10.1-BIO-CHEM-Enzymes.Introduction
advertisement

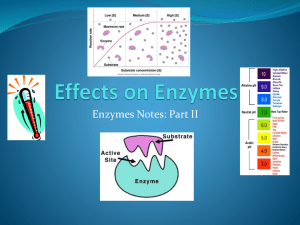
Chemical Reactions & Enzymes Q! What is Activation Energy? Many chemical reactions need a source of energy to occur Activation Energy = the energy needed to get the reaction going e.g. What will happen to a pile of wood sitting in a fireplace? Nothing! It needs the energy from a lit match to get the wood burning! Graph of Energy Lower energy = faster reaction! Q! What do Enzymes Do? Enzymes lower the activation energy and speed up chemical reactions in cells Q! What type of macromolecule are Enzymes? 4 macromolecules lipids nucleic acids carbohydrates proteins Enzymes are proteins! Q! How do Enzymes work in Our Body? In our body… 1. Enzymes speed up digestion by breaking down food 2. Enzymes speed up cell respiration to make ATP Q! How do Enzymes Work? Active Site (a groove that fits a substrate) Enzyme Substrate How Enzymes Work Enzyme Substrate Substrate moves into the active site How Enzymes Work Substrate Enzyme Substrate moves into the active site How Enzymes Work Substrate Enzyme Substrate moves into the active site How Enzymes Work Substrate Enzyme Fits tightly into the groove! How Enzymes Work Product Enzyme When the reaction is done, the products are released How Enzymes Work Products Enzyme The enzyme is free to start all over! Q! What is the Lock and Key Model? One enzyme fits one substrate (like one key fits one lock) Lock and Key Model Enzymes Summary Enzymes… 1. Are proteins 2. Lower the activation energy 3. Speed up chemical reactions 4. Are not destroyed or used up 5. Bond to a substrate 6. Are also called catalysts Cracker Challenge! 1. Take a cracker and lick it. Record how it tastes. 2. Chew it for 10 seconds and again record how it tastes. 3. Why did the taste of the cracker change? The cracker became sweeter as amylase, an enzyme in your saliva, broke down the starch into sugar! Enzymes All Around Us Copy this table in your notes 1 Enzyme Substrate Products 2 3 4 5 6 Enzymes All Around Us Use these products to fill in your table! Amylases Detergents for dish washing to remove starch Meat tenderizers (Papain) To soften meat for cooking Contact lens cleaners (Proteases) To remove proteins on contact lens to prevent infections. Fruit juices (Pectinases) To make fruit juices clear Baby foods (Trypsin) To predigest baby foods Q! What Conditions to enzymes depend on? Enzyme activity is affected 3 things: 1. pH 2. Concentration of substrate 3. Temperature Q! Hos does pH affect enzymes? • Stomach enzymes work best at an acidic pH (pH 2-4) • Small intestine enzymes work best at a basic pH (pH 8-9) (graphs on next slide) HSA Question: Cells in the stomach produce pepsin, an enzyme, to help digest food. Pepsin works best at a pH of 2. Which of these graphs most likely shows what will happen to the activity of pepsin as the pH of the stomach is increased? Q! How does the Concentration of Substrate affect enzymes? The more substrate that is available, the more reactions can take place at once. Substrate Substrate E Substrate Substrate E Substrate E Concentration of Substrate The more substrate that is available, the more reactions can take place at once. Substrate E Substrate Substrate E E Concentration of Substrate The more substrate that is available, the more reactions can take place at once. Substrate E Substrate Substrate E E Q! How does Temperature Affect enzymes? Some enzymes like it warm… but some like it hot! • Enzymes in humans work best at 98F • Enzymes in thermophilic bacteria work best at MUCH hotter temperatures! Temperature * In general, enzymes work better in warmer temperatures because the molecules move more quickly and cause more interactions. ** However, if the temperature gets TOO hot, it can damage the enzyme so that it stops working. This is called denaturation. Q! What is Denaturing? Denature= when the structure of a protein changes so that it no longer functions Can be caused by: • high temperatures • changes in pH Toothpick Demo I need 1 volunteer to race against time! Objective: To pick up as many toothpicks as possible in 15 seconds Rules: 1. only use one hand 2. only pick up one toothpick at a time 3. NO cheating! What was the enzyme? What was the substrate? The product? HSA Question: A researcher is testing the effect of acid rain on living organisms. She takes a tissue sample and places it in acid rainwater, which decreases its pH. As the pH decreases, what will most likely happen to the enzyme reaction rates in the cells of this tissue? A. They will increase. B. They will decrease. C. They will stay the same. D. They will increase and level off. HSA Question : Catalase is an enzyme found in plant and animal cells. Catalase causes hydrogen peroxide to break down into water and oxygen. A student conducted an experiment to determine whether plant and animal cells have the same amount of catalase. She measured and recorded the amount of oxygen that is given off by each of the tissues when mixed with the enzymes. The student conducted a second experiment. She boiled the liver tissue completely and added it to the hydrogen peroxide solution. She observed that little to no oxygen was released in the second experiment. Which of these statements best supports the student’s observations? A. Exposing catalase to high temperatures makes it inactive. B. Exposing catalase to high temperatures changes it into a different enzyme. C. Boiling liver breaks down hydrogen peroxide faster. D. Boiling removes oxygen from the liver.