Mutations PPT
advertisement

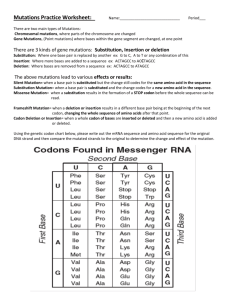
MONSTROUS MUTATIONS!!! What is a mutation? • Mutations are changes in DNA! • However, these simple changes or mistakes can cause big changes in phenotypes of organisms! Mutations in reproductive cells… • If a mutation happened during the creation of the reproductive cells… – – – – There could be non-functioning cells New traits might be produced Proteins may not work correctly Embryo may not survive • There can be positive effects though! – Faster or stronger cells! Mutations in body cells… • If mutation is caused by radiation and it is a non-reproductive cell, the mutation may not be passed on to the offspring. • However, the mutation could cause problems for the individual. • Damage to the gene could impair the function of the cell. – Muscle cell may lose its ability to make the protein necessary for contraction – Skin cell may lose its elasticity. Mutations in body cells… • When the cells divide, the new cells will have the same mutation! • Aging may be caused by a buildup of these mutated cells! • Cancer is also caused by a mutation in the cell’s rate of division. Point Mutations • A point mutation changes a single base pair in the DNA sequence. • What could this cause? – Change in amino acid sequence – EX: THE DOG BIT THE CAT. THE DOG BIT THE CAR. This is a BIG difference! • In general, point mutations are less harmful than other mutations because it only changes one base in the sequence. Frameshift Mutations • A frameshift mutation occurs when a single base is added or deleted from the DNA sequence. • This is a problem because it shifts the reading of codons by one base and thus a totally different protein is produced! Chromosomal Mutations • Chromosomal mutations are changes at the chromosomal level. • Some of these changes may be caused by: – – – – Chromosome parts breaking off Lost parts of chromosomes Parts that rejoin incorrectly Parts that rejoin backwards or even the wrong chromosome part Effects of Chromosomal Mutations: • Occurs most often in plants! • Few chromosomal mutations are passed on to the next generation because the zygote usually dies. • If the zygote lives and grows up, usually it is sterile and cannot produce offspring or pass on the mutated genes. Causes of Mutations • Some mutations just happen! Similar to a silly mistake on a math problem. These are called SPONTANEOUS mutations! • Many mutations are caused by environmental factors, such as, radiation. • MUTAGENS are agents that can cause errors in DNA. – EX: high energy radiation, chemicals, high temperatures.