Cell division: mitosis and meiosis

Cell division: mitosis and meiosis
I.
Dividing cells
II. Mitosis and the cell cycle
III. Stages of mitosis
A. Prophase
B. Metaphase
C. Anaphase
D. Telophase
IV. Stem cells
V. Telomeres and telomerase
VI. Cancer cells
VII. Meiosis
VIII. Gametogenesis
Binary Fission- prokaryotes
Meiosis, mitosis, and the chromosome number
Ploidy levels: diploid (2N) and haploid (1N)
In mitosis, ploidy level is maintained
In meiosis, ploidy level is halved.
Human = 46
Dog = 78
Chicken = 78
Chimpanzee = 48
Record > 1000!
II. Mitosis and the cell cycle
10 hours
5 hours
8 hours
1 hour
If a cell, like a red blood cell, were to stop dividing, what stage of the cell cycle would be terminal for that cell?
a. G1 b. G2 c. S d. mitotic
If a cell that was 4N at the start of meiosis, the end result would be _______ cells .
a. 1N b. 2N c. 3N d. 4N
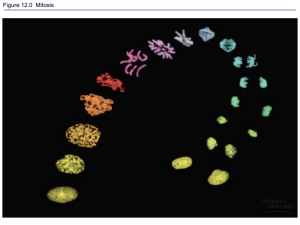
III. Stages of mitosis
What is the ploidy of a cell in anaphase of mitosis?
a. Haploid b. diploid c. triploid d. quatraploid
In what phase do chromosomes line up at the equator?
a. metaphase b. anaphase c. prophase d. telophase
When attached together , what are the two replicated DNA strands of a single chromosome called?
a. centromeres b. chromosomes c. chromatids d. chromatin
Mitosis
Mitosis animation
DNA before and after mitosis
IV. Stem cells
Tissues without adult stem cells?
Stem cell research
Adult stem cell research
Embryo stem cell research
Stem cell potential
Incompatibility, ethics, and the law
Adult cell cloning
IVF/ PGD and stem cell research
How does the ‘PGD technique’ circumvent the ethical issues surrounding the use of embryos in stem cell research?
a. it doesn’t b. embryos are not used in any way for this technique c. embryos are not destroyed d. only dead embryos are used
What is the advantage of using embryonic stem cells over other types of stems cells?
a.They divide more quickly b.There is less controversy in using them c.They are easier to work with d.They are more versatile
Even with tissues derived from embryonic stem cells, patients still face the problem of tissue incompatibility. What is one way this could be overcome?
a. Use tissues derived from modified PGD b. Use tissues derived from adult stem cells c. Use tissues derived from cloned embryos
What is the current federal law regarding embryonic stem cell research?
a. There are no restrictions b. Federal funding is allowed only for research on existing lines c. All embryonic stem cell research is illegal d. Embryonic stem cell research is allowed on defective embryos only
V. Telomeres and telomerase
TTAGGG embryos stem cells cancer cells
What exactly are telomeres?
a. Caps at the ends of chromosomes b. An enzyme that allows cells to keep dividing c. A repeated sequence of nucleotides at the ends of chromosomes d. Structures found only in embryos
Which of the following cells do not have telomerase?
a. Mature skin cells b. Liver stem cells c. Early embryonic cells d. Cancer cells
VI. Cancer
A. Two types of tumors (neoplasms)
B. Cancer cell anatomy and physiology
1. differentiation
2. shape
3. embryonic proliferation
4. non-programmed cell death
C. Genes and cancer
1. oncogenes
2. tumor suppressing genes
3. teleomerase
A. Two types of tumors (neoplasms)
An inappropriate proliferation of cells
Neoplasms: two types benign malignant
Metastasis
B. Cancer cell anatomy and physiology
1. differentiation
2. shape
3. proliferation
4. Non-programmed cell death
5. Telomerase
Stem cells, cancer, and aging
Ink4
C. Genes and cancer
1. oncogenes
2. tumor suppressing genes
3. Telomerase genes
Progression of cancer
What is the problem with enhancing the activity of Ink4?
a. Increased risk of cancer b. Speeding up of the aging process c. Both a and b d. Neither a or b
What are oncogenes?
a. Genes that regulate cell division b. Genes that suppress tumors c. Genes that reestablish telomeres d. Mutated proto-oncogenes
VII. Meiosis
A. Overview
1. Homologues/ homologous pairs
Why half?
2. 2 goals: reducing the chromosome number by half and shuffling (recombining) the genes
Human Life Cycle
Crossing over
Meiosis I
Meiosis II
Independent
Assortment
Crossing Over
Independent Assortment
2 n = number of unique gametes
Meiosis II
Meiosis animation
In what phases of meiosis do genetic recombination take place?
a. Prophase I and Prophase II b. Metaphase I and Anaphase I c. Prophase II and Metaphase II d. Prophase I and Metaphase I
If an organism has 3 pairs of chromosomes, based on independent assortment, how many genetically unique gametes would it have?
a. 3 b. 6 c. 8 d. 9
Problems in meiosis:aneuploidy
Nondisjunction and Trisomy: Anaphase II
Problems in meiosis
Nondisjunction and Trisomy
Women over 35, 2 to 6 times the number of mutations
Implantation of embryo more likely
Most common trisomy is trisomy 21 (Down Syndrome)
Trisomy 21: Down syndrome
Trisomy 21 karyotype
Klinefelter’s Syndrome
Turner Syndrome
Monosomy
Which of the following is the most accurate statement concerning aneuploidy?
a. Nondisjunction of chromosomes during meiosis b. A condition in which there are not the correct number of chromosomes c. Three chromosomes at position number 21 d. The result of early implantation of the embryo
What would be the result of a nondisjunction in Anaphase I?
a. Two normal gametes, one with an extra chromosome, and one missing a chromosome b. Two normal gametes, two with an extra chromosome c. Three gametes with a missing chromosome, one with an extra chromosome d. Two gametes with an extra chromosome, two with a missing chromosome
Meiosis compared to mitosis
Purpose
Number of cells produced
Genetics of cells produced
Ploidy of cells produced
Where they occur
Somatic cells Sex cells
Meiosis compared to mitosis
Meiosis compared to mitosis
VIII. Gametogenesis
Spermatogenesis
Puberty
Average sperm production =
100 million per day
Oogenesis
Arrested at
Prophase I
Arrested at
Metaphase II
Meiosis completed at fertilization
In embryo
At birth
Approximately 400, 000
Ovulation
400 released
When does oogenesis start in female mammals?
a. At birth b. Before birth c. At puberty d. At fertilization
When does oogenesis end in female mammals?
a. At birth b. Before birth c. At puberty d. At fertilization
In oogenesis, what is the end result of interkinesis?
a. Two secondary oocytes b. One secondary oocyte and one polar body c. One secondary oocyte and two polar bodies d. Two secondary oocytes and two polar bodies
Contributions of egg and sperm to embryo egg sperm
1. Haploid set of chromosomes 1. Haploid set
2. X to males and females
3. Protection
2. X to females;
Y to males
4. Nourishment
5. Directions for early development
6. Mitochondria
Mutations?
Which of the following is a contribution of the sperm to the embryo?
a. Mitochondria b. Directions for early development c. Protection d. Nourishment e. Most mutations
The contribution of the sperm above is __________ .
a. Beneficial b. Detrimental c. Neutral d. Could be any or all of the above
The end