Making Biochemistry Meaningful
advertisement

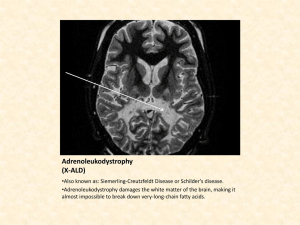
Biochemistry? I can’t do chemistry! I thought I was taking Biology!! Cell Compounds and Biological Molecules What is your favorite element? ____________________ Listen to Tom Lehrer’s Element Song to get us back to the periodic table? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DYW50F42ss8 and Daniel Radcliffe sings "The Elements" - The Graham Norton Show - Series 8 Episode 4 - BBC One http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rSAaiYKF0cs&feature=related Yikes! Biology + chemistry = ☺ . The Periodic Table (Rapping the elements!) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lDp9hUf_SV8&feature=watch_response The main elements in the human body Quick review of covalent and ionic bonding. Give each pair of students a beaker with water and one with salt. Examine salt crystals Discuss ionic bonding Dissolve table salt in water. Introduce solute and solvent. Bring out the molecules WATER Discuss covalent bonding. Make water molecules B2 Describe the characteristics of water and its role in biological systems B2.1 describe the role of water as a solvent, temperature regulator, and lubricant B2.2 describe how the polarity of the water molecule results in hydrogen bonding Peer group discussion: Is it important to study water when you are studying life? Why? Have students move molecules to show Hydrogen bonding. Show differences between water liquid, gas and solid. Some ideas http://www.johnkyrk.com/H2O.html water in a beaker to demonstrate adhesion, cohesion and surface tension. Flow of water through a tree video on Campbell textbook website. Float ice on water discuss density and point at which water is least dense Ice in an alcoholic drink Have them push the water molecules around as you discuss this. simulate What is happening here? Spark some discussion around the effect of solute on density. Water as a solvent. Hydrophilic Dissolve substances in it. Hydrophobic Add oil to their beaker of water. Fun to do: Colour eruption – child's play! Cream in a glass bowl with drops of food coloring added. Add a drop of detergent – discuss why the detergent causes the colour to disperse. This can be linked in later when proteins, fats, hydrophilic and hydrophobic substances have been studied. Science behind the storm in a saucer! Proteins and fats interact in water. A good example of this is how proteins form around droplets of butterfat in cream and whole milk, stabilizing the emulsion of fat in water. We can destabilize the emulsion by adding something that combines with fat and water better than the proteins do. Soaps and detergents do exactly that, and we can demonstrate their effect with a very colorful display. The detergent has molecules where one end likes to stay in water, and the other end likes to stay in fats and oils. Many of the proteins in the milk also have parts that are water loving (hydrophylic) and other parts that are water avoiding (hydrophobic). ( a result of various amino acids) The detergent moves in to replace the proteins at the interface between the butterfat and the water. But the detergent also attaches to the proteins at their water loving and water avoiding parts, and this changes the shapes of the proteins, and changes how the proteins attach to one another. All of this rearranging can take some time, up to several minutes, to complete. As the molecules rearrange, they push the water and the food coloring around, causing them to stir up into beautiful blossoms of color. Like dissolves like ! http://www.chemistryland.com/CHM107/Water/WaterTutorial.htm B3 Describe the role of acids, bases, and buffers in biological systems in the human body http://www.johnkyrk.com/index.html Complete a lab testing various chemicals including: Saliva Urine Tears Milk Liver potato Sodium phosphate Sodium hydroxide Hydrochloric acid Making associations! Bring out the molecules again! B4 Analyse the structure and function of biological molecules in living systems, including – carbohydrates – lipids – proteins – nucleic acids Start with making organic molecules. Isomers What was the issue with the isomer of Thalidomide? Dopamine Find some more interesting ones How are estrogen and testosterone different? Functional Groups Make Hydroxyl Carboxyl Amino group Have students make theirs and then have their peers check them. “Practice leads to mastery!” Macromolecules: monomers to polymers and back again. Carbohydrates Starch Cellulose Try mixing it in water Use examples in common Examine potato cells under vegetables Examine cellulose in potato cells and other plant cells Pull a termite apart and examine the Trichonympha the microscope – lab. Students design own lab to investigate the necessity of light in starch production. Chew a cracker until sweet Introduce amylase and maltase enzymes. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NOzwGSAPpmo Lipids Fats Phospholipids Good animation my students enjoyed http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3xF_LK9pnL0 Part of cassiopeiaproject Have a few fats and oils available. Reference made to ‘Lorenzo’s Oil’ ALD – Adrenoleukodystrophy Silly you tube video “Phospholipids on the Town” http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jdzLasyT1uc Love this one! http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/chemistry/laur eates/2003/chemanim2.mpg What is ALD? The 1992 movie "Lorenzo's Oil" brought a rare disorder called adrenoleukodystrophy (ALD) to the world's attention. It is a progressive degenerative myelin disorder, meaning that myelin, the "insulation" around nerves, breaks down over time. Without myelin, nerves can't function normally, or at all. Unfortunately, the body can't grow replacement myelin, so the disorder is progressive -- it gets worse over time. ALD is an inherited recessive genetic disorder linked to the X chromosome. Because of the way genetic inheritance works, only boys have the most severe form of ALD. The disorder leaves the body unable to break down big fat molecules, either ones the body makes itself or ones that enter the body through food. Research has shown that this is most likely due to a carrier protein that fails to work correctly and carry the fat molecules to where they would be broken down. The fat molecules build up and clog up cells, and hurt nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord. ALD affects about one in 20,000 males. One gene, called ABCD1, has been identified as being associated with ALD. Genetic testing can be done to see if a woman has the defective gene. This way, a woman who may have inherited an abnormal gene will know for certain whether or not she has it (is a carrier) and could pass it on to her children. (http://rarediseases.about.com/cs/ald/a/041301.htm) Lorenzo’s Oil Makes reference to: DNA Inheritance of genes Myelin sheath and its function Enzymes Lipids Involves Critical thinking Asking pertinent questions Synthesize concepts across disciplines Identify assumptions and biases Encourages: Researching reliable sources Advocating for self Respect for others Proteins Have students make amino acids using molecules. Add R groups to the amino acids. Have them join them together to make a polypeptide by dehydration synthesis. Simulate a primary, secondary, tertiary structure. Use the Fischer Price Toys too. Good time to introduce amino acid sequencing. Making connections: Lorenzo’s Oil and enzymes. Their bodies and their enzymes Other enzyme related conditions apart from ALD. Lactose intolerance Hormones Sickle cell anemia Co evolution with malaria Nucleic Acids Back to Lorenzo’ Oil -Discussion about DNA and coding Make models of DNA Each student or pair to make a gene. Join the gene. Change order of bases. Different protein may be coded for and result in abnormal condition. What is this all about? ♥Meaningful connections Analogies Interesting concepts ☺Having Fun Taking risks to ask if your connections are correct. Thinking critically. Involving emotions ♥ WHY? To understand your own body! The world Make good choices in later life Be more scientifically literate Take responsibility for self. Biochemistry? I can do Biochemistry! I love Biology!!