Cell Growth & Division
advertisement
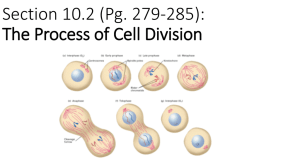
Cell Growth & Division Chapter 10 Section 10-1: Cell Reproduction Why do cells reproduce in a growing organism? - because when an organism grows its cells don’t get larger, they have to make more. Why do cells reproduce in an adult organism? - to replace old, dead or damaged cells. Why is there a limit on cell size? Give two reasons. 1. Cell size is limited by the surface area to volume ratio. Smaller cells are more efficient at taking in nutrients & disposing of wastes. 2. The larger a cell is the more proteins it needs to maintain it. The more proteins the quicker the instructions in DNA have to be copied. Genes & Chromosomes Tell how genes and chromosomes are related. - A gene is a segment of DNA that codes for a protein. DNA is made up of thousands of genes. DNA is organized and packaged into structures called chromosomes. How is genetic material organized in a prokaryotic cell? - A prokaryote has a single circular molecule of DNA. What makes it challenging to package genetic material in eukaryotic cells? - Eukaryotes have many thousands of genes arrange on several linear pieces of DNA. Ex. Humans have 46 separate strings of DNA that are all packaged into chromosomes. What is chromatin? - Chromatin is DNA that has been “wound up” on many “spools” called histones. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. DNA is wrapped around “spools” called histones. 8 of these histone “spools” come together to form a histone core. These histone cores are wound up into a structure called a nucleosome. These nucleosomes are wound up to form a nucleosome cord. These cords are wrapped around a protein scaffold to form a looped domain which are then wound up to form a chromatid. Two chromatids connected at the middle by a centromere form a chromosome. All this means is that DNA is wound around spools which are then coiled into coils, those coils are then coiled into bigger coils that coil up to form a chromsome. Don’t let the details bog you down. Chromosomes Why do chromosomes become more condensed during cell reproduction? - So that they don’t become tangled during cell division (think Xmas lights). What are sister chromatids? What happens to them during cell division? - Sister chromatids are an identical pair of long molecules of DNA attached at the center by a centromere. During cell division the chromatids are pulled apart into opposite new daughter cells to ensure that each new cell has the exact same genetic information as the parent cell. Cell Division in Prokaryotes 1. DNA is copied. 2. A new cell membrane forms between the two DNA copies. 3. The cytoplasm divides and the cell grows, doubling in size. 4. The cell develops a squeezed part in the middle. 5. A new cell wall forms around the new membrane, pushing inward. 6. The cell is pinched into two independent cells. Section 10-2: Mitosis The cell cycle is a repeating sequence of growth and ________ division during the life of a cell. The first three phases of the cell cycle are collectively called _____________ interphase. Nucleus divides into two nuclei: - mitosis Cytoplasm divides and daughter cells become physically separated: - cytokinesis Preparations are made for the cell to divide, such as the organization of microtubules: - G2 phase DNA is copied: - S phase Cell carries out its routine functions: - G1 phase Spindles & Centrosomes What function do spindles perform during mitosis? - Spindles form a link between the cell’s poles and the centromere of each chromosome. They shorten and pull the sister chromatids apart and to opposite sides of the cell. What function do centrosomes perform during mitosis? - They help assemble the spindle. Steps of Mitosis 1. Prophase: Chromosomes begin to condense, and the nuclear membrane begins to dissolve. 2. Metaphase: Chromosomes move to the cell center, lining up there. Spindle fibers link the centromeres to the poles. 3. Anaphase: Sister chromatids move toward opposite poles as the spindle fibers attached to them shorten. 4. Telophase: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AhgRhXl7w_g A nuclear envelope forms around the chromatids at each pole. The spindle dissolves. Cytokinesis Cytokinesis begins after mitosis. During cytokinesis in animal cells, the cell is pinched in half by a belt of proteins. In plant cells, a new cell wall is formed by cell plates holding cell wall materials. These fuse to form a membrane-bound cell wall. The Cycle Continues After cytokinesis, the new daughter cells enter the G1 phase of interphase. Each daughter cell is about half the size of the original cell. Find the daughter cells. Section 10-3: Regulation A scientist places a few healthy cells in a dish that contains nutrients for the cell. What happens? - They divide rapidly How is the process you described in question 1 similar to what happens with a wound? - The cells reproduce rapidly until they have closed up the wound at which time they slow down and stop reproducing. What are three sources of signals related to the regulation of cell growth and division? 1. Proteins within the cell 2. Signals from surrounding cells or organs 3. Environmental conditions like the availability of nutrients. Many ________ signals within the cell control the phases of the cell cycle. Feedback signals at key _____________ in the cell cycle can trigger or delay checkpoints the continuation of the cycle. Checkpoints Describe when and how each of the checkpoints listed below functions to regulate the cell cycle. G1 checkpoint - The cell checks to see that it is large and healthy enough to reproduce. If so DNA copying proceeds, if not it goes into a resting phase. G2 checkpoint - Newly synthesized DNA is checked for mistakes. If the DNA has been fixed and the cell is large enough to divide mitosis will proceed. Mitosis checkpoint - The cell checks that the chromosomes are lined up properly and that the spindle fibers are correctly attached. http://www.cellsalive.com/cell_cycle.htm Cancer What is cancer? - A group of severe diseases that are caused by uncontrolled cell growth. How do cancer cells affect healthy cells? - They invade and destroy healthy tissues. What is the reason that cancer cells do not respond properly to cell signals and controls? What is the result? - The cancerous cell’s DNA has been damaged. Lung Cancer Breast Cancer Tumors What is the difference between a benign tumor and a malignant tumor? - A benign tumor does not spread to other parts of the body & can usually be removed by surgery. A malignant tumor invades and destroys nearby healthy tissues and organs. Malignant Tumors Cancer Treatments What are three treatments for cancer? - Chemotherapy: using drugs or chemicals to kill cancerous cells - Surgery: physical removal of tumor or cancerous cells - Radiation therapy: high energy rays are focused on a specific area to destroy cancerous cells. Cancer Prevention What are two things you can avoid to help prevent getting cancer? 1. Avoid unnecessary exposure to UV radiation. 2. Avoid intake of chemicals like those found in cigarette smoke. http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/cancer-prevention/CA00024