Nervous system/Sensory
Organs
Same size as fish
No care process for
young
Small cerebrum
Sight-well developed
Good size optic lobe
Eyes=large @ top
Detect prey
Eyelids
Nictitating membrane
“goggles” while
swimming
Keep eyes moist
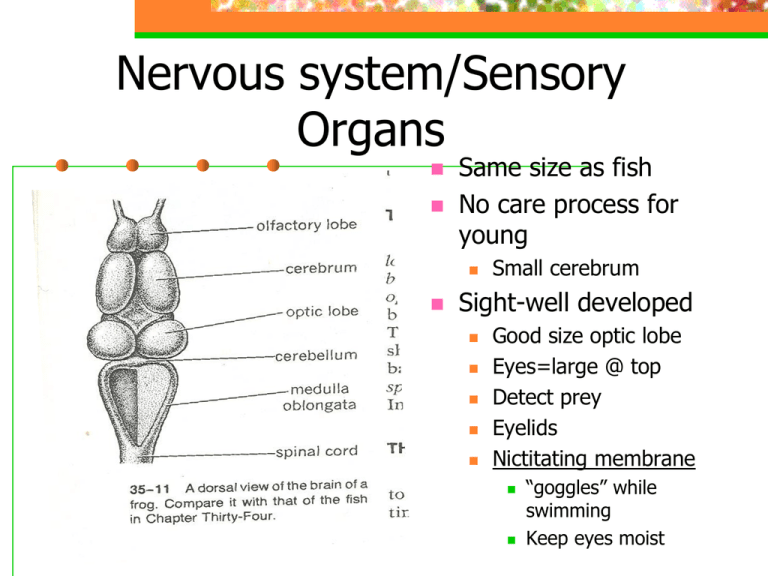
1) Olfactory lobe (scent)
-connects to nostrils (draws in odors from
water) by nerves
2) Cerebrum
- reasoning
- maternal care
- controls higher brain functions
3) Optic lobe
- sight (lens, optic nerve)
- hearing
4) Cerebellum
- coordinates balance/movement
5) Medulla
- controls internal organs
6) Spinal cord
- nerves transmitted
Nervous System/Sensory
Organs
Sound- tympanic
membrane
Pick up vibrations
Connects to
Eustachian Tube
NOT EARS!!!!
Smell-Nares
Internal & External
High Set
Sight:
Eyes: Covered with nictitating membrane
-clear covering
-lower eyelid
-like googles
Sound:
Frogs bring in air through nostrils. Mouth
fills with air, as the air is forced back and forth
between mouth and lungs it passes through the
vocal sac. Vocal sac produces sound.
In many species only the males make
crocking sound.
Skeletal System
Land/terrestrial animals
rely on an endoskeleton
for support.
Inner skeletal system
Few modifications for
being successful jumping:
To
support
force of
jump
Few vertebrae
Bones in forearm are fused
Radio-ulna
Bones in hindlimb are larger
than others and fused
Tibiofibula
Digestive System
Larvae-herbivores
Adult-carnivores
Digestion starts in the mouth
2 kinds of teeth
Used for gripping/holding
prey and forcing it down
gullet
DO NOT CHEW!!!!!
Food proceeds to the:
Pharynx (back of throat)
Gullet (opening to esophagus)
Esophagus
-very elastic, allows them to
swallow large prey.
Stomach
-Where protein digestion
occurs using gastric juices
Small intestine
No pyloric caeca
Proteins, lipids, & carbs.
Digestion
Get enzymes from:
pancreas
liver
Small
gall bladder
intestines
Held in place with
mesentery (cloudy
membrane)
Food molecules absorbed
Large
into blood
intestines
Large intestine
NO DIGESTION
Removes excess H2O
Storage of undigested
food until sent to cloaca
to be removed
heart
liver
Cloaca
Similar to the urogenital opening BUT…
Digestive AND urogenital systems meet here
Stores urine, sex cells, & feces until released
Vent
Similar to anus BUT everything exists here urine, sex cells, feces.
The VENT ………
(the end for those lacking a sense of humor!!)
Circulatory System
Larvae
(fish-like)
1 loop system
2 chambered heart
Adult:
2 loop system
3 chambered heart
2 Loop Circulatory System
Pulmonary Circulation
blood travels from heart
to lungs and back to
heart
Systemic Circulation
blood travels from heart
to body and back to
heart
Advantage of 2 loop system:
-faster blood flow to body
-heart pumps blood to lungs then the
heart pumps the blood to the rest of the
body.
3 Chambered Heart:
Deoxygenated blood
to the lungs
Deoxygenated blood
from the body
Right atrium
Oxygenated blood
to the body
Oxygenated blood
from lungs
Left atrium
Ventricle
3 chambered
heart is inefficient
because the
“clean” and
“dirty” blood mix
in the ventricle.
Pathway of blood:
1. O2 blood from lungs enters left atrium.
cLean blood = left side
2. CO2 blood from body enters right atrium
diRty blood = right side
3. Heart pumps sending O2 blood and CO2
blood into the ventricle. Both blood types mix.
4. Heart pumps forcing “clean” blood to body
and “dirty” blood to the lungs.
Respiratory system:
Larvae:
-respire or exchange O2 and CO2
through gills and skin
Adults:
-respire through lungs and skin
2 types:
Respire through moist
skin-cutaneous
respiration
Respire with lungs –
pulmonary respiration
Lungs
Nostrils
Glottis
(opening to trachea)
Trachea
Bronchi
Bronchioles
Air sacs
of lungs
Excretory System
-Primary organ of excretion
is the two kidneys.
-Filters nitrogenous/cellular
waste out of the blood.
-Waste and excess water
collected travel through
ureter to the bladder as
urine.
-Passes into cloaca.
-Exits out the vent.
Excretory System
Kidney
Uterer
Cloaca
Bladder
Reproductive System
Reproductive System
Male Frog:
Sperm made in
testes
Travels through
sperm ducts to
cloaca
Exits out vent
Enlarged thumbs
Reproductive System
Female Frog:
Eggs made in ovaries
Travel along oviduct
where jelly-coating is
applied
Eggs empty out into
cloaca & exit out vent
when amplexus occurs
Fat Bodies
Female Eggs &
Oviducts
Fall: Large amounts…..getting ready for hibernation
Spring: Small amounts…..used during hibernation as energy supply.
See “Love is In the Air”
Fun Bio-Nerdy Amphibian Facts
Group of frogs= Army
Group of toads= Knot
Fears…
Batrachophobia- Fear of amphibians
Ranidaphobia- Fear of frogs.
Bufonophobia- Fear of toads.
Smallest frog= ~1cm
Largest Frog= 30cm
Close Eyes to Swallow
Toads CANNOT give you warts!!!
Human Papilloma Virus (HPV)
Gastric-Brooding Frog
Glass Frog-See Heart Beating
The End-Hop to It!!!