no sigma falls off after initiation
advertisement

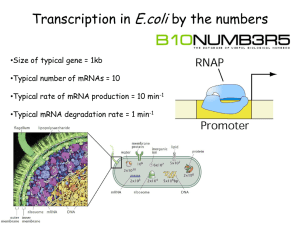
MBLG1001 Past Paper Questions 33-46 Central Dogma 33. Transcription • Which of the following statements about transcription in procaryotes is TRUE? A. After cell division, the entire genome is copied into mRNA as a back-up. crazy! B. During transcription, both strands of DNA are simultaneously copied in opposite directions. no C. During transcription, the 3’ end of mRNA remains attached to the DNA template. yes! D. Before a gene is transcribed, its entire length must be unwound into single stranded DNA. no E. As RNA polymerase transcribes a gene, the sigma subunit unwinds DNA ahead of it. sigma falls off after initiation 34. Termination of Transcription • Which of the events results in TERMINATION of procaryotic transcription? A. When RNA polymerase reaches a STOP codon. translation stop signal B. When the rho protein falls off RNA polymerase rho kicks off RNA pol C. When the RNA polymerase reaches the START codon for the next gene. another translation theme D. When a recently transcribed part of mRNA forms intramolecular base pairs factor independent termination E. When the transcription bubble reaches a section of DNA that is blocked by a group of stationary holoenzymes. plausible but genes not that close 35. Polycistronic mRNAs • Which statement regarding polycistronic mRNAs is TRUE? A. A single polycistronic mRNAs can be translated to give several proteins. the definition of polycistronic! B. A polycistronic mRNA contains just one start and one stop codon. must have one for each protein C. Polycistronic mRNAs are the only transcripts that can be produced in multiple copies after initiation of a gene. all mRNAs have this potential D. Polycistronic mRNAs are the only transcripts that can be simultaneously translated as they are being transcribed all mRNAs have this potential E. Polycistronic mRNAs are formed by post-transcriptional splicing of small transcripts. would be interesting, but no! More interesting if bits of protein could! 36. CAP • What does NOT describe the function of the procaryotic catabolite activator protein (CAP)? A. CAP binds to the DNA downstream of the initiation site binds upstream at promoter B. CAP displaces the repressor from DNA repressor has its own site C. CAP interacts with the alpha subunits of RNA polymerase it does D. CAP requires cyclic AMP to properly bind to DNA it does E. After binding to DNA, CAP simulates the transcription of genes it does 37. Repressor • Which statement BEST describes the function of the repressor used to regulate expression of the gene that codes for lactose metabolizing enzymes? A. This repressor also inhibits expression of the genes that code for glucose metabolism. glucose not inducible – important! B. Binding of lactose to this repressor lessens it’s affinity for DNA. removes the inhibition C. This repressor is only produced when lactose is around. repressor produced constitutively D. This repressor stimulates the termination of transcription. just inhibits initiation E. This repressor displaces CAP from the DNA. geographically separate binding sites 38. Translation Direction • Which of the following statements about directionality in procaryotic translation is FALSE? A. The mRNA is translated in the 5’ to 3’ direction. it is! B. Codon:anti-codon base pairing is complementary and antiparallel all base pairing is C. The protein is made in the C- to N- direction. D. The ribosome moves down the mRNA in the 5’ to 3’ direction other way – N-fmet group at start relatively speaking E. The tip of a polypeptide chain emerging from a ribosome is a formyl group. similar to C 39. Ribosomes • Which of the following statements regarding procaryotic ribosomes is CORRECT? A. The 30S and 50S subunits are held together by proteins called initiation factors actually kept apart by the initiation factors B. The 50 S subunit contains 16 S rRNA this is in the 30 S subunit C. The 30 S subunit contains rRNA that catalyses the formation of the peptide bond this is in the 30 S subunit D. A mixture of ribosomal RNAs and proteins can self assemble to produce functional ribosomes they sure can! E. The 30 S subunit contains the P- and A-sites for tRNA these caverns are in the big one 40. Translation Elongation • Which statement regarding the elongation phase of procaryotic protein synthesis is FALSE? A. In the aa-tRNA coming into the ribosome, the carboxylic acid group of the amino acid is in a bond with the tRNA. correct. remember N-formy-met on end B. During peptide bond formation, the peptide on the tRNA at the P-site moves onto the tRNA at the A-site. correct. strange to move the big bit! C. Empty tRNAs are ejected before the ribosome moves down the mRNA not until the ribosome moves on D. EF-G catalyses the relative movement of the ribosome and the mRNA translocase E. New aa-tRNAs come into the A-site yes 41. Translation • Which statement about procaryotic translation is TRUE? A. Only polycistronic mRNAs can be translated by more than one ribosome at a time they all can B. An mRNA can only be translated once it has been fully transcribed can be simultaneous C. The rate of transcription of mRNA is much faster than the rate of translation both 40 nucleotides/s D. The rate of translation of mRNA is much faster than the rate of transcription. both 40 nucleotides/s E. The presence of polysomes makes an mRNA less prone to nuclease digestion less easy for nucleases to attack 42. Degeneracy & Wobble • Considering that there is degeneracy and wobble in the code, which statement about the relationship between mRNA and protein sequence is TRUE? A. Given an amino acid sequence of a protein, it would be impossible to predict the correct nucleotide sequence of its mRNA can’t tell which codons used B. Given an amino acid sequence of a protein, it would be possible to predict the correct nucleotide sequence of its DNA. as for A C. Given an mRNA sequence, it would be impossible to determine the amino acid sequence of the protein just need the table of Genetic Codes D. Sequence predictions are only possible in some species a silly statement E. Given the DNA sequence, it would be impossible to determine the amino acid sequence of the protein. if know DNA, know RNA and thus protein 43. Pro vs Eu • Which statement regarding the differences between procaryotic and eucaryotic molecular biology is FALSE? A. In eucaryotes, DNA is located in organelles nucleus B. In eucaryotes, DNA is wrapped around a core of protein histones, nucleosomes, chromatin C. In procaryotes, most of the DNA is in introns no introns/exons in procaryotes D. In eucaryotes, mRNA must be transported into the cytoplasm before translation more precisely the endoplasmic reticulum E. mRNA molecules tend to be longer-lived in eucaryotes they are 44. Eucaryotic Transcription • Which statement regarding eucaryotic transcription is FALSE? it is made by RNA pol II A. mRNA is transcribed by RNA polymerase II B. Sections of DNA that are being transcribed are more prone to nuclease digestion naked C. Eucaryotic promoters bind multiple transcription factors very complicated D. Eucaryotic enhancer sequences can be located within the transcribed portion of the gene almost anywhere in fact E. The eucaryotic promoter sequence is the same as the procaryotic consensus sequenece. similar but not identical 45. mRNA Processing • During post-transcriptional processing, what does NOT happen to a primary mRNA transcript? A. A guanine nucleotide is attached to the 5’ end B. Several hundred adenine nucleotides are attached to the 3’ end tailing C. Intronic sequences are cut out and assembled into a mature transcript splicing… but introns are destroyed! D. The transcript is acted on by spliceosomes E. The transcript is cleaved by small nuclear ribonuceloproteins capping splicing apparatus components of spliceosomes 46. Eucaryotic Translation • Which statement about the initiation of eucaryotic translation is TRUE? A. The mRNA binds to the ribosome through the Shine Dalgarno sequence procaryotic. scanning in eucaryotes B. The first tRNA to come in contains N-formyl-methionine just plain old met C. The first AUG codon in the transcript is normally the first to be translated scanning D. The 5’ cap of mRNA is positioned into the P-site first AUG in P-site E. The initiating complex is between the mRNA and the 60 S subunit the 40S subunit