.
Chapter 3
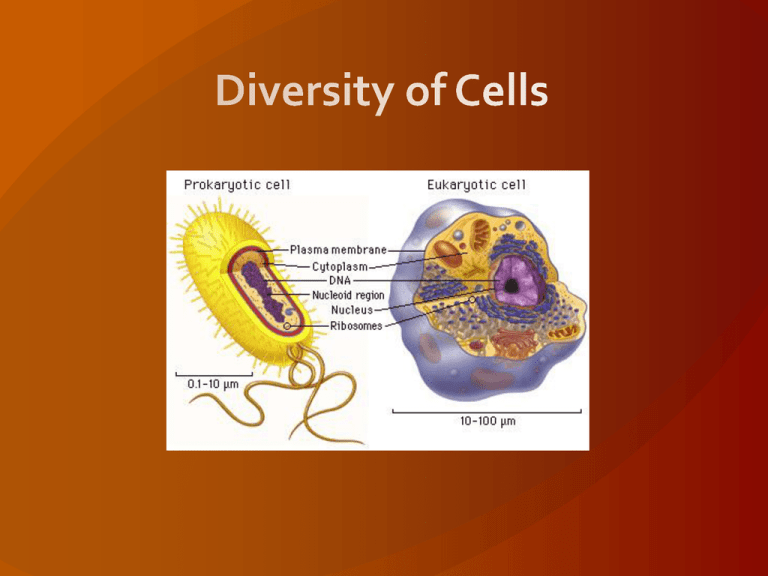
Section 1 The Diversity of Cells
Chapter 3
Section 1 The Diversity of Cells
.
Chapter 3
Section 1 The Diversity of Cells
Chapter 3
Section 1 The Diversity of Cells
Chapter 3
Section 1 The Diversity of Cells
Chapter 3
Section 1 The Diversity of Cells
Chapter 3
Section 1 The Diversity of Cells
Chapter 3
Section 1 The Diversity of Cells
Chapter 3
Section 1 The Diversity of Cells
Chapter 3
Section 2 Eukaryotic Cells
Chapter 3
Section 2 Eukaryotic Cells
Chapter 3
Section 1 The Diversity of Cells
Chapter 3
Section 2 Eukaryotic Cells
Chapter 3
Section 1 The Diversity of Cells
.
Chapter 3
Section 2 Eukaryotic Cells
Chapter 3
Section 2 Eukaryotic Cells
Chapter 3
Chapter 3
Section 2 Eukaryotic Cells
Chapter 3
Section 2 Eukaryotic Cells
Chapter 3
Section 2 Eukaryotic Cells
Chapter 3
Section 2 Eukaryotic Cells
Chapter 3
Section 2 Eukaryotic Cells
Chapter 3
Section 2 Eukaryotic Cells
Chapter 3
Section 2 Eukaryotic Cells
Chapter 3
Section 2 Eukaryotic Cells
Chapter 3
Section 2 Eukaryotic Cells
.
Chapter 3
Chapter 3
Section 3 The Organization of
Living Things
Cells Working Together
• A tissue is a group of cells that work together to
perform a specific function.
• Animals have four basic types of tissues: nerve
tissues, muscle tissue, connective tissue, and
protective tissue.
• Plants have three types of tissues: transport tissue,
protective tissue, and ground tissue.
Chapter 3
Section 3 The Organization of
Living Things
Tissues Working Together
• A structure made up of two or more tissues working
together to perform a specific function is called an
organ.
• The heart, stomach, intestines, brain, and lungs are
examples of organs in humans.
• Leaves, stems, and roots are examples of plant
organs.
Chapter 3
Section 3 The Organization of
Living Things
Tissues Working Together, continued
Organs Working Together
• A group of organs working together to perform a
particular function is called an organ system. Each
organ system has a specific job in the body.
• Examples of organ systems are the digestive system,
the respiratory system, and the cardiovascular
system.
• Examples of plant organ systems are leaf
systems, root systems, and stem systems.
Chapter 3
Section 3 The Organization of
Living Things
Chapter 3
Section 3 The Organization of
Living Things
Overview of Organ Systems
Chapter 3
Section 3 The Organization of
Living Things
Organisms
• Anything that can perform life processes by itself is
an organism.
• An organism made of a single cell is a unicellular
organism. A unicellular organism must carry out all
life processes in order for that cell to survive.
• In contrast, multicellular organisms have
specialized cells that depend on each other for the
organism to survive.
Chapter 3
Section 3 The Organization of
Living Things
Structure and Function
• In organisms, structure and function are related.
• Structure is the arrangement of parts in an
organism. Structure refers to the shape and material
of a part.
• Function is the job that the part does.
Chapter 3
Section 3 The Organization of
Living Things
Structure and Function, continued
• The structures of alveoli
and blood vessels
enable them to perform
a function. Together, they
bring oxygen into the
body and get rid of its
carbon dioxide.
Chapter 3
Cells: The Basic Units of Life
Chapter 3
Cells: The Basic Units of Life
End of Chapter 3 Show
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 3
Standardized Test Preparation
FCAT
For the following questions, write your answers on a
separate sheet of paper.
Chapter 3
Standardized Test Preparation
1. Cardiac muscle tissue is only found in the heart.
Cardiac muscle tissue contracts to help the heart
pump blood throughout the body. The heart is an
organ in the cardiovascular system. Describe how
this system helps perform maintenance for
organisms, such as humans.
Chapter 3
Standardized Test Preparation
1. Cardiac muscle tissue is only found in the heart.
Cardiac muscle tissue contracts to help the heart
pump blood throughout the body. The heart is an
organ in the cardiovascular system. Describe how
this system helps perform maintenance for
organisms, such as humans.
The cardiovascular system helps maintain the body
by providing cells with oxygen and nutrients, and by
removing wastes such as carbon dioxide. The
cardiovascular system also helps maintain the
body by fighting pathogens.
Chapter 3
Standardized Test Preparation
2. Organelles are vital parts of cells that carry out
specialized functions. Additionally, the body’s
cells combine to form structures that perform
specialized functions. Which of the following body
structures is made up of similar cells that work
together to perform a specific function?
A. organ
B. tissue
C. organism
D. organ system
Chapter 3
Standardized Test Preparation
2. Organelles are vital parts of cells that carry out
specialized functions. Additionally, the body’s
cells combine to form structures that perform
specialized functions. Which of the following body
structures is made up of similar cells that work
together to perform a specific function?
A. organ
B. tissue
C. organism
D. organ system
Chapter 3
Standardized Test Preparation
3. Cells in the body must receive nutrients to
perform life processes. Cells must also be able
to get rid of their wastes. If wastes could not be
removed, they would build up in cells and cause
the organism to become sick and die. Which of
the following structure help the cell remove
wastes?
F. vesicles
G. mitochondria
H. Golgi complex
I. endoplasmic reticulum
Chapter 3
Standardized Test Preparation
3. Cells in the body must receive nutrients to
perform life processes. Cells must also be able
to get rid of their wastes. If wastes could not be
removed, they would build up in cells and cause
the organism to become sick and die. Which of
the following structure help the cell remove
wastes?
F. vesicles
G. mitochondria
H. Golgi complex
I. endoplasmic reticulum
Chapter 3
Standardized Test Preparation
4. Diya left her plant near an open window during
the day. After a few days, she noticed that her
plant was bending towards the window. Why did
the plant bend towards the open window?
A. The plant was getting sick.
B. The plant was responding to the sunlight.
C. The plant was not getting watered evenly.
D. The plant’s stem was weaker on one side
than the other.
Chapter 3
Standardized Test Preparation
4. Diya left her plant near an open window during
the day. After a few days, she noticed that her
plant was bending towards the window. Why did
the plant bend towards the open window?
A. The plant was getting sick.
B. The plant was responding to the sunlight.
C. The plant was not getting watered evenly.
D. The plant’s stem was weaker on one side
than the other.
Chapter 3
Standardized Test Preparation
5. Ahmad has to make a model of body tissue. He knows
that a body tissue is made up of many cells that have
specific characteristics. Which of the following
statements describes the characteristics of the cells that
make up a tissue?
F. The cells have similar structures and similar
functions.
G. The cells have different structures and similar
functions.
H. The cells have similar structures and different
functions.
I. The cells have different structures and different
functions.
Chapter 3
Standardized Test Preparation
5. Ahmad has to make a model of body tissue. He knows
that a body tissue is made up of many cells that have
specific characteristics. Which of the following
statements describes the characteristics of the cells that
make up a tissue?
F. The cells have similar structures and similar
functions.
G. The cells have different structures and similar
functions.
H. The cells have similar structures and different
functions.
I. The cells have different structures and different
functions.
Chapter 3
Standardized Test Preparation
6. Jennifer is learning about cells in her biology class. She knows
that organisms can be classified into domains based on the
characteristics of their cells. Some cells have a nucleus, such
as the one shown below, and some cells do not have a
nucleus.
Into which domain would you classify an
organism that had a cell similar to the one below?
A. domain Eukarya
B. domain Archaea
C. domain Bacteria
D. domain Prokarya
Chapter 3
Standardized Test Preparation
6. Jennifer is learning about cells in her biology class. She knows
that organisms can be classified into domains based on the
characteristics of their cells. Some cells have a nucleus, such
as the one shown below, and some cells do not have a
nucleus.
Into which domain would you classify an
organism that had a cell similar to the one below?
A. domain Eukarya
B. domain Archaea
C. domain Bacteria
D. domain Prokarya
Chapter 3
Standardized Test Preparation
7. Antwone examined a single-celled organism in his
biology class. He saw an organism similar to the one
below. Which of the following conclusions could
Antwone make about this organism?
F. It is eukaryotic.
G. It has many structural
levels of organization.
H. It undergoes cell division
to repair damaged tissues.
I. It has special structures to
perform its life functions.
Chapter 3
Standardized Test Preparation
7. Antwone examined a single-celled organism in his
biology class. He saw an organism similar to the one
below. Which of the following conclusions could
Antwone make about this organism?
F. It is eukaryotic.
G. It has many structural
levels of organization.
H. It undergoes cell division
to repair damaged tissues.
I. It has special structures to
perform its life functions.
Chapter 3
Section 1 The Diversity of Cells
Chapter 3
Section 2 Eukaryotic Cells
Chapter 3
Section 2 Eukaryotic Cells
Chapter 3
Section 2 Eukaryotic Cells
Chapter 3
Section 2 Eukaryotic Cells
Chapter 3
Section 2 Eukaryotic Cells
Chapter 3
Section 2 Eukaryotic Cells
Chapter 3
Section 3 The Organization of
Living Things