Chemical Reactions Powerpoint
advertisement

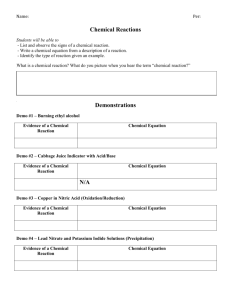
Chemical Reactions Chemical Reaction… Not a Chemical Reaction… What is a Chemical Reaction? • A process in which new substances with new chemical and/or physical properties are formed. • A burning piece of paper (Chemical Reaction): paper ashes, water vapor, and carbon dioxide • Dissolving salt in water (No Reaction): Salt + Water → Salt + Water Parts of a Chemical Equation Na+ Cl → NaCl sodium and chlorine yields sodium chloride Reactants The substances that you start with. In this case: Sodium and Chlorine “Yields” This arrow tells you that the reactants become the products through a chemical reaction. Products The substances you end with. In this case: Sodium Chloride Chemical Equations Mg + O2 → MgO magnesium and oxygen yields magnesium oxide H2O → H2 + O2 water yields hydrogen and oxygen C4H10 + O2→CO2 + H2O butane and oxygen yields carbon dioxide and water Types of Chemical Reactions Type 1: Synthesis • In a synthesis reaction, two (or more) simple substances form a more complex substance. • Synthesis: Two Become One • A + B → AB Synthesis Example Na + Cl → NaCl sodium and chlorine yields sodium chloride Types of Chemical Reactions Type 2: Decomposition • In a decomposition reaction, a complex substance is broken down into two (or more) simpler substances. • Decomposition: One Becomes Two • AB → A + B Decomposition Example H2O2 → H2O + O2 hydrogen peroxide yields water and oxygen Types of Chemical Reactions Type 3: Single Replacement Reaction • In a single replacement reaction, a single element replaces another element in a compound. • Single Replacement: Start with one compound, end with a different compound. A + BC B + AC Single Replacement Reaction Single Replacement Example Zn + HCl → H2 + ZnCl2 zinc and hydrochloric acid yields hydrogen and zinc chloride Types of Chemical Reactions Type 4: Double Replacement Reaction • In a double replacement reaction, elements from two compounds switch places and form two new compounds. • Double Replacement: Start with two compounds, end with two different compounds. AB + CD CB + AD Double Replacement Reaction