131110 COS ATP - Community of Reason
advertisement

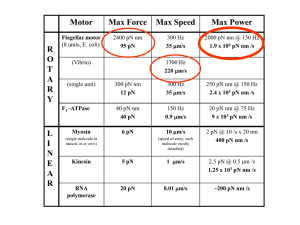
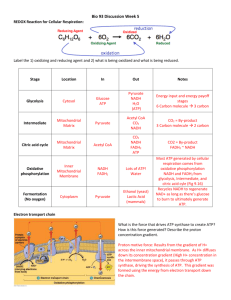
MITOCHONDRIA III: ATP - THE ENERGY CURRENCY OF THE CELL Karen Bame, Ph.D. Associate Professor School of Biological Sciences UMKC Energy Energy is defined as the capacity to do work, i.e. to move matter. Cells, tissues and organisms need energy for a variety of processes • • • • Muscle contraction Maintaining ion gradients for nerve transmission Biosynthesis of molecules Removal of waste products Energy Cells generate energy by oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions • redox reactions move electrons (and H) between molecules Energy is generated when reduced molecules are oxidized • more reduced a molecule is, the more energy it contains metabolism • catabolic pathways are a series of chemical reactions that oxidize molecules into CO2, H2O and NH3 • some of the energy released in the pathway can be used to make ATP and NADH • the ATP and NADH can then be used in anabolic processes that require energy NADH and FADH2 Coenzymes derived from B vitamins • niacin • riboflavin Accept electrons and become reduced in catabolic reactions Donate electrons to the electron transport chain (ETC), which generates energy to make ATP ATP Called the energy currency of the cell, since hydrolysis of ATP releases energy ATP + H2O ADP + Pi ATP is generated in the mitochondria citric acid cycle oxidative phosphorylation • electron transport chain • ATP synthase NADH and FADH2 donate electrons to the ETC Electron transport chain • • • Complexes I, II, III, IV Coenzyme Q (CoQ) Cytochrome c Movement of electrons through ETC sets up a proton (H+) gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane ATP synthase uses the proton gradient to make ATP F0 subunit = H+ channel H+ move back into matrix from IMS F1 subunit = catalytic activity ADP + Pi ATP • movement of H+ through F0 causes the c-ring of the F0 subunit and the ge-shaft of F1 to rotate. • rotation of the ge-shaft causes conformational changes in the ab-subunits of F1 • these conformational changes drives the chemical reaction: ADP + Pi ATP Youtube video: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PjdPTY1wHdQ Summary • Cells require energy to perform a variety of functions. • Energy is generated in catabolic processes, when molecules • • • • are oxidized to CO2 and H2O. Some of the energy released in catabolic processes is used to make ATP. ATP is mostly synthesized in the mitochondria, via the electron transport chain (ETC) and ATP synthase. Oxidation-reduction reactions of the ETC sets up a proton gradient; energy “stored” in the proton gradient is converted to mechanical energy (rotation), which drives the synthesis of chemical energy (ATP). ATP is used to power cellular processes that require energy to occur.