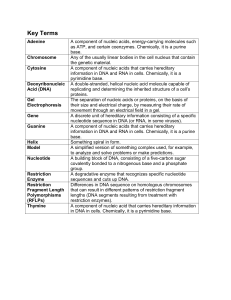
Nucleic Acids

Chapter 2
Nucleic Acids
Guest Lecture: Israel Lidsky
Quizzes
• What you need to know on quizzes is covered in lecture
• You will have one of today’s structures on the quiz
Aims
• Nucleic Acids: fine structure
• Nucleic Acids: Multiple cellular roles
• Genes: sequence matters
Learning Outcomes
• Draw a dinucleotide
• List functional properties of nucleic acids
• List properties of nucleic acids that make them suitable as carriers of hereditary information
Clues
Keywords
Ribose
Ribonucleic Acid
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
Phosphate Group
Ribose
Nitrogenous Base
Dehydration
Negative Charge
How to actually draw it
Figure 02.09A: A step-wise method for drawing a deoxyribonucleotide.
Keywords
Nitrogenous Base
Ring Structure
Purines
Pyrimidines
Adenine
Thymine
Guanine
Cytosine
Hydrogen Bonds
GC Content
Figure 02.09B: A step-wise method for drawing a deoxyribonucleotide.
Keywords dNTP
Figure 02.09C: A step-wise method for drawing a deoxyribonucleotide.
Keywords
Ribonucleic Acid
Uracil
Mono- Di- Tri-
Figure 02.10: Distinctinctive features of ribonucleotides.
Keywords
Linear Polymer
Elongation
5’ to 3’
Phosphate Backbone
Pyrophosphates
~Hint Quiz Hint~
Figure 02.11: The general structure of a nucleic acid.
Sample Quiz Question
Two ______ are released whenever DNA elongates by addition of a single ______ a) Nitrogenous bases : Phosphate Group b) Water Molecules : Nucleotide c) Phosphate Groups : Nucleotide d) SyFy Rip-Offs : Sci-Fi Blockbuster
Keywords
DNA
Double Helix
Double Stranded
Antiparallel
5’ to 3’
Right Hand Rule
Hydrogen Bonds
Base Pair
Figure 02.12A: Level 1 of DNA organization is a double stranded, antiparallel double helix held together by hydrogen bonds between base pairs.
Figure 02.12B: A 3D drawing showing the spatial arrangement of the nucleotides in a
DNA double helix.
RNA
• Single Stranded (except for SiRNA)
• Can carry information
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
• Has Enzymatic, Structural, and Interfering properties
• Not limited to simple structures
Transfer RNA
• Anticodons which recognize codons
• Bound to amino acids
• Deliver amino acids to rRNA
Yeast Phenylalanine tRNA
Graphic submitted to
Wikipedia by Yikrazuul
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
• Two Subunits
• Contains proteins
• Site of protein synthesis
Small Subunit
Thermus thermophilus
(animated by David S. Goodsell)
Large Subunit
Animated
Figure 02.05: An overview of translation in eukaryotes.
Central Dogma
DNA
Replication
Transcription
RNA
Translation
Protein
DNA has “cellular information” in nucleus
RNA has intermediate roles towards protein synthesis in the cytosol
Other forms of information are used by the cell
Figure 02.01: Some forms of information storage in cells.
DNA and Genes
• DNA carries genetic information (not obvious)
• DNA is :
– Linear
– Polar
– Reproducible (minimal error, nucleotides easily recognized)
– Transcribes efficiently (dNTPs are small and plentiful)
– Language with few letters and small words for all 20 amino acids
– Mutable
Keywords
DNA
Gene
Regulatory Sequence
Coding Sequence
Exon
Intron
RNA
Splicing
Figure 02.04: The smallest function unit of DNA is a gene.
Keywords
DNA
Gene
Regulatory Sequence
Transcription factors
Proteins
Figure 02.03: DNA information is "read" by proteins.
Figure 02.02: Mistakes in DNA replication may cause mutations.
Figure 02.06: Mutations can alter amino acid sequence and protein function.
Mutation in code brings change.
Affects to survival: good bad benign
Survival itself is context dependent
Figure 02.07: A single point mutation causes sickle cell disease.
Wear Sunscreen
Figure 02.08: Mutations accumulate slowly in a population of cells.
Learning Outcomes
• Draw a dinucleotide
• List functional properties of nucleic acids
Information storage, regulatory control, information transfer & conversion, enzymatic, structural, interference
• List properties of nucleic acids that make them suitable as carriers of hereditary information
Linear molecule, polarity, quickly transcribed, synthesizing four nucleotides is efficient, simple codons call for all amino acids and starts and stops, and mutable