huang_p_bms265
advertisement

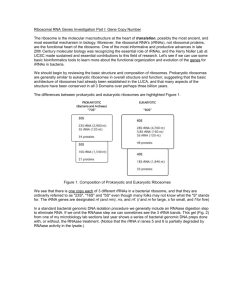
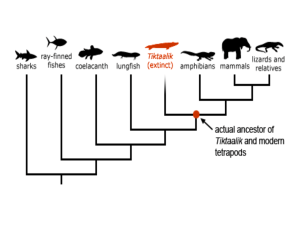
Ribosomal RNA Phillips Huang BMS 265 rRNA Nomenclature • Named based on sedimentation rates, measured in Svedberg units (S) • Larger sedimentation coefficients indicate faster sedimentation rates • Larger rRNAs sediment faster rRNA Discovery • First discovered in the 1930s as part of the microsome by Albert Claude • Characterized as a ribosomal component in the 1950s by George Palade Large Ribosomal Subunit • rRNA largely responsible for 3D structure • Peptidyl transferase center (PTC) composed of rRNA • A, P and E sites made up mainly of rRNA Small Ribosomal Subunit • Atomic structure published in 2000 • Decoding center composed entirely of rRNA rRNA Biogenesis in Eukaryotes • In prokaryotes, rRNAs are also synthesized as one primary transcript Mechanism of action: Translation initiation in Prokaryotes • Translation initiation in eukaryotes involves binding of ribosomal components first to the mRNA 5’ cap Mechanism of action: Translation elongation Residues of rRNA help to stabilize the mRNA:tRNA complex Peptide Bond Formation • Involves nucleophilic attack of α-amino group of aminoacyl-tRNA on carbonyl carbon of peptidyltRNA Target carbonyl carbon is protected from hydrolysis prior to reaction Hypothesized transition state Mechanism of action: Translation termination rRNA as a Tool • Phylogenetic studies – rRNA sequences are highly conserved across species • In vitro translation systems – Used when overexpressed protein is toxic, rapidly degraded or insoluble in cells lancelets hagfish lamprey gnathostome Role in Human Disease • Mutations in mitochondrial rRNA – Susceptibility to aminoglycoside-induced hearing loss • Changes to rRNA in cytoplasmic ribosomes – Defective pseudouridylation and X-linked Dyskeratosis Congenita (X-DC)