Enhancers
advertisement
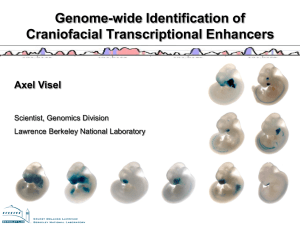
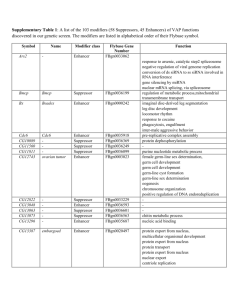
P300 Marks Active Enhancers Ruijuan Li Chao He Rui Fu Main contents • Background and conclusion • Experimental approaches • Data processing • Summary and discussion Background • Problems Enhancers • Previous researches Existing work • Authors introduction Research interests Problems • Enhancers prediction Accurate When and where enhancers are active in vivo Previous researches • Comparative genome methods Evolutionary sequence constraint failed to reveal when and where enhancers are active in vivo Some regulatory elements are not sufficiently conserved to be detectable. • Conservation-independent approach ChIP-seq with an antibody specific for an enhancerbinding protein • P300 has been showed to be associated with enhancers Authors introduction • Axel Visel – Staff scientist in the Genomics Division, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory – Comparative genomics, sequencing-based chromatin studies (ChIP-seq), and transgenic reporter assays – Systematic identification and functional characterization of distant-acting enhancers • Matthew J. Blow – Comparative genomics, RNA editing • Prabhakar S, Visel A, ..., Pennacchio LA, Rubin EM, Noonan JP (13 authors). Human-specific gain of function in a developmental enhancer. Science 2008 • Visel A, ..., Rubin EM, Pennacchio LA (10 authors). Ultraconservation identifies a small subset of extremely constrained developmental enhancers. Nature Genet 2008 • Rahimov F, Marazita ML, Visel A, ..., Murray JC (23 authors). Disruption of an AP-2alpha binding site in an IRF6 enhancer is associated with cleft lip. Nature Genet 2008 • De Val S, ..., Visel A, ..., Black BL (15 authors). Combinatorial regulation of endothelial gene expression by ets and forkhead transcription factors. Cell 2008 • Lein ES, Hawrylycz MJ, ..., Visel A, ..., Jones AR (108 authors). Genomewide atlas of gene expression in the adult mouse brain. Nature 2007 • Pennacchio LA, ..., Visel A, Rubin EM (19 authors). In vivo enhancer analysis of human conserved non-coding sequences. Nature 2006 Corresponding Author • Len A. Pennacchio • Molecular biologist, Senior staff scientist in the Genomics Division, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory • Head of the Genetic Analysis Program and the Genomic Technologies Program, Joint Genome Institute • 2007 White House Presidential Early Career Award for Scientists and Engineers (PECASE); • Contributed to the human genome project with an analysis of human chromosome 16. • Gene regulation, the genetic basis of differences in body shape between different individuals, conserved sequences in the genome, and connections between junk and heart disease Conclusion • P300 binding sites accurately identifies enhancers and their associated activities in vivo. • The data will be useful to study the role of tissue-specific enhancers in human biology and disease on a genome-wide scale. Experimental approaches ChIP-seq: map p300 binding sequences in vivo Transgenic mouse enhancer assay: test the activity of predicted p300 peaks Workflow of ChIP-seq http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chip-Sequencing ChIP-seq to predict putative enhancer sites Comparison with previous method comparative genomic method ChIP-seq method ChIP-seq to predict putative enhancer sites Workflow of transgenic mouse enhancer assay Selection of 86 candidate regions for testing Cloning human genomic sequences into Hsp68-LacZ reporter vector Pronuclear injection and staining at E11.5 Examples of successful prediction Transgenic mouse enhancer assay • Advantage accurate • Disadvantage effect of endogenous regulatory elements Data processing • Peak Calling to identify p300 binding sites • Validate p300 binding sites are active enhancers Peak Calling 1. Reads extend to 300bp 2. Identify candidate peak 3. Merge nearer peaks 4. Discard artefact peaks Dr Wang’s PPT for molecular computational biology Validation Evidence1: Transgenic Experiment Validated Validation Evidence2: Functional Elements are more likely to be Conserved Validation Evidence3: Active enhancer are nearer to active gene Summary • p300 binding sites are probably to be celltype specific enhancer. • Most p300-bound regions are conserved • p300 binding sites are significant nearer to expressed genes than random sites. Improvement • Peak Calling Arbitrary to extend the reads to 300bp No control to test peak quality • Active enhancer prediction Sensitivity is low Still some errors Nowadays • More marks: H3K4me1, H3K27ac • Enhancers are transcribing bidirectional smRNA • Locate enhancers target promoters by new experiments Thank you