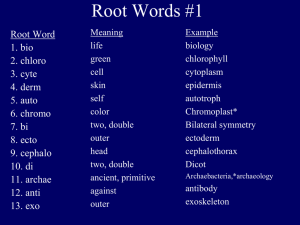
The Epidermis
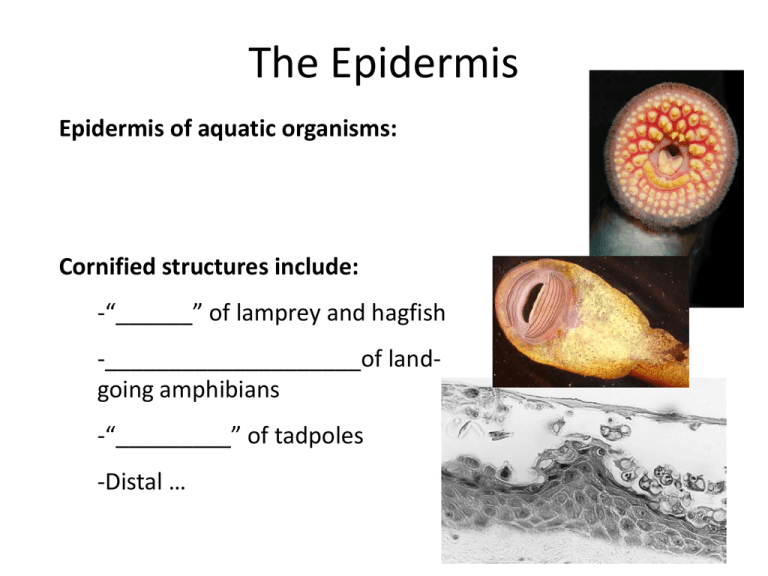
Epidermis of aquatic organisms:
Cornified structures include:
-“______” of lamprey and hagfish
-____________________of landgoing amphibians
-“_________” of tadpoles
-Distal …
The Epidermis
Epidermis of terrestrial organisms:
Stratified layers gave rise to 2
categories of unique features…
1) Glands
2) Stratum corneum
The Epidermis
Epidermis of terrestrial
organisms:
Glands fall in 2 main
categories based on
shape…
1)
2)
The Epidermis
Epidermis of terrestrial
organisms:
Glands produce their
secretions via 3 main modes…
1) Cell membrane
(_____________)
2) Whole cells and their
contents (_____________)
3) Cell fragments
(_____________)
The Epidermis
Epidermis of terrestrial organisms:
Mucous glands not abundant…
occur in areas with need for
lubrication
Why not abundant on terrestrial
animals?
What other skin structures would
interfere?
What areas need lubrication?
The Epidermis
Epidermis of terrestrial organisms:
Granular glands found mainly in
terrestrial amphibians and reptiles
Can produce ____________ and
some ____________________
Concentrations of “noxious”
granular glands found on “warts”
and ___________________of toads
Lizards have ___________________
Musk or ________________ in
turtles and snakes
The Epidermis
Epidermis of terrestrial organisms
(birds):
Few integumentary glands in birds…
however, avian oil glands
_______________ gland at rump,
large in aquatic birds and some
domestic birds
Oil glands also line …
Sometimes found around the …
The Epidermis
Epidermis of terrestrial organisms (mammals):
2 major types of glands in mammals…
1)
(oil glands)
2)
(sweat glands)
The Epidermis
Epidermis of terrestrial
organisms (mammals):
_________________(saccular)
usually associated with hair.
Exceptions...
Sebum secreted into hair
follicle
Modified (_______________)
in ear canal to secrete _______
___________________ keep
conjuctiva moist (plugged =
________________)
The Epidermis
Epidermis of terrestrial
organisms (mammals):
_________________________
(coiled tubular glands)
Evaporative cooling primary
function of _________ sweat glands
Found in least hairy regions
Some mammals lack sweat glands
Humans have greatest # per cm2
___________ sweat glands involved
with secondary sex characteristics
The Epidermis
Epidermis of terrestrial
organisms (mammals):
Scent glands can be sebaceous
or sudoriferous
Found in varying locations…
-
The Epidermis
Epidermis of terrestrial
organisms (mammals):
___________________ present
in both sexes and derived from a
line of ectoderm called the
_____________________
This tissue invades the dermis
and spreads
Distinct tissue above these
glands develops (____________)
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Illu_breast_anatomy.jpg
The Epidermis
Epidermis of terrestrial
organisms (mammals):
Nipples can be multiple…
-
-
Different species… different
placement
http://www.healthcentral.com/images/ency/fullsize/8659.jpg
The Epidermis
Epidermis of terrestrial
organisms (mammals):
During lactation, products
accumulate in _____________
(usually)
Suckling releases _____ and
_____________ facilitates by
causing smooth muscle
contractions
“_____________” reflex
The Epidermis
Stratum corneum:
Epidermal scales found only in
_____________.
Squamates (snakes & lizards)
thickened corneum except at …
Varying forms… _________,
____, __________, _________
Birds have epidermal scales on
areas lacking feathers
What about mammals?
http://www.richard-seaman.com/USA/States/Nevada/ValleyOfFire/Sampler/HornedLizard.jpg
The Epidermis
Stratum corneum:
Thick skin
The Epidermis
Claws, hoofs and nails:
Claws appeared in basal
amniotes
Tigers have claws… are
they homologous to those
of Idaho Giant
Salamanders?
The Epidermis
Claws, hoofs and nails:
Claws, nails and hooves
homologous
Similar structure…
*
http://anatomy.iupui.edu/courses/histo_D502/D502f04/lecture.f04/integument.f04/nail.jpg
*
*
Birds can have claws on
wings too
Are claws shed or worn
down?
http://www.science-art.com/gallery/170/170_8212006165155.jpg
The Epidermis
Feathers:
3 basic types…
*
*
*
Feathers comprised of a
quill (_________), _____
and ________. Parallel
extensions from the shaft
barbs are crosslinked with
________ (hooklets and
flanges)
http://www.explorebiodiversity.com/BIRDS/Adaptations/pics/featherstypes.jpg
The Epidermis
Feather development:
_____________induces
overlying ____________
to divide mitotically…
resulting bump is called
_____________________
Why is presence of
papillary vasculature
important?
Tall columns form a
_______________and
push toward tip, becoming
barbs
http://cache.eb.com/eb/image?id=1712&rendTypeId=4
The Epidermis
Feather development:
When the barbs are still in
protective feather sheath
it is called a
________________
At feather maturity… bulk
of papilla dies back
Basale tissue retracts and
then starts over again
http://climate.uvic.ca/people/ewiebe/eggs/09_may_1.jpg
Developing feathers push
old feathers out
_____________________
http://www.catsandcritters.com/newsletter.php
The Epidermis
http://www.gavinrymill.com/dinosaurs/feathers/sinosauropteryx2.jpg
Feather origins:
One hypothesis is that
they are derived from
reptile scales…
Sinosauropteryx
Early development of
dermal papilla is similar
but remaining scenario is
not
Some propose they are
novel structures
http://www.prehistoria.piwko.pl/Obrazki/sinosauropteryx2.jpg
The Epidermis
http://www.brownlog.dreamhost.com/scrapbook/1998_09_tacoma/zoo_walrus.jpg
Hair:
Functions of hair…
_________________
(underfur and guard
hairs)
__________(vibrissae)
__________ (spines
and quills)
http://brotherpeacemaker.files.wordpress.com/2008/10/pitbull_v_porcupine-1.jpg
The Epidermis
Hair morphology:
Similar to feathers in that
there is a ___________
__________has ________
__________ with much
mitosis
__________is portion
under the dermis where
cells are dying
__________is portion of
hair that is separate from
follicle wall
http://www.haircolorpros.com/images/science_hair1.gif
The Epidermis
Hair morphology:
Thin outer covering is the
___________
Underlying zone called
___________
Inner pith is the ________
Smooth muscle associated
with the follicle and
originating in the dermis is
the ______________
http://www.asylumresearch.com/Gallery/FeaturedScience/Hair!.jpg
The Epidermis
Horns:
*
*
*
http://www.skullsunlimited.com/graphics/pronghorn_skull.jpg
http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/site/resources/phil_myers/horns_antlers/giraffe.jpg/thumbnail.jpg
http://www.oucom.ohiou.edu/dbms-witmer/images/Rhino_horn_UV_large.jpg
The Epidermis
Baleen and
miscellaneous:
*Toothless whales
(mysteceti) rely on
__________ to filter fish
and/or crustaceans
(krill)
http://www.coreresearch.org/images/baleen2.jpg
*
*
http://courses.washington.edu/vertebra/452/
photos/diapsids/rattlesnake_rattle.jpg
*
*
*
http://www.peteducation.com/images/articles/tfh_crusty_footpads.jpg
http://anthro.palomar.edu/primate/images/gelada_bab
oon_showing_ischial_callosities.jpg
Integuments by Taxa
Agnathans:
Epidermis… stratified,
unicellular glands, mitotically
active throughout
Dermis… thinner than
epidermis but dense/tough
http://wupcenter.mtu.edu/education/Ecology_of_the_Great_Lakes_03/13lamprey_hickey.jpg
Integuments by Taxa
Cartilaginous fishes:
Epidermis… stratified,
multicellular glands show up
Dermis… ______________
and melanophores
http://www.gla.ac.uk/centres/marinestation/research/bask-shark/shark_gape_450.jpg
Integuments by Taxa
Bony fishes:
Epidermis… many
mucous glands
Dermis… dermal bone/scales
Integuments by Taxa
Amphibians:
Epidermis… stratified,
multicellular glands (mucous and
granular)
Dermis… attached to
musculature in some, loose in
others, presence of
chromatophores
http://farm1.static.flickr.com/149/415329423_cd21aeb1cb_o.jpg
Integuments by Taxa
Non-avian reptiles:
Epidermis… stratified, thick
stratum corneum (scales)
Dermis… tough, some with
dermal bone
Integuments by Taxa
Birds:
Epidermis… thin, lacks glands
(except uropygial), modified
epidermal layers to form feathers
(scales)
Dermis… thin, arrector pili
muscles
Integuments by Taxa
Mammals:
Epidermis… Distinct strata,
variety of glands, hair
Dermis… exceptionally thick and
tough