Cell Cycle
advertisement
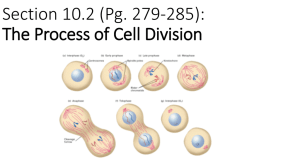
They grow and divide! The process of cells growing and dividing is known as the cell cycle. Why do cells need to do this? Hmmm… Cell cycle – cells growing and dividing There are 3 stages 1. Interphase 2. Mitosis 3. Cytokinesis ◦ All of the cell cycle occurs in the nucleus! We need to understand some parts of the cell before we begin looking at each step. ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Centrioles Chromatin DNA Chromosomes ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Come in pairs Look like a macaroni noodle or barreled shape Found in the cytoplasm Like to hang out at the north pole of the cell They are orange here Definition: Mass of genetic material composed of DNA and proteins. Chromatin is located in the nucleus of a cell. During mitosis (2nd stage), chromatin condenses to form chromosomes. I mentioned that chromatin is made of DNA. What is DNA? DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the hereditary material in humans and almost all other organisms. Most DNA is located in the cell nucleus. So, chromatin is composed of DNA and chromatin condenses to form chromosomes. Once again chromatin is composed of DNA and chromatin condenses to form chromosomes. What are chromosomes? ◦ It is a single piece of coiled DNA The centromere acts like a button. It keeps the 2 chromatids together making the double rod “X” structure. Interphase: Growth Phase This is the period where the cell grows and prepares for division. It is divided into three parts: ◦ G1: The cell grows ◦ S: The cell replicates its chromosomes (DNA). ◦ G2: The cell replicates its organelles and prepares for division. During interphase, the chromosomes are not visible. They are uncoiled. When the DNA is in this uncoiled form it’s called chromatin. The reason it’s uncoiled is this allows it to be copied more easily. The cell spends most of its life in the interphase stage. http://www.phschool.com/atschool/phsciexp /active_art/cell_cycle/index.html Now the cell is ready to divide. Next stage… Mitosis: Division of the Nucleus This is divided into four steps: 1. 2. 3. 4. Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Chromatin condenses to form chromosomes Centrioles move to opposite ends of cell Nuclear envelope starts to break down. http://www.phschool.com/atschool/phsciexp /active_art/cell_cycle/index.html Time to move to the next step of mitosis… The chromosomes line up in the MIDDLE of the cell. The centrioles are at north & south poles. MMMMetaphase……..MMMMiddle http://www.phschool.com/atschool/phsciexp /active_art/cell_cycle/index.html Time to move to the next step of mitosis… Remember the centromeres that act like a button and hold the chromosomes together? Well, not anymore. The centromeres break. Thus, the chromosome is seperated and becomes two chromatids again. Each chromataid moves to opposite ends of cell. AAAnaphase…AAAway http://www.phschool.com/atschool/phsciexp /active_art/cell_cycle/index.html Time to move to the last step of mitosis… A new nuclear envelope has formed around each region of chromosomes TTTwo Nucleus(Nuclei)…TTTelophase http://www.phschool.com/atschool/phsciexp /active_art/cell_cycle/index.html The last step of mitosis. cyto- (cell) and kinesis (motion, movement) Cytokinesis is the process in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. http://www.phschool.com/atschool/phsciexp /active_art/cell_cycle/index.html A look at the last stage of the cell cycle.