RNA Protein Synthesis - Panhandle Area Educational Consortium

Biology Partnership
(A Teacher Quality Grant)
RNA and Protein Synthesis
Nancy Dow
Jill Hansen
Tammy Stundon
October 20, 2012
Gulf Coast State College
5230 West Highway 98
Panama City, Florida 32401
850-769-1551 www.gulfcoast.edu
Panhandle Area Educational Consortium
753 West Boulevard
Chipley, Florida 32428
877-873-7232
Pre-test
Q and A board
What is RNA
How do we use RNA?
What are the different forms of RNA?
How do we produce an actual human from just a series of letters??
Florida Next Generation
Sunshine State Standards
SC.912.L.16.3 Describe the basic process of DNA replication and how it relates to the transmission and conservation of the genetic information.
Also Assesses
SC.912.L.16.4 Explain how mutations in the DNA sequence may or may not result in phenotypic change. Explain how mutations in gametes may result in phenotypic changes in offspring.
SC.912.L.16.5 Explain the basic processes of transcription and translation, and how they result in the expression of genes.
SC.912.L.16.9 Explain how and why the genetic code is universal and is common to almost all organisms
Florida Next Generation
Sunshine State Standards
Benchmark Clarifications
• Students will describe the process of DNA replication and/or its role in the transmission and conservation of genetic information.
• Students will describe gene and chromosomal mutations in the DNA
• sequence.
• Students will explain how gene and chromosomal mutations may or may not result in a phenotypic change.
• Students will explain the basic processes of transcription and/or translation, and their roles in the expression of genes.
• Students will explain that the basic components of DNA are universal in organisms.
• Students will explain how similarities in the genetic codes of organisms are due to common ancestry and the process of inheritance.
Florida Next Generation
Sunshine State Standards
Content Limits
• Items requiring the analysis of base pairs for gene mutations are limited to changes in a single gene.
• Items may refer to but will not assess the cell cycle, mitosis, and/or meiosis.
• Items will not require memorization of specific conditions resulting from chromosomal mutations .
• Items may refer to the process of meiosis in the context of mutations but will not assess meiosis in isolation.
• Items addressing transcription or translation will not require specific knowledge of initiation, elongation, or termination
Blame it on the DNA
Structure of DNA
DNA is made of subunits called nucleotides
DNA nucleotides are composed of a phosphate, deoxyribose sugar, and a nitrogencontaining base
The 4 bases in DNA are: adenine (A), thymine
(T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C)
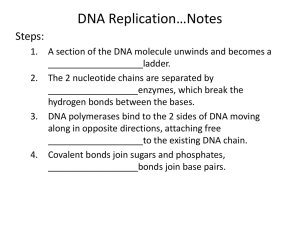
Remember Replication?
8
Hold up,
wait a minute….
• DNA is only found in the nucleus
• Who we are, how we look, and the mechanisms that make are body function are all determined by proteins
• Proteins are only made in the ribosome ..
Why do we need both DNA and RNA?
• DNA holds
all the genetic information
• DNA damage = mutation
• Safer in the nucleus
• RNA acts as messenger
Why do we need both DNA and RNA?
Central Dogma holds that genetic information is expressed in a specific order. This order is as follows
Central Dogma Video
DNA vs
RNA
Sugar
Bases
Strand
DNA vs RNA
Types of RNA
RNA Foldable
Types of
RNA
1
2
1
2
3
3
.
Three Types of RNA
1. Messenger RNA
(mRNA) copies DNA’s code & carries the genetic information to the ribosomes
2. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA), along with protein, makes up the ribosomes
3. Transfer RNA (tRNA) transfers amino acids to the ribosomes where proteins are synthesized
Protein Synthesis: Step 1
DNA unwinds and mRNA is made complementary to the
DNA
A=U
G=C
Transcription –the making of messenger
RNA (mRNA) from
DNA in the nucleus
3 nitrogen bases in mRNA is called a codon
Protein Synthesis: Step 1
Where to start?
1. DNA unzips along hydrogen bonds
2. Free RNA nucleotides pair with the complementary DNA bases (C-G and U-A) along the exposed DNA strand forming an RNA transcript
3. RNA transcript released from the DNA
4. DNA closes again
Protein Synthesis: Step 1
The transfer of information in the nucleus from a DNA molecule to an RNA molecule
• Only 1 DNA strand serves as template
• Starts at promoter DNA (TATA)
• Ends at terminator (AAAAA)
• When complete, preRNA molecule is released
Protein Synthesis: Step 1 ½
Not all the RNA
codes for something!
• A specialized nucleotide is added to the beginning of each mRNA molecule which forms a cap. It helps the mRNA strand bind to a ribosome and prevents the strand from being broken down too fast.
• The end of the mRNA molecule gets a string of AAAA nucleotides (poly A tail) that helps the mRNA molecule exit the nucleus.
• The extra footage takes the form of nucleotide segments that are not included in the final protein.
Cleaning Up the Message
• Contains unwanted bases
• The ‘junk’ sequences (called
introns) are removed from the message and the remaining sequences (exons) are linked together to produce a sequence of codons that will translate into a polypeptide.
• This process occurs before the message leaves the nucleus.
Protein Synthesis: Step 1 ½
There’s
Junk in
My
DNA!
Final processing of the mRNA includes removal of introns , leaving the exons to direct protein synthesis
Let’s Catch Up
DNA Codes for RNA,
Which Codes for Protein
The Language of Proteins
• Each 3 nucleotide sequence in an mRNA strand is called a codon.
• Each codon codes for a 1 amino acid.
• The codon sequence codes for an amino acid using specific rules. These specific codon/amino acid pairings is called the
Genetic Code .
The Language of Proteins
• There are 64 (4 3 ) possible codes, but only 20 amino acids.
• More than 1 triplet may code for the same amino acid. This is fine as long as no triplet can code for more than one a.acid.
• Note that several codons can also act as start (AUG) or stop
(UAA) signals.
Toss the Ball Review
The Genetic Code
Codon Music
Time to
Practice!
Mutations
• Mutation: change in DNA
• If a base is substituted or deleted, the triplet(s) are different
• This sometimes leads to difference in the protein
Putting it All Together
Putting it All Together
1) rRNA (ribosomal RNA) attaches to mRNA and starts reading the codons
2) tRNA (transfer RNA) – carries amino acids and attaches them to the growing protein chain
3) When protein production is complete, the ribosome releases the protein chain
Putting it All Together
Structure
• Two subunits, each composed of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and protein
Function
• Bring tRNA bearing an amino acid close enough to mRNA to interact
– Permit alignment of anticodon and codon
DNA Codes for RNA,
Which Codes for Protein
Transcription
Translation
39
Scavenger hunt
Q/A board
Follow Up
UAG
Post Test
Try It - Simulations
Awesome
Scarf
Cool Stuff
Genome Quilts
From Gamer to Scientist
Some Other Goodies
• • Trippy Protein Synthesis Dance
•
•
Tik Tok (Protein Synthesis)
(Blame it on the
• • Translation Mario Style
(Central dogma)
•
•
The Cell Will Survive (Sing Along)
• • Genetic Music (mario translation)
•
•
DNA Song
(sing along)?
• http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tQv5Ho8zsKI codon bell ringer
• DNA, Hotpockets, and the Longest Word Ever
• http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tVrkBJz9q0g Born to be wildtype
(bad singing)