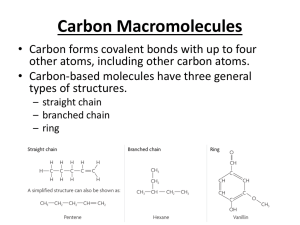
CH 3
advertisement

Introduction to Metabolism Joe vs. Josie Jack Blazyk Professor of Biochemistry Associate Dean for Research & Grants Major Dietary Fuel Molecules Carbohydrates Starch, Sucrose, Lactose mostly Glucose Lipids Triglycerides Contains 3 Fatty Acids Proteins Polymer of Amino Acids Contain N in addition to C, H, O Design of Metabolism Activated Precursors Macromolecules UDP-Glucose Fatty Acyl-CoA Aminoacyl t-RNA Glycogen Triglycerides Proteins CHEMICAL POWER Anabolism (Biosynthesis) Precursors Glucose Fatty Acids Amino Acids 40% O2 Oxidation (Combustion) ENERGY 60% HEAT Catabolism CO2 H2O NH3 What is essential in our diet? Proteins Amino acids Lipids Unsaturated fatty acids Carbohydrates Glucose ?? How do we store our energy reserves? Glycogen Liver Muscle Triglycerides Adipose Where? Carbohydrates <1% e.g., Glucose Lipids e.g., Fatty Acids Proteins Amino acids 85% 15% Design of Metabolism Activated Precursors Macromolecules UDP-Glucose Fatty Acyl-CoA Aminoacyl t-RNA Glycogen Triglycerides Proteins CHEMICAL POWER Anabolism (Biosynthesis) Precursors Glucose Fatty Acids Amino Acids 40% O2 Oxidation (Combustion) ENERGY 60% HEAT Catabolism CO2 H2O NH3 O CH3 - C - S - CoA HS - CoA 3 H2O Located in mitochondrial matrix Why are lipids our primary energy reserves? 1 gram of carbohydrate = 4 Cal/g 1 gram of protein = 4 Cal/g 1 gram of fat = 9 Cal/g Why are lipids our primary energy reserves? Carbohydrates 4 Cal/g e.g., Glucose C6H12O6 9 Cal/g Lipids e.g., Palmitic Acid C16H32O2 Proteins 4 Cal/g e.g., Glycine C2H5O2N More Reduced Joe 16 yo, 5’10” tall, 160 pounds Joe eats 4000+ calories per day After 6 months, Joe weighs 210 pounds Joe drinks 6 to 8 20-ounce Cokes per day Previous Nutrition Label 1440 - 1920 Cal/day Body Mass Index Joe 5’10” Initial BMI 160 lbs. 23.0 Final BMI 210 lbs. 30.1 What is happening in Joe’s liver? What is its metabolic response to feasting? Glycolysis Glycogenesis Well-Fed Liver Pentose Shunt Triglyceride Synthesis Fatty Acid Synthesis What is happening in Joe’s adipose tissue? What is its metabolic response to feasting? Glycolysis Pentose Shunt Cholesterol Synthesis Triglyceride Synthesis Well-Fed Adipose Fatty Acid Synthesis What is happening in Joe’s skeletal muscle? What is its metabolic response to feasting? Glycogenesis Well-Fed Muscle Josie 16 yo, 5’6” tall, 130 pounds Josie eats < 600 calories per day After 6 months, Josie weighs 105 pounds Pria Power Bars Chocolate Peanut Crunch Serving Size: 1 Bar = 28g Calories Calories From Fat 110 30 Amount/Serving Total Fat Saturated Fat Trans Fat Sodium Total Carb Dietary Fiber Sugars Protein % DV* 3.5g 2g 0g 85mg 16g 1g 10g 5g 5% 10% 4% 5% 4% 10% Josie 5’6” Initial BMI 130 lbs. 21.0 Final BMI 105 lbs. 16.9 What is happening in Josie’s liver? What is its metabolic response to fasting? Fasting Liver Gluconeogenesis Glycogenolysis Ketone Body Synthesis Fatty Acid Oxidation What is happening in Josie’s adipose tissue? What is its metabolic response to fasting? No Uptake Fasting Adipose Triglyceride Breakdown Fatty Acid Oxidation What is happening in Josie’s skeletal muscle? What is its metabolic response to fasting? No Uptake Fasting Muscle Ketone Body Utilization Fatty Acid Oxidation Fasting Liver Gluconeogenesis Glycogenolysis Ketone Body Synthesis Fatty Acid Oxidation Why does Josie’s liver make ketone bodies? Aren’t ketone bodies bad? Palmitic Acid CH3-(CH2)14-COOH vs. Acetoacetate = CH3 – C – CH2 – COOH OH _ O b-Hydroxybutyrate CH3 – CH – CH2 – COOH Acetoacetate = O CH3 – C – CH2 – COOH Acetone = O CH3 – C – CH3 + CO2 Well-Fed State Brain Pancreas Gut Insulin Glycogen Glucose aa Portal Vein CO2 + H2O Glucose aa Liver Urea Adipose CO2 + H2O Protein Chylomicrons Pyruvate TG TG Lymphatics VLDL CO2 + H2O Lactate Glycogen Muscle Lactate RBC Early Fasting State Brain Pancreas Gut Glucagon Glycogen Portal Vein CO2 + H2O Glucose Adipose Liver FA Pyruvate FA CO2 + H2O CO2 + H2O Lymphatics Lactate Muscle Lactate RBC Extended Fasting State Brain Pancreas Gut Glucagon CO2 + H2O Glucose Portal Vein KB Urea Glycerol FA Liver Pyruvate Adipose FA CO2 + H2O CO2 + H2O Lymphatics aa Protein Lactate Cortisol RBC Muscle = O CH3 – C – CH2 – COOH Acidosis CH3 – C – CH2 – COO pH OH _ _ CH3 – CH – CH2 – COOH H O b-Hydroxybutyrate OH + = Acetoacetate CH3 – CH – CH2 – COO- + H Compensation + HCO3- + H H2CO3 H2O + CO2 Respiration pH Fig. 16-10 Table 16–3. Summary of the Major Metabolic Features of the Principal Organs Organ Major Pathways Main Substrates Major Products Exported Specialist Enzymes Liver Glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, lipogenesis, -oxidation, citric acid cycle, ketogenesis, lipoprotein metabolism, drug metabolism, synthesis of bile salts, urea, uric acid, cholesterol, plasma proteins Free fatty acids, glucose (in fed state), lactate, glycerol, fructose, amino acids, alcohol Glucose, triacylglycerol in VLDL, ketone bodies, urea, uric acid, bile salts, cholesterol, plasma proteins Glucokinase, glucose 6phosphatase, glycerol kinase, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, fructokinase, arginase, HMG CoA synthase, HMG CoA lyase, alcohol dehydrogenase Brain Glycolysis, citric acid cycle, amino acid metabolism, neurotransmitter synthesis Glucose, amino acids, ketone bodies in prolonged starvation Lactate, end products of Those for synthesis and catabolism neurotransmitter metabolism of neurotransmitters Heart -Oxidation and citric acid cycle Ketone bodies, free fatty — acids, lactate, chylomicron and VLDL triacylglycerol, some glucose Lipoprotein lipase, very active electron transport chain Adipose tissue Lipogenesis, esterification of fatty acids, lipolysis (in fasting) Glucose, chylomicron and Free fatty acids, glycerol VLDL triacylglycerol Lipoprotein lipase, hormonesensitive lipase, enzymes of pentose phosphate pathway Fast twitch muscle Glycolysis Glucose, glycogen Lactate, (alanine and ketoacids in fasting) — Ketone bodies, chylomicron and VLDL triacylglycerol — Lipoprotein lipase, very active electron transport chain Free fatty acids, lactate, glycerol, glucose Glucose Glycerol kinase, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase Glucose Lactate Hemoglobin, enzymes of pentose phosphate pathway Slow twitch muscle Kidney -Oxidation and citric acid cycle Gluconeogenesis Erythrocytes Anaerobic glycolysis, pentose phosphate pathway Harper's Illustrated Biochemistry, 28e Abbreviation: VLDL, very low density lipoproteins. Robert K. Murray, David A Bender, Kathleen M. Botham, Peter J. Kennelly, Victor W. Rodwell, P. Anthony Weil