Unit 4-6 Diagram Book
advertisement

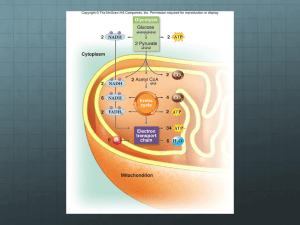
Ecology, Trophic Levels, ATP /ADP, Flower Anatomy, Anatomy of a Leaf, Photosynthesis, and Cellular Respiration The cover should represent the theme of Unit 4-6-> Ecology, Plant Anatomy, Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration. Consider the vocab: Consumers, Producers, Autotrophs, Heterotrophs, Sunlight, Kreb’s Cycle, Calvin Cycle, Cellular Respiration, ATP, ADP, Glycolysis, H2O, O2, C6H12O6, CO2, Chloroplast, Mitochondria, Fermentation, and Energy. Define food web. Under the food web picture write “The arrows show the direction in which energy flows.” On the trophic level chart fill in the correct animals from the food web that fit each category. Label the levels producer, primary consumer, secondary consumer, and tertiary consumer. Define Energy Pyramid. How much energy is transferred from trophic level to trophic level? Write this on the page. Color and label Adenine blue Color and label ribose red Color and label the phosphates yellow Color and label the high energy bonds green Answer the questions. Color the picture of the flower. Make sure the table fills the entire page. The labels need to correspond with the numbers on the flower. Fill in the functions of each structure. # Structure 1 Anther 2 Filament 3 Stamen 4 Stigma 5 Style 6 Ovary 7 Pistil / Carpel 8 Ovule 9 Petal 10 Sepal Function Color the anatomy of the leaf according to the key. Cuticle, labeled A- color light blue Epidermis, labeled B- color yellow Guard Cells, labeled C- color pink Palisade Mesophyll, labeled D, color dark green Phloem, labeled H, color purple Xylem, labeled G, color orange Spongy Mesophyll, labeled F, color light green Bundle Sheath, labeled E, color dark blue Structure Cuticle Epidermis Guard Cells Palisade Mesophyll Phloem Xylem Spongy Mesophyll Bundle Sheath Function Prevents Water Loss Covers the upper and lower sides of the leaf. Protects the internal tissues. Translucent= allows light to reach the mesophyll. Modified epidermal cells that are photosynthetic and they open and close the stomata (pores in the leaves). Main function= Photosynthesis Has the most chloroplasts Carries products of photosynthesis via active transport Products = oxygen and glucose PHLOEM IS FOOD! Carries water and nutrients from the roots to the rest of the plant. Allows CO2 and O2 to reach the palisade cells, also functions in photosynthesis. Regulates the movement of substances. Helps protect the vascular tissue (xylem and phloem). Define photosynthesis in the top box. Write the equation for photosynthesis in the bottom box. Make sure to label the products and reactants, as well as write out the molecules of the equation. Label the chloroplast: 1. Chloroplast 2. Sunlight 3. H2O 4. Thylakoid contains chlorophyll 5. Oxygen 6. Energy carrying molecules transferred to light independent reactions. 7. CO2 from atmosphere 8. Calvin Cycle 9. Glucose, C6H12O6 Define cellular respiration in the top box. Write the equation for cellular respiration. Label the reactants and products, as well as writing out the molecules of the equation. Fill in the Glycolysis box: anaerobic, makes 2 ATP, occurs in the cytoplasm, splits one glucose into 2-3 carbon chains. Label the mitochondria: 1. Mitochondria 2. 2-3 carbon chains (broken down glucose) 3. Krebs cycle takes place in the mitochondrial matrix. Produces 2 ATP 4. Carbon dioxide 5. Energy transferred to second stage 6. Energy from glycolysis and O2 enter 7. Water is produced, ATP is produced. On the bottom write: ATP comes from: 2 from glycolysis, 2 from Krebs Cycle, and 34 from the Electron Transport Chain. Totaling 38 ATP.