ANTIBIOTIC SUSCEPTIBILITY TESTING AND DRUG RESISTANCE
advertisement

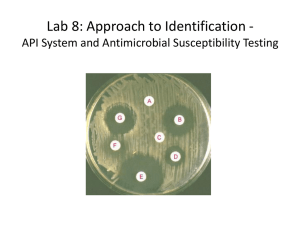
ANTIBIOTIC SUSCEPTIBILITY TESTING AND DRUG RESISTANCE Rashmi S ANTIBIOTIC SUSCEPTIBILITY TESTING(AST) DEFINITION: AST is the “study of the susceptibility of bacteria to a specific antibiotic” Susceptibility testing is done using following methods: Dilution methods a) Agar dilution b) Broth dilution Diffusion methods Disc diffusion- Kirby-Bauer method KIRBY –BAUER DISC DIFFUSSION METHOD Uses small discs impregnated with antibiotics These discs are placed on the surface of the inoculated Mueller Hinton agar plate, and incubated at 37oC for 24 hrs. After incubation ,plates are observed for the zone of inhibition. The diameter of zone of inhibition is measured using a scale& compared with Kirby-Bauer chart Mueller Hinton Agar Plate Swabbing Disc Placement AST plate with zone of inhibition Measurement of zone of inhibition MINIMUM INHIBITORY CONCENTRATION (MIC) MIC is the least concentration of antimicrobial that will inhibit the growth of an organism Clinical use: For organisms from patients suffering serious infection like “infective endocarditis” DRUG RESISTANCE DEFINITION: Organism develop tolerance for the drug Genetic mechanism of drug resistance: Mutation Gene Transfer MUTATIONAL DRUG RESISTANCE It is of 2 types 1.Step wise mutation 2.One-Step mutation CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE: Mutational resistance is of great importance in Tuberculosis DRUG RESISTANCE DUE TO GENE TRANSFER It can be due to Transformation Conjugation Transduction Transposition Biochemical mechanism of Drug Resistance Decreased permeability to the drug. Development of alternative metabolic pathway. Production of enzymes inactivating the drugs. Modification of target site of the antimicrobial agent.