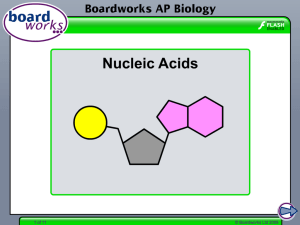
Nucleic Acids
advertisement
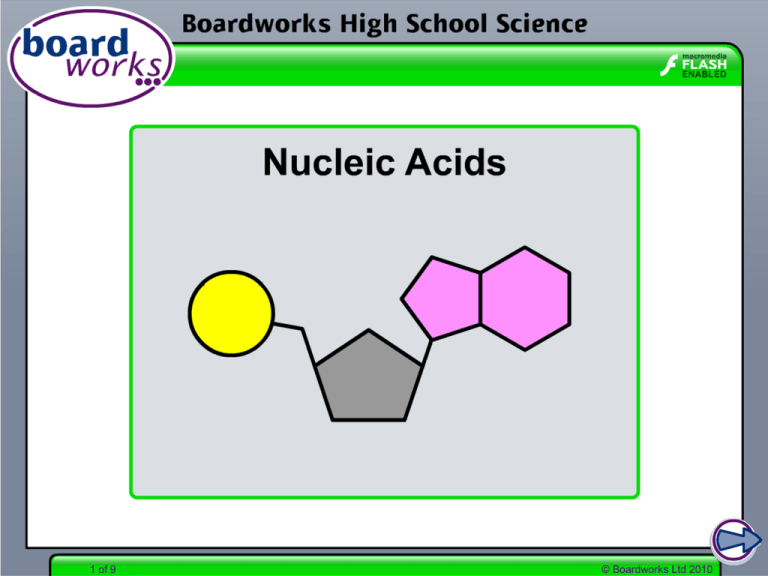
1 of 9 © Boardworks Ltd 2010 Introduction to nucleotides Nucleotides are nitrogen-containing organic substances that form the basis of the nucleic acids DNA and RNA. All nucleotides contain the following three groups: a phosphate group a nitrogencontaining base a pentose sugar In DNA the sugar is deoxyribose, whereas in RNA the sugar is ribose. 2 of 9 © Boardworks Ltd 2010 Bases There are five bases, split into two types: adenine (A) and guanine (G) are purine bases. A thymine (T), cytosine (C) and uracil (U) are pyrimidine bases. T G C U DNA contains A, G, T and C, whereas RNA contains A, G, U and C. 3 of 9 © Boardworks Ltd 2010 Identifying bases 4 of 9 © Boardworks Ltd 2010 Base pairing rules 5 of 9 © Boardworks Ltd 2010 Formation of nucleotides 6 of 9 © Boardworks Ltd 2010 Formation of polynucleotides 7 of 9 © Boardworks Ltd 2010 Determining the structure of DNA The double-stranded structure of DNA was determined in 1953 by the American biologist James Watson and the British physicist Francis Crick. X-ray diffraction studies by British biophysicist Rosalind Franklin strongly suggested that DNA was a helical structure. The Austrian chemist Erwin Chargraff had earlier showed that DNA contained a 1:1 ratio of pyrimidine:purine bases. 8 of 9 © Boardworks Ltd 2010 Structure of DNA 9 of 9 © Boardworks Ltd 2010







![Direction_and_Scale[1]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005432475_1-80ce3065f13008250a8cdec135db9846-300x300.png)