale at Walmart for $5.00 Polybutenes • Synthezied through controlled polymerization of butenes and isobutenes • High dielectrics constant – electrical insulating oils • Low thermal stability – metal working and compressor lubes to decompose to gases • High molecular weight polybutenes or polyisobutenes are used as VI improvers Alkylated aromatics • Synthesized from alkylation of benzenes • Very low pour point and low viscosity – subzero temperature applications Cycloaliphatics • Synthesized naphthenes, multi-ring-structured molecules • Develop a glasslike structure under high stresses to yield high traction • Used as traction-drive fluids, also used in rolling bearings to reduce roller skidding Synthesized non-hydrocarbons • • • • • Organic esters Polyglycols Phosphate esters Silicate esters Polyphenyl esters Organic esters • Dibasic acid esters: • Polyol esters: Wide temperature range and good thermal stability Used as base stocks for essentially all jet engine lubes Polyglycols • The largest single class of synthetic lubricant bases • High VI and low pour point • Used mainly as brake fluids and hydraulic fluids Phosphate esters • High fire resistance • Used mainly as hydraulic fluids and compressor lubes • Also used as antiwear additives by its formation of phosphide films on metal surfaces Silicate ester • Extremely high VI > 300 • Used mainly as heat exchanger fluids Polyphenyl esters • Most thermally and oxidatively stable • Used mainly as heat transfer fluids