Mus musculus Homo sapiens
advertisement

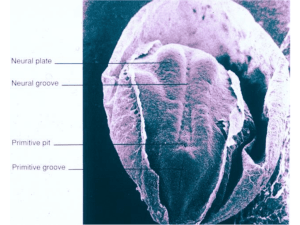
Mammals: Mus musculus Homo sapiens Close Genomic Relationships 2.5Gb, 20 chromosomes ~20,500 genes Eukaryotic Branch of the Tree of Life 3Gb, 23 chromosomes ~20,500 genes The Mouse Trap (Trans-species Enhancer Trapping) QuickTime™ and a Sorenson Video 3 decompressor are needed to see this picture. Zona Pellucida Fertilization QuickTime™ and a Sorenson Video decompressor are needed to see this picture. Pronuclei Vitelline Layer ART Cinema Cleavage PGD Morula QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Embryo Sheds the ZP Compaction Implantation of the Blastocyst (Blastula) Epiblast develops into embryonic body Amniotic cavity develops here Gastrulation First Endoderm Then Mesoderm Leaving Ectoderm "It is not birth, marriage, or death, but gastrulation, which is truly the most important time in your life.” - Lewis Wolpert (1986) cilia, microfilaments and nuclei Hensen’s Node The Layered Embryo Regulatory Conversations Fibroblast Growth Factors (FGF) pathway Mesoderm differentiation, axonal projections, blood vessel formation Hedgehog pathway Patterning of the neural tube, the L-R axis and the gut Notch pathway Somitogenesis and other patterning events Wnt pathway Induction of somitic muscle, limb polarity, the urogenetal system Transforming Growth Factor (TGF)- Beta pathway Regulate bone formation (via Bone Morphogenetic Proteins or BMPs) and cell division Forming the Vertebrate: Neurulation and Somitogenesis Hoxb1 Hoxb4 Hoxb9 Hox Expression Patterns the A-P axis Morphogenesis at the Movies QuickTime™ and a Animation decompressor are needed to see this picture. Mouse Human Flip-book QuickTime™ and a Video decompressor are needed to see this picture. Pharyngula Stage Human Ontogeny recapitulates Phylogeny Human FGF Signaling Mutations Limb Development Flip-book Apical ectodermal ridge (FGF) Progress zone (RA) Zone of polarizing activity (SSH) RA Hox genes Segment identity Shaping Limbs Shaping the Skeleton Stem Cells Embryonic Stem Cells Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer (“Cloning”) Hello Dolly! QuickTime™ and a Sorenson Video 3 decompressor are needed to see this picture. Reprogramming Development A Few Questions for Thought: • In what ways does comparative genomics offer us a window onto understanding life? • Discuss the roles of stem cells in development and maintenance of multicellular organisms (plants as well as animals) • Compare and contrast mammalian gastrulation with the development of the other model metazoa that we have considered. • Describe, in a “big picture” way, the process of neurulation in vertebrates. • Recapitulate the complex interplay of mosaic and regulatory mechanisms in metazoan development. • How has evolution morphed simpler embryos into more complex body plans by enriching the content of regulomes and signal transduction pathways? Coda I thank all of you for the effort you continue to put into studying biological systems, into seeing the inner beauty of the cells and organisms with whom we share this planet. It has been my special privilege to be your guide. May what you have learned in this text push you to question, to pursue new knowledge and understanding, and to find the answers to life’s most interesting questions. And always remember to take time to smell the flowers! - Karl Johnson, Professor of Biology, Haverford College