Plant Structure and Function 2014using
PLANT STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
IS IT A STEM, LEAF, ROOT,
FLOWER, FRUIT OR SEED?
Food Part of Plant
Broccoli
Cabbage
Carrot
Celery Stalk
Corn Kernel
Garlic
Onion
Potato
Tomato
Zucchini
IS IT A STEM, LEAF, ROOT,
FLOWER, FRUIT OR SEED?
Food Part of Plant
Broccoli
Cabbage
Carrot
Celery Stalk
Corn Kernel
Garlic
Onion
Potato
Tomato
Zucchini
Flower
Flower
Root
Stem
Seed
Root
Root
Root
Fruit
Fruit
PLANT BODY
Shoot system = leaves + stem
Root system
THREE TYPES OF PLANT TISSUES
Vascular Tissue
Transport
Support
Ground Tissue
Synthesis of Sugars
Storage
Support
Dermal Tissue
Protection
PLANT BODY
Leaf = blade + petiole
Functions
Exposes surface to sunlight
Major site of photosynthesis
Conserves water
Provides for gas exchange
Blade
Petiole
Stoma = opening in the leaf for gas exchange, water evaporation
Conserves water
Photosynthesis
STRUCTURES OF THE LEAF
Transports water and sugar to stem and roots
PLANT BODY
Stem: series of nodes and internodes
Functions
Holds leaves up to light
Transports substances through vascular tissue
Xylem conducts water and minerals
Phloem transports sugar
Root
PLANT BODY
Functions
Anchors plant in soil
Takes up water and minerals from soil
FLOWERING
PLANT
REPRODUCTION
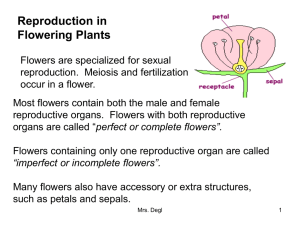
Flowers are modified leaves, specialized for reproduction.
Mitosis
Mitosis
Flower
Meiosis
Pollen grains
Ovule
Angiosperms are seed bearing & fruit producing or flowering plants.
Flowers
Come in many different shapes, sizes and colors, but they all have the same functions:
help plants reproduce.
where seeds are made.
Flowers are the sexual reproductive organs of plants.
All flowers, regardless of variety, have the function of seed formation and the production of more plants.
Flowers contain both non-reproductive and reproductive structures.
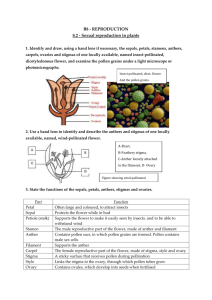
THE PARTS OF A FLOWER
Most flowers have four parts: sepals, petals, stamens, carpels.
THE PARTS OF A FLOWER
Sepals protect the bud until it opens.
Petals attract insects.
Stamens make pollen.
Carpels grow into fruits which contain the seeds.
Male Parts
Anther
This is the part of the stamen that produces and contains pollen. It is usually on top of a long stalk that looks like a fine hair.
When the grains are fully grown, the anther splits open.
Draw and label this sketch in your notes.
Filament
Male Parts
This is the fine hair-like stalk that the anther sits on top of.
The part of a stamen that supports the anther of a flower
(the stalk of the stamen).
Draw and label this sketch in your notes.
Male Parts
Stamen
This is the male part of the flower. It is made up of the filament and anther, it is the pollen producing part of the plant. The number of stamen is usually the same as the number of petals.
Draw and label this sketch in your notes.
Female Parts
Stigma
The sticky surface at the top of the pistil.
It traps and holds the pollen and starts the fertilization process.
Female Parts
Style
The tube-like structure that holds up the stigma.
Female Parts
Ovary
The part of a plant, usually at the base of the flower, that has the seeds inside and turns into the fruit that we eat.
Female Parts
Ovule
The structure in a flower that develops into a seed when fertilized.(egg s)
Female Parts
Carpel/Pistil
The carpel is the female reproductive organ of a flower. It makes the seeds.
It is made up of the stigma, style, and ovary.
There may be more than one carpel in a flower.
Pollen - powdery grains that contain the male reproductive cells of most plants.
Pollen is produced by the anthers.
POLLINATION
Flowering plants use the wind, insects, bats, birds and mammals to transfer pollen.
When pollination occurs, pollen moves from the male parts to the female parts. Pollen grains land on the stigma and a tiny tube grows from it and down the style into the ovary.
The fertilized ovule becomes the seed and the ovary becomes the fruit.
Pollen is the powdery grains that contain male reproductive cells of most plants produced by anther.
Flowering plants use the wind , insects bats, birds and mammals to transfer pollen, When pollination occurs, pollen moves from the male parts to the female parts
. Pollen grains land on the stigma and a tiny tube grows from it and down the style into the ovary.
The fertilized ovule becomes the seed and the ovary become the fruit.
Pollen grains land on the stigma and a tiny tube grows from it and down the style into the ovary. The fertilized ovule becomes the seed and the ovary become the fruit.
MALE AND FEMALE PARTS
Anther
Filament
Produces pollen
Attracts pollinator
Female part
Stigma
Style
Ovary
Produces egg
Petal
Sepal
Encloses and
Protects Bud
2. pollen tubes grow down stigma to ovary
Mature Pollen
Grain Sperm Cells
Tube Cell Nucleus
1. pollen grains land on stigma
Stigma
3B: Fusion of 2 nd sperm + two polar nuclei
Sperm
Style
3. double fertilization
Ovary
Ovule
Polar nuclei
Egg
3A: Fusion of
POLLINATIO
N AND
FERTILIZATIO
N IN A
FLOWER
DEVELOPMENT OF FRUIT AND SEEDS
FROM FLOWER PARTS
Provides nutrition
Endosperm
Triploid
Endosperm
Cell
Ovary
Fresh
Fruit
Integument
Seed
Coat
Diploid
Zygote
Embryo
(new plant)
Seed = embryo + stored food + seed coat
Fruit = ovary wall, mechanism for seed dispersal