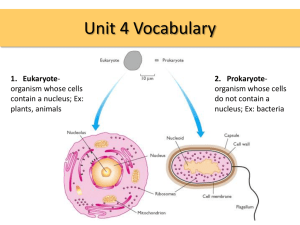
Biology EOC Review
advertisement

Biology EOC Review Session Biology EOC Test is the second week back in January! You will be taking the test during your regularly scheduled science class 5-6 scenarios 40 questions total 40-45% Cells, Genetics, DNA 30-35% Populations and Ecology 25-30% Evolution Test-taking Tips Go SLOWLY. Take your time, READ everything. Look at the pictures, charts and graphs…they are there for a reason. Pay attention to words in bold or italics. They are often clues to help you with the answer. Vocabulary Variables Validity Manipulated, responding, control What you did during the experiment (procedure) to obtain good data (NOT repeating, recording, calculating or measuring) making sure equipment is calibrated correctly for example. Reliability Repeat the experiment, multiple trials, obtain more data using same procedure Making sure you have consistent results Hypothesis If…then…because format I predict…reason Most importantly you have to include a reason for your statement. “Foaming Spuds” Conclusion writing practice 1. Answer the investigative question Was your hypothesis supported/rejected and why 2. Include supporting data from entire range of experiment (high and low) 3. Explain how data supports or rejects your answer to investigative question 4. Use scientific explanation to explain results/trends “Foaming Spuds” Procedure Re-write Create a procedure for a new variable that is being tested. Tips when re-writing a procedure… Procedure steps are logical and can be easily repeated by another person Variables are identified/implied Two controls Manipulated and Responding variable Procedure includes information about recording measurements Information about repeating trials is included Includes a validity measure not included in original procedure… Macromolecules “Giant Molecules” (polymers) Linked together with smaller subunits (monomers) Carbohydrates Proteins Fats (lipids) Carbohydrates Compounds made of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen Used as a main source of energy for many organisms Used for structural purposes Breakdown of sugars supplies energy for cell activities Proteins Macromolecules that contain nitrogen, carbon, hydrogen and oxygen Composed of smaller molecules called amino acids 20 amino acids found in nature Each protein has a specific role Reaction rates, cell processes, form bones and muscles, transport substances in and out of cells, fight disease Fats (lipids) Compounds made of carbon, oxygen and hydrogen atoms Glycerol + Fatty acid = Lipid Fats, oils, waxes Saturated and unsaturated Not soluble in water Used to store energy Parts of biological membranes and waterproof coverings Osmosis and Diffusion Cell Membrane and Cell Wall regulate what enters and leaves cells This occurs during two processes Osmosis Diffusion Diffusion Movement of dissolved molecules from one side of cell membrane to another Particles move from an area where they are more concentrated to an area where they are less concentrated Substances diffuse across a membrane without the cell using any energy Osmosis Diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane Most membranes selectively permeable some substances can pass through and others cannot Water passes easily across most membranes Cells Cell: smallest unit of life Prokaryotic: no nucleus Eukaryotic:with a nucleus Organelle: Specialized structure that performs important functions in the eukaryotic cell Organelles Cell Membrane Allows passage of oxygen, nutrients, and wastes in and out of the cell Provides protection and support Found in plant and animal cells Cell Wall Protects the plant cell, maintains its shape, prevents excessive water intake Found only in plant cells Organelles Nucleus Contains all genes (genetic information), chromatin, chromosomes and nucleolus Controls protein synthesis Found in plant and animal cells Chromosome Tightly coiled strands of DNA and protein Organelles Chloroplast Site of photosynthesis, convert solar energy to chemical energy Found only in plant cells Mitochondria Site of cellular respiration (generates energy) Convert chemical energy in food to a form cells can use Found in plant and animal cells Organelles Cytoplasm Portion of the cell outside the nucleus Helps to maintain cellular shape Found in plant and animal cells Ribosome Where proteins are made Found throughout the cytoplasm Found in plant and animal cells Cell Cycle Cell cycle – The series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide. Has three main parts: Interphase, Mitotic Phase, Cytokinesis Cell Cycle (Mitosis) Interphase: Cells increase in size and make new proteins and organelles. Chromosomes are replicated. Mitosis: division of the nucleus. Divided into 4 phases. Cytokinesis: division of the cytoplasm. **Produces IDENTICAL Cells** DNA DNA is a double helix “twisted ladder” Sides of ladder made of sugar (deoxyribose) phosphate Rungs of ladder made of nitrogenous bases Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine and Guanine DNA Base-Pairing In a DNA molecule…. Adenine pairs with Thymine Cytosine pairs with Guanine DNA is made of molecules called: Nucleotides Sugar, phosphate and nitrogenous base (ATCG) Protein Synthesis Gene: coded DNA instructions that control the production of proteins within the cell Contain instructions for assembling amino acids into proteins Instructions for making proteins comes from DNA…must first be converted into RNA to leave the nucleus DNA can’t leave the nucleus! Protein Synthesis Process that produces protein using instructions from DNA (gene) Uses RNA as an intermediate step between DNA and proteins Two parts: Transcription (nucleus) DNA mRNA Translation (ribosome) mRNA protein (amino acid sequence) Genetics A gene is a section of DNA that forms a trait (protein). For example: Hair color, Height, ear lobes…. Alleles are different forms of a gene. For example: brown hair, blond hair or Tall and short. You get one allele for each trait from your parents… Genetics Dominant allele – the allele that “wins”. We use a capital letter “R” Recessive allele – the allele that is hidden or loses . We use a lower case letter “r”. RR = Dominant, Dominant - Homozygous This person can roll their tongue Rr = Dominant, recessive – Heterozygous (hybrid) This person can roll their tongue rr = recessive, recessive - Homozygous This person can’t roll their tongue Genetics Each organism must inherit a single copy of a gene (allele) from each of its parents Organisms have two copies of each gene (genotype 2 letters) Gametes (sperm and egg cells) each contain one copy of each gene Cells and Chromosomes Diploid: 2 copies of each chromosome All cells except sperm and egg cells Mitosis Haploid: one copy of each chromosome sperm and egg cells only Meiosis Humans 46 chromosomes Reproductive cells have 23 chromosomes Meiosis What are the differences between mitosis and meiosis? Allows for genetic variation “Meiosis is the process in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half” Mitosis produces two cells; cells are identical Meiosis produces four cells; cells are unique; occurs only in sperm/egg cells What are the similarities between mitosis and meiosis? First phase identical (meiosis phase 1); form of cell division Evolution Evolution – change over time It is the process by which modern organisms have descended from ancient organisms. How well an organism is adapted to its environment Current scientific facts, observations and hypotheses all combine to create current evolutionary theory a well-supported, testable explanation of the biological diversity on Earth. 1. Tortoises longer neck for sparse vegetation. Shorter neck where vegetation was more abundant. 2. Finches Darwin noticed that these birds have different shaped beaks, adapted to their food source (seeds) Evidence for Evolution Fossil Record – transitional fossils show us intermediate stages. Example: horse and camel Evolution by Natural Selection Definitions: 1. struggle for existence – members of a species compete for resources 2. Fitness – ability to survive and reproduce 3. Adaptations – inherited characteristics that increase an organisms chance of survival. Variation Caused by mutations (changes in DNA sequences Results in physical or behavioral changes May be beneficial or harmful Increase or decrease survival rates Inheriting different alleles from parents (causes individuals to look different) Results of meiosis are different every time Why we don’t look exactly like our siblings! Photosynthesis and Cell Respiration What happens during photosynthesis? Plants (autotrophs) use energy from sunlight to convert water and carbon dioxide into carbohydrates (energy) and oxygen 6CO2 + 6H2O (light) → C6H12O6 + 6O2 Reactants? Carbon dioxide (CO2) and Water (H2O) Products? Glucose—Sugar (C6H12O6) and Oxygen (O2) Photosynthesis and Cell Respiration Cellular respiration… is the process that releases energy by breaking down food molecules (glucose) in the presence of oxygen; occurs in heterotrophs 6O2 + C6H12O6 6CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy oxygen+ glucose carbon dioxide + water+ energy Compare this to the equation for photosynthesis….what do you notice? Carbon Cycle Essential molecule that makes up all organisms Proteins, fats, carbohydrates Carbon is cycled… Between the atmosphere, land, water and organisms Short and long-term cycles Carbon Cycle In an ecosystem… 1. Plants convert carbon dioxide into carbohydrates (photosynthesis) 2. Consumers eat producers, get carbon from carbohydrates (glucose) 3. Consumers release carbon to atmosphere in carbon dioxide (breathing) Population Ecology Population – group of individuals of the same species that live in the same area. Population Density = # individuals/area Population Growth Populations may stay constant or change drastically from year to year. 4 factors affect population size 1. 2. 3. 4. Natality – birth rate Mortality – death rate Immigration – movement of individuals IN Emigration – movement of individuals OUT Limiting Factors Limiting factors cause population growth to decrease. Density dependent – a factor that depends on population size. Occurs when populations are large and dense. Competition Predation Parasitism Disease Density Independent: A factor that affects all populations in similar ways, regardless of population size. Unusual weather Natural disaster Seasonal cycles Human activity Exponential vs. Logistic Growth Exponential growth – population grows at a constant rate…with unlimited resources this will occur. Logistic Growth- occurs when growth slows or stops. -The largest number of individuals the environment can support is called the carrying capacity. Biomes and Biodiversity Biodiversity: the number of different species living in an ecosystem Biomes: Rainforest, Tundra, Savanna Sustainability Sustainability: using natural resources at a rate that does not deplete them Condition in which human needs are met in such a way that a human population can survive indefinitely “The traditional definition of sustainability calls for policies and strategies that meet society’s present needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.” (epa.gov) Sustainability Issues in Washington Invasive Species Non-native species causing ecosystem damage Pollution (air and water) Hydroelectric Dams Overfishing Forest Management Field Study Scenario Include method for collecting data Imply a consistent sampling strategy Identify one manipulated variable Multiple measurements, 2 sampling areas Record environmental conditions How often, specific technique for recording measurements Repeat trials What is being measured Record measurements Three conditions to be credited (3 areas) Identify one responding variable “count at the same time every day” Temperature, weather, etc. Steps of procedure are logical