A hierarchical model for evolution of ribosomal RNA
advertisement
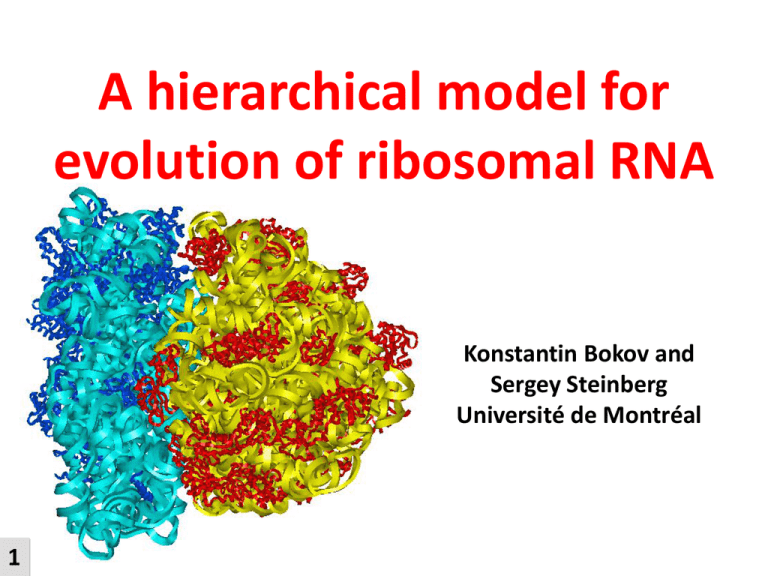
A hierarchical model for evolution of ribosomal RNA Konstantin Bokov and Sergey Steinberg Université de Montréal 1 The ribosome is a universal machine producing proteins LARGE SUBUNIT GROWING PROTEIN - addition of new peptides to the growing protein chain (in PTC); PTC P A SMALL SUBUNIT 5’ 2 TRANSPORT RNA DR - correct decoding of the messenger RNA (in DR); - precise movement along the messenger RNA; - coordination of the work of all co-factors and ligands; MESSENGER RNA The evolution of Life on Earth directly depends on the emergence of the ribosome ! Protein World 3 The ribosome and LUCA Bacteria Archaea Eukarya Last Universal Common Ancestor 4 Functionality of the ribosome depends primarily on its RNA Small subunit + RNA Large subunit + proteins RNA RNA+proteins proteins Protein-WORLD RNA-WORLD 5 RNA-body Major periods in the evolution of the ribosomal RNA Unlimited reshuffling of RNA chains F PROTO RIBOSOME 6 F F Restricted step-wise increase of the ribosome size MODERN RIBOSOME Preserve functional structure ! gene sequence insertion 5’ 7 3’ 5’ 3’ Accommodation of an insertion gene sequence insertion Broken 8 Unstable gene sequence Stable General principle of insertion: Structural integrity of more ancient elements cannot be dependent on the presence of more recently acquired elements. 9 Integrity of each strand of a double helix depends on the presence of the other strand 10 5’ 3’ 3’ 5’ The A-minor motif as an evolutionary determinant 23S rRNA A-minor motif 11 Nissen, P., Ippolito, J.A., Ban. N., Moore, P.B., Steitz, T.A. (2001) RNA tertiary interactions in the large ribosomal subunit: the A-minor motif. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. No 98(9), pp. 4899-4903. In a newly emerged element: 1. The 3’- and 5’-termini must be close to each other 2. For each double helix, both strands must be present 3. When such element forms an A-minor interaction with the other elements of the ribosome, it must provide the adenosine stack and not the double helix 12 Dismantling the ribosomal RNA: removal of those elements that are qualified as the most recent acquisitions of the ribosomal structure MODERN RIBOSOME PROTORIBOSOME core 13 Last acquisitions 2-nd last acquisitions Dismantling the structure of the 23S rRNA 14 Inter-domain A-minor interactions double helix A-min 15 stack of adenosines Dismantling the structure of the 23S rRNA 16 The symmetrical structure in Domain V is the proto-ribosome P-site A-site t-RNA 17 The network of dependencies does not contain cycles 18 59 54 If the orientations of all A-minor interactions in the 23S rRNA were chosen randomly, the probability of a cycle-free arrangement would be P< -9 10 . The absence of cycles of dependency is a fundamental characteristic of the 23S rRNA, which is directly related to the particular trajectory of its emergence. 19 Growing support for PTC 20 Appearance of the protuberances and of the small subunit 22 What about 16S rRNA? SSU 21 LSU The hypothetical structure of the primordial ribosome and two tRNAs 25 Small world... 26 Acknowledgment We appreciate the help of NSERC and CIHR for financing this project. presentation Chain of A-minor interactions E-coli, 23S E-coli, 23S A-stack (in red) E-coli, 23S A-stack (in red) Non-covalent dependency A-stack (in red) H69 H92 H71 H71 H68 H69 H95 H92 H93 H95 H74 H93 H74 H68 A Double helix is older than stack of A-s packing in its minor groove Pseudoknot B A C The loop of a stem-loop structure (A) forms a double-helix (B) with a region outside this stem-loop for example with another stem-loop (C) B Pseudoknots in the 23S rRNA C - local - non-local Long-distance pseudoknots in the 23S rRNA 33 40 D 40 The approach is applicable Along-groove packing” motif as a mean of structural fitting E-coli, 23S H25 minor groove G17-C523 G539-U554 H2 H25 (G-C) (G-U) H2 minor groove F Along-groove packing motif Along-groove packing motif G AGPM-s in 23S rRNA H What about evolutionary deletions ? X B evolution A L C =A-D Accommodation must not provoke structure weakening ? M Additional Notion of dependency Covalent dependency Non-covalent dependency (A-min) E-coli, 23S E-coli, 23S E Core A B C D B yellow A-stacks In PCK WC helices A E B C D C A Core The new RNA insertion covalently depends on the structure where it emerged N B A C A A The element containing stack of adenosines is noncovalently dependent on its complimentary WC helix Domain-V is the most ancient part of the ribosome P 16S mitochondrial versus prokaryotes Only prokaryotes R Mito and prokaryotes 23S mitochondrial versus prokaryotes Only prokaryotes S Mito and prokaryotes Dismantling versus evolution PROTORIBOSOME MODERN RIBOSOME T MODERN RIBOSOME PROTORIBOSOME AGPMs in the ribosome of E.coli 19 54 26 26 11 11 25 47 36 27 45 57 40 51 20 40 The evolution of Life on Earth directly depends on the emergence of the ribosome ! Protein World 2