Presentation slides
advertisement

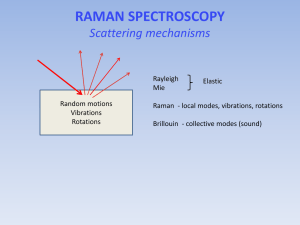
Sergey Kucheryavski svk@bio.aau.dk Raman spectroscopy Acquisition, preprocessing and analysis of spectra Raman spectrometer scheme Credits: http://www.doitpoms.ac.uk/tlplib/raman/method.php Acquisition, preprocessing and analysis of Raman spectra 2 Raman spectrometer Acquisition, preprocessing and analysis of Raman spectra 3 Raman spectrometer Acquisition, preprocessing and analysis of Raman spectra 4 Probes and fibers Acquisition, preprocessing and analysis of Raman spectra 5 Non contact probe Acquisition, preprocessing and analysis of Raman spectra 6 Acquisition of Raman spectra Acquisition, preprocessing and analysis of Raman spectra 7 Raman signal is weak Only around 1 in every 30 million photons is Raman scattered Acquisition of Raman spectra Issues Parameters Preprocessing • Cosmic rays • Laser frequency • Spectral truncation • Noise • Laser power • Noise reduction • Detection limits • Exposure time • Baseline correction • Fluorescence • Number of scans • Derivatives Acquisition, preprocessing and analysis of Raman spectra 9 Preprocessing Preprocessing – a way to improve signal for further analysis What can be improved – Noise reduction – Correction of baseline – Resolving merged meaks – Removing physical effects How it works: – X’ = F(X) – xij = fj(xij) 6. Data preprocessing 10 Cosmic spikes Noise and detection limits Fluorescence and background correction Cosmic spikes • occasionally appears in spectra as very narrow peaks • caused by high energy cosmic rays • typical issue for CCD based instruments • most of the acquisition software include algorithms to remove the effect Credits: Confocal Raman Microscopy. ed. Thomas Dieing, et al. Acquisition, preprocessing and analysis of Raman spectra 12 Cosmic spikes Noise and detection limits Fluorescence and background correction Noise and detection limits CCD detectors have photon noise, dark noise and read noise Raman signal is weak To get a good signal/noise ratio • cool CCD • higher concentration • longer exposure time • more scans for the same sample • de-noising preprocessing Acquisition, preprocessing and analysis of Raman spectra 14 Noise and detection limits CCD detectors have photon noise, dark noise and read noise Raman signal is weak To get a good signal/noise ratio • cool CCD • higher concentration • longer exposure time • more scans for the same sample • de-noising preprocessing Acquisition, preprocessing and analysis of Raman spectra 15 Acquisition parameters and concentration 25% ethanol t = 5s t = 3s t = 1s Acquisition, preprocessing and analysis of Raman spectra 16 Acquisition parameters and concentration 10% ethanol t = 3s t = 1s t = 1s Acquisition, preprocessing and analysis of Raman spectra 17 Acquisition parameters and concentration 10% ethanol t = 3s t = 1s Acquisition, preprocessing and analysis of Raman spectra 18 Acquisition parameters and concentration 1% ethanol t = 5s t = 3s t = 1s Acquisition, preprocessing and analysis of Raman spectra 19 Trancating spectra 1% ethanol t = 5s t = 3s t = 1s Acquisition, preprocessing and analysis of Raman spectra 20 Acquisition parameters and concentration 1% ethanol t = 5s t = 3s t = 1s Acquisition, preprocessing and analysis of Raman spectra 21 Acquisition parameters and concentration Butter t = 1s, 5 scans t = 1s, 3 scans t = 1s, 1 scan Acquisition, preprocessing and analysis of Raman spectra 22 Acquisition parameters and concentration Butter t = 1s, 5 scans t = 1s, 3 scans t = 1s, 1 scan Acquisition, preprocessing and analysis of Raman spectra 23 Playing with acquisition parameters Butter t = 3s, 5 scans t = 1s, 1 scan Acquisition, preprocessing and analysis of Raman spectra 24 Using filters for noise removal • Linear filters: moving average, gaussian • Wavelet decomposition • Savitzky-Golay smoothing 1100 1000 900 1100 1000 w=5 800 800 700 700 600 600 500 500 400 1150 1155 d=1 900 1160 1165 1170 1175 1180 1185 1190 1195 1200 400 1150 1155 1160 1165 1170 1175 1180 1185 1190 1195 1200 1100 1000 900 800 700 600 500 400 1150 1155 1160 Acquisition, preprocessing and analysis of Raman spectra 1165 1170 1175 1180 1185 1190 1195 1200 25 Using filters for noise removal SG filtered noised original Acquisition, preprocessing and analysis of Raman spectra 26 Cosmic spikes Noise and detection limits Fluorescence and background correction Fluorescence Mechanism • appears if molecules can absorb the laser radiation at particular wavelength • the absorbed light excites electrons to higher energy levels • electrons return to the ground state by emitting light of longer wavelength Acquisition, preprocessing and analysis of Raman spectra 28 Fluorescence Features • very common for colored (especially dark) samples • several orders of magnitude stronger than Raman scattering • has a broad emission How decrease/get rid of fluorescence: • remove impurities from solid samples • using microprobes or confocal Raman microscopy (for solid samples) • using lasers with wavelength in NIR range • proper preprocessing (baseline correction) Acquisition, preprocessing and analysis of Raman spectra 29 Fluorescence Color of samples Acquisition, preprocessing and analysis of Raman spectra 30 Laser wavelength • Visible — higher energy, stronger signal, deeper penetration, better resolution, fluorescence (good for inorganic materials) • NIR — lower energy, weaker signal, worse resolution, smaller fluorescence effect (suitable for organic materials) Credits: http://www.horiba,com Acquisition, preprocessing and analysis of Raman spectra 31 Baseline correction Baseline shift and curvature caused by noise, fluorescence, CCD background, interference, etc. Automatic baseline correction Acquisition, preprocessing and analysis of Raman spectra 32 Baseline correction Automatic baseline correction d=4 Acquisition, preprocessing and analysis of Raman spectra 33 Baseline correction Automatic baseline correction d=6 Acquisition, preprocessing and analysis of Raman spectra 34 Baseline correction Semi-automatic baseline correction Acquisition, preprocessing and analysis of Raman spectra 35 Conclusions Issues Parameters Preprocessing • Cosmic rays • Laser frequency • Spectral truncation • Noise • Laser power • Noise reduction • Detection limits • Exposure time • Baseline correction • Fluorescence • Number of scans • Derivatives Acquisition, preprocessing and analysis of Raman spectra 36