chapter12
advertisement

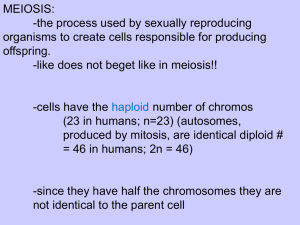
Mitosis, Meiosis, and Life Cycles Chapter 12 LEARNING OBJECTIVE 1 • Distinguish between a haploid cell and a diploid cell • Define homologous chromosomes KEY TERMS • DIPLOID (2N) • • • The condition of having two sets of chromosomes per nucleus In somatic cells of diploid organisms, chromosomes are present in pairs HAPLOID (N) • The condition of having one set of chromosomes per nucleus KEY TERMS • HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES • Members of a chromosome pair that are similar in size, shape, and genetic constitution LEARNING OBJECTIVE 2 • Identify the phases in the cell cycle • Describe the main events of each phase KEY TERMS • CELL CYCLE • Cyclic series of events in the life of a dividing eukaryotic cell KEY TERMS • INTERPHASE • Stage of the cell cycle between successive mitotic divisions Interphase • During interphase • • • cell grows and prepares for next division DNA replicates Interphase is divided into • • • first gap phase (G1) synthesis phase (S) second gap phase (G2) KEY TERMS • MITOSIS • Division of the cell nucleus resulting in two daughter nuclei, each with the same number of chromosomes as the parent nucleus KEY TERMS • CYTOKINESIS • Stage of cell division in which the cytoplasm divides to form two daughter cells Cell Cycle S (Synthesis phase) G1 (First gap phase) G2 (Second gap phase) M PHASE (Mitosis and cytokinesis) Fig. 12-1, p. 242 LEARNING OBJECTIVE 3 • Describe the events that occur in each stage of mitosis Stages of Mitosis • • • • Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Prophase • Chromatin condenses into chromosomes • • • • Nucleolus disappears Nuclear envelope breaks down Mitotic spindle begins to form At the end of prophase, each duplicated chromosome is composed of two sister chromatids A Duplicated Chromosome Centromere region Microtubules Kinetochore Sister chromatids Fig. 12-3, p. 245 KEY TERMS • SPINDLE • Structure consisting mainly of microtubules that provides the framework for chromosome movement during cell division Metaphase • Duplicated chromosomes line up along midplane of cell Anaphase • Sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles of the cell • Each chromatid is now a separate chromosome Telophase • Nuclear envelope forms around each set of chromosomes • • • Nucleoli reappear Chromosomes lengthen and become chromatin Spindle disappears KEY TERMS • CELL PLATE • • Structure that forms during cytokinesis in plants, separating two daughter cells produced by mitosis Cytokinesis generally takes place in telophase Cytokinesis Nucleus Vesicles gather Small vesicles Eventually one New cell walls on cell's fuse, forming large vesicle (from vesicle midplane larger vesicles exists contents) Plasma Cell membrane wall Cell plate forming Cell plate forming New plasma membranes (from vesicle membranes) Fig. 12-4, p. 247 Interphase and Mitosis (a) Interphase (b) Prophase (c) Metaphase Condensing Spindle chromosome microtubules (consists of 2 sister chromatids) (d) Anaphase (e) Telophase Sister chromatids Cell New (now called plate nuclei chromosomes) move to opposite ends of cell Fig. 12-2, p. 244 (a) Interphase (b) Prophase (c) Metaphase Condensing Spindle chromosome microtubules (consists of 2 sister chromatids) (d) Anaphase (e) Telophase Sister chromatids Cell New (now called plate nuclei chromosomes) move to opposite Stepped Art ends of cell Fig. 12-2, p. 244 LEARNING OBJECTIVE 4 • Explain why meiosis is needed at some point in the life cycle of every sexually reproducing organism • Describe the events that occur during meiosis I and meiosis II KEY TERMS • MEIOSIS • • Process in which a 2n cell undergoes successive nuclear divisions, potentially producing four n nuclei Leads to formation of spores in plants Meiosis • Meiosis must occur at some time in the life of a sexually reproducing organism if gametes are to be haploid • Meiosis consists of two cell divisions • • Meiosis I Meiosis II Meiosis I • Members of each homologous pair of chromosomes separate and are distributed into separate nuclei in two daughter cells • Chromosomes were duplicated prior to meiosis I, so each consists of two chromatids Meiosis II • Chromatids separate into individual chromosomes and are distributed into different haploid daughter cells • Four haploid cells form KEY TERMS • SYNAPSIS • Physical association of homologous chromosomes during prophase I of meiosis Crossing Over • Crossing over • • Exchange of segments of homologous chromosomes Synapsis and crossing over occur during prophase I of meiosis Crossing Over Sister chromatids Crossing over Kinetochores Fig. 12-6, p. 249 Meiosis Meiosis (a) Prophase I (b) Metaphase I (c) Anaphase I (d) Telophase I Cell plate Each chromosome consists of two chromatids Homologous chromosomes Spindle microtubules New nuclei Fig. 12-5 (a-d), p. 248 (e) Prophase II (f) Metaphase II Chromosomes (each with two chromatids) (g) Anaphase II Spindle microtubules (h) Telophase II New nuclei New cell walls and plasma membranes Fig. 12-5 (e-h), p. 249 LEARNING OBJECTIVE 5 • Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis Mitosis • Involves a single nuclear division in which the two daughter cells formed are genetically identical to each other and to the original cell • Synapsis of homologous chromosomes does not occur during mitosis Meiosis • Involves two successive nuclear divisions and forms four haploid cells, each with a different combination of genes • Synapsis of homologous chromosomes occurs during prophase I of meiosis Mitosis and Meiosis Synapsis (pairing of homologous chromosomes) Chromosomes Parent cell (2n = 4) Parent cell (2n = 4) Prophase I Prophase Nuclear envelope Mitosis 1st meiotic division Nuclear envelope Prophase II 2nd meiotic division Two daughter cells (each 2n = 4) identical to parent cell Mitosis Four daughter cells (each n = 2) genetically different from parent cell Meiosis Fig. 12-7, p. 250 LEARNING OBJECTIVE 6 • Define alternation of generations KEY TERMS • Alternation of generations • • SPOROPHYTE • • Plants alternate haploid and diploid generations 2n, spore-producing stage in plant life cycle GAMETOPHYTE • n, gamete-producing stage in plant life cycle The Sporophyte • The 2n, spore-producing stage in the life cycle of a plant • A diploid sporophyte plant forms haploid spores by meiosis • A spore divides mitotically to form a haploid gametophyte plant The Gametophyte • The n, gamete-producing stage in the life cycle of a plant • The gametophyte produces haploid gametes by mitosis • Two gametes fuse to form a diploid zygote, which divides mitotically to produce a diploid sporophyte Plant Life Cycle Gametophyte (n) (multicellular haploid organism) Mitosis Spores (n) Mitosis Gametes (n) Meiosis Fertilization Zygote (2n) Mitosis Sporophyte (2n) (multicellular diploid organism) Fig. 12-8, p. 251 Animation: The Cell Cycle CLICK TO PLAY Animation: Comparing Mitosis and Meiosis CLICK TO PLAY