Worms
Chapter 1 Section 4
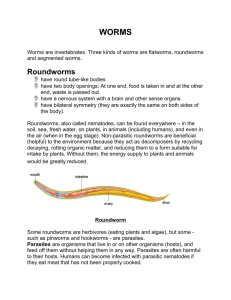
What Worms have in Common
• What are the 3 major phyla of worms we
are discussing?
– Flatworms
– Roundworms
– Segmented worms
Flatworm
http://img.ehowcdn.com/article-new/ehow/images/a05/70/fq/symptoms-tapeworms-horses-800x800.jpg
http://www.astrographics.com/GalleryPrints/Display/GP2104.jpg
Flatworms
http://aapredbook.aappublications.org/content/1/SEC131/SEC269/F2258.large.jpg
http://www.freeendlessinfo.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/04/caninetapeworms.jpg
Flatworm
http://www.daviddarling.info/images/flatworm_section.jpg
http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/2/2a/NZ_Flatworm.JPG
Roundworm
http://www.petsandparasites.org/images/uploads/images/AscaridInIntestine.gif
Segmented Worms
http://www.arcodiv.org/seabottom/images/orange_ploychaet_400x300.jpg
http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/biobk/annelidbody.gif
Segmented Worms
http://ichef.bbci.co.uk/naturelibrary/images/ic/credit/640x395/a/an/annelid/annelid_1.jpg
Segmented Worms
http://www.historyforkids.org/scienceforkids/biology/animals/segmentedworms/pictures/earthworm.jpg
What Worms have in Common
• Which phylum do flatworms belong to?
– Platyhelminthes
• Which phylum do roundworms belong to?
– Nematoda
• Which phylum do segmented worms
belong to?
– Annelida
What Worms have in Common
1. Invertebrates
2. Long, narrow bodies without legs
3. Have tissues, organs, and organ
systems
4. Bilateral symmetry
5. Head and tail end
Worms
• Do worms have a brain?
– Yes
– Simplest organism with a brain
– Knot of nerve tissue located in the head end
– Detect food, mates, and predators quickly
– Responds to the information from the brain
Reproduction
• How do worms reproduce?
– Sexually
• Male and female worms = sexually
• Have both sex organs – 2 worms mate and
exchange sperm
• Break into pieces – asexually
– Earthworms can’t do this
• Regeneration :
– Ability to regrow body parts
Flatworms
• Flat bodies
• Examples:
– Planarians
– Flukes
– Tapeworms
• Bodies soft like jelly
• Almost too small to be seen except
tapeworms can grow to 12 meters
Flatworms
• Most are parasites that obtain food from
their hosts
• Parasite:
– Organism that lives inside or on another
organism
• Host:
– The organism that a parasite lives on or in
– The parasite takes nutrients from the host
Tapeworms
• 1 kind of parasitic flatworm
• Absorbs food from the host’s digestive
system
• Most live in more than 1 host during their
lifetime
Planarian
• Nonparasitic flatworm
• Glide over rocks, damp soil, and swim
slowly through oceans
• Scavengers:
– Feed on dead or decaying material
Planarian
• They also are predators towards animals
smaller than they are
• Have eyespots
– Function sort of like eyes but can not see
specific images
• Head has cells to pick up odors
– Use smell to locate food
Planarian
• Feeds like a vacuum cleaner
– Inserts a feeding tube into its food
• Sucks up partly digested food
• Distributed to body cells by diffusion
– Only have 1 opening
– Undigested food leaves through the feeding
tube
Roundworms
• Million roundworms live in each square meter of
sand
• Live in moist environment
• Tiny and hard to see
• May be the most abundant animal on Earth
Roundworms
• Cylindrical body
– Tiny strands of spaghetti
• Can be carnivores, herbivores, or
parasites
• Hookworms are a roundworm parasite
Hookworm
http://www.foxvalleyvet.net/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/2011/09/hookworm2.jpg
Roundworms
• Have a digestive system that is open at
both ends
• Waste exits through the anus
• Having a one-way digestive system allows
the worm to use its food efficiently and
absorb more nutrients
Segmented Worms
• You can find them in your
own backyard
• Leeches are parasitic
segmented worms
• More closely related to crabs
and snails
http://news.discovery.com/human/2010/11/12/leech-278x225.jpg
Segmented Worms
• Occupy nearly all environments
• Use burrows to hide from predators
• Sit-and-wait predators
Segmentation
• Bodies are made up on many linked
sections called ___________
– Segments
• Earthworms usually have more than 100
segments
• Some organs are repeated in most
segments
Segmentation
• Ex:
– Each segment has tubes that remove wastes
– Reproductive organs are found in only certain
segments
– Nerve cords and the digestive tube run the
whole length of the body
• 1 way digestive tract which means they
have an anus
Closed Circulatory System
• Blood moves only within a connected
network of tubes called blood vessels
• In an open system the blood leaves the
circulatory system and sloshes inside the
body
• A closed system can move the blood
faster
Closed Circulatory System
• If you have a
closed
system you
can be larger
and more
active
– Blood carries
oxygen and
food to cells
http://www.infusion.allconet.org/webquest/img010.jpg
Earthworms
• Earthworms scavenge for
– Dead and decaying plant and animal remains
in the soil
• When it is damp they come out of their
burrows
– They only come out when it is damp because
their skin can’t dry out
Earthworms
• They mainly come out at night because
they are safer from predators
• Obtain oxygen through the moisture on
their skin
• Bristles on the segments help the worms
move
Earthworms
• Benefit us:
– Make the soil more fertile with their droppings
– Loosen soil when they tunnel
– Allow air, water, and roots to move through
the soil when they tunnel