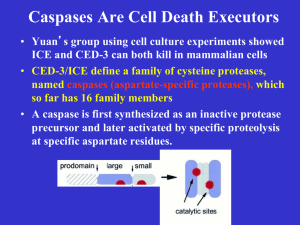
Mechanisms of Apoptosis/Review Anti-bcl
advertisement

Mechanisms of Apoptosis/Review Ribozyme Inhibition of Bcl-2 Expression/Summary Sandra A. Gibson Hudson Ph.D. APOPTOSIS “a distinct and important type of cell death” (Kerr 1971). • A regulated decision triggered by the appearance or loss of an external signal. • Cell shrinkage and apoptotic body production. Morphology Apoptosis Necrosis Purposes of programmed cell death II I Achieve and maintain normal physiology: -EMBRYONIC DEVELOPMENT -PROPER III MAINTENANCE OF CERTAIN ORGANS Checkpoint mechanisms in cell division cycle: - P53 - RB1 - SURVIVIN Survival of the organism: -RESPONSE TO EXTERNAL STIMULI Apoptotic Pathway • Cell death triggers: • Cell death receptors: • Cell death effector domains: • Cell death enforcers: • Cell death substrates: external or physiologic factors TNFR-1; FAS/APO-1/CD95 TRADD; RAIDD; FADD; RIP; FLICE caspases; endonucleases PARP; actin; DNA Multiple pathways/ Multiple mechanisms Hetts,1998 Multiple pathways/ Multiple mechanisms Jaattela, 1999 Therapeutic applications of regulating apoptosis Promote apoptosis Prevent apoptosis in cancer cells: in certain disorders and degenerative Lymphoma/leukemia diseases: Oral cancer AIDS Brain tumors Ischemia Prostate Alzheimer's/Parkinson's Colon etc. etc. Ribozyme Inhibition of Bcl-2 Expression • Apoptosis removes damaged cells from the body. The bcl-2 gene prevents this. • The role of bcl-2 in oral cancer and glioblastoma is unexplored. • We constructed a hammerhead ribozyme that would digest the bcl-2 mRNA message and delivered it to oral cancer and glioblastoma cells with an adenovirus vector. Potential applications of ribozymes in gene therapy • Inhibit viral replication • Inhibit gene expression or protein expression • Repair defective RNAs B-cell Leukemia/Lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) • Bcl-2 is an integral membrane protein with many possible functions. • Bcl-2 represses apoptotic cell death. • Bcl-2 becomes deregulated in tumor cells. • Overexpression of Bcl-2 protein allows for further genetic changes. Bcl-2 family of proteins • Bcl-2 family members participate in cell death regulation. • Heterodimerization verses homodimerization of various bcl-2 family members can help determine the fate of a cell. • Inhibiting Bcl-2 protein production in cells where it is overexpressed will eliminate a survival advantage and allow apoptosis to occur. Bcl-2 family members Anti-apoptotic: • Bcl-2 • Bcl-XL • Bcl-W • Mcl-1 • A1 (BFL-1) • Boo Pro-apoptotic: • Bax • Bad • Bak • Bik • Bid • Diva • Bim • Bcl-Xs • Hrk • Blk Viral Vectors • Retroviruses (permanent integration). • Adeno-associated viruses (permanent integration, small genome, requires helper virus for growth, nonpathogenic). • Adenoviruses (transient expression, infect non-replicating cells, large genome). • Herpes simplex virus (transient expression, infect non-replicating cells, large genome). The anti-bcl-2 ribozyme and its target Growth curves of ribozyme-infected cells TU183 cells Immunoblot of Bcl-2 protein expression in ribozyme-infected cells (24 hours) Apoptosis after 24 hour infection with Av1Rz279 or Av1LacZ4 Apoptosis after 24 hour infection with Av1Rz279 or Av1LacZ4 Summary • A hammerhead ribozyme was designed that would cleave bcl-2 mRNA. • The ribozyme was expressed from an adenovirus vector. • When oral cancer cells were infected with the vector they underwent apoptosis. • Anti-bcl-2 ribozymes offer a new approach to treatment of tumors that express Bcl-2 such as, oral cancer, lymphomas and glioblastomas. Future Directions • Use a promoter that is stronger than the MMTV promoter. • Design ribozymes with shorter and longer binding arms. • Test the ribozyme in multiple cancer cell lines. • Test the ribozyme in an animal model. • Test the ribozyme with chemotherapeutic agents.