RNA - jpsaos
advertisement

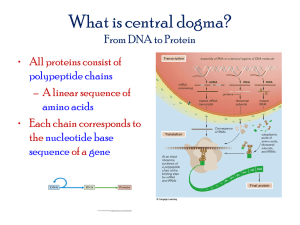
Station 1 What is the purpose of genes? What is the purpose of RNA? In what 2 ways is RNA different from DNA? Station 2 What are the three types of RNA? What How do they stand for? are they different? Stage 3 What is transcription? What is RNA polymerase’s role in transcription? What is a promoter? Transcribe: ATGTGGCTA Station 4 What happens when RNA polymerase binds to a promoter? How is transcription different from DNA replication? What determines which nucleotide is added next to form an RNA chain? Station 5 What is the purpose of a termination signal? What are transcripts? What happens to mRNA after it is made? Station 6 What are proteins made up of? How many amino acids are there? What does the sequence of amino acids tell us? RNA DNA Replication The strand that is copied to form a new strand is called a template In replication of a double-stranded DNA, both original (parental) DNA strands are copied When copying is finished, you have two separate helices, each consist of one of the original strands plus its copy. Do Now: What is the complement? AGTCGGAT TAGCCTAC CTGAGGAT RNA Also made up of nucleotides Sugar molecule: Ribose Uracil (U) pairs with Adenine (A) in RNA Types of RNA Messenger RNA (mRNA) Carries info from DNA to the cytosol Transfer RNA (tRNA) Binds to specific amino acids Aids in translation (RNA proteins) Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) Makes up ribosomes Protein Synthesis Genes are made up of DNA. Genes code for proteins. Proteins are made from long chains of amino acids. How do we get from DNA to proteins? STEP 1: Transcription DNA is transcribed (copied) into RNA. RNA binds to a promoter. Single gene in eukaryotes Several genes in prokaryotes Where RNA polymerase binds, the DNA separates. DNA is transcribed until the termination signal is reached. At this point the RNA molecule releases the DNA Transcription DNA Strand ATC AGG TAC GGA What’s the mRNA strand? Protein Synthesis DNA Strand ATC AGG TAC GGA Check you answer. Did you have: UAG UCC AUG CCU Proteins Composed of amino acids 20 different types of amino acids The sequence of the amino acids determines how the polypeptide twists and folds (shape). Step 2: Translation mRNA is converted into an amino acid sequence. The mRNA sequence is read in groups of 3 bases (codons) and the proper amino acids are found and linked together. How do you know the right amino acid to use? Let’s Make our own strand DNA Strand is: TAC GTA CTT ATT mRNA strand is: Codes for amino acids: Check your strand: DNA Strand is: TAC GTA CTT ATT mRNA strand is: AUG CAU GAA UAA Codes for amino acids: MET HIS GLU STOP