Cell Introduction
advertisement

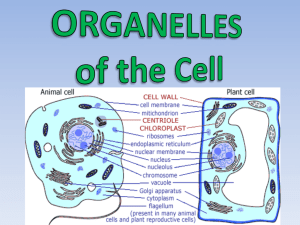
Cell Introduction 4.1 History Robert Hooke, in mid-1600’s, coined the phrase ‘cell’ after looking at cork b/c it looked like a monk’s room. Anton van Leeuwenhoek saw inside the cell. cell theory: All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic unit of structure & function of organisms Cells come from other cells SIZE average plant/animal is 10 to 50 µm (micrometer = 0.0000001 or 10-6) all nutrients enter the cell thru its surface Greater surface area allows in more nutrients (potato demo) As cell grows, its volume inc more rapidly than surface so, eventually it doesn’t get enough nutrients quickly enough to meet it’s needs SHAPE is related to function e.g. Blood cell changes shape: allows it to move thru narrow openings to isolate, engulf & destroy bacteria Cell membrane surrounds the cell Regulates movement in/out of cell http://sun.menloschool.org/~cweaver/cells/c/cell_membrane/ Note: Extracellular fluid – outside of cell Cytoplasm – inside of cell Both are watery (aqueous) environments (review) Organelles – cell parts that perform a specific function Nucleus – lg, near ctr, has genetic info & directs activities Eukaryotes – (eu = true; kary = nucleus) contains membrane bound nucleus & organelles e.g. animals & plants Prokaryotes – (pro = before; kary = nucleus) no membrane around nucleus or organelles e.g. bacterium Prokaryote Eukaryote Found only in bacteria & archaebacteria: unicellular Found in the Kingdoms: protista, fungi, plantae, & animalia No true nucleus; lacks nuclear envelope True nucleus; bound by nuclear envelope Genetic material in nucleoid Genetic material w/in region nucleus No membrane-bound organelles Contains cytoplasm with cytosol and membranebound organelles Prokaryote Eukaryote Parts of the Eukaryotic Cell 4.2 Membrane – regulates movement in/out of cell - Selectively permeable or semi-permeable Made of lipids & proteins Lipid bilayer (bi means 2) Arrangement in membrane facing outside/inside of cell (remember - Phospholipid – head is polar/tail is nonpolar -- See fig. 4-5 on pg.74) phospholipid – heads outward facing water environment so water can come in hydrating the cell while tails inward, keeping water inside steroids – between phospholipids – cholesterol in animal cells (see picture of bi-layer) Peripheral proteins – located on the edge of bilayer membrane Integral proteins – embedded in bilayer Both used for transporting molecules thru layer Fluid mosaic model membrane is dynamic acts like fluid lipids & proteins move laterally view short animations on membrane: http://telstar.ote.cmu.edu/Hughes/tutorial/cellmembrane s/ ORGANELLES Animal & Plant model - http://www.cellsalive.com/cells/cell_model.htm Cytoplasm – area between membrane & nucleus Cytosol – gelatin, aqueous fluid within cytoplasm Mitochondria (mitos = thread; chondrion = grain) “POWERHOUSE” large organelle where chemical reactions that transfer energy from organic compounds to produce ATP (molecule used by cells as main energy source) Number in cell varies – related to function of cell e.g. liver needs more b/c needs more energy Moves within cell Cellular respiration occurs here Contains enzymes to catalyze chemical reactions mtDNA (mitochondrial DNA)– grow & divide to produce new mitochondria Smooth outer membrane – lipid bilayer – permeable to small solutes; blocks macromolecules Cristae – inner membrane w/folds to enlarge surface area for chemical reactions to take place (cell respiration) New Theory – mitochondria developed because as a prokaryote it gained protection by living inside the eukaryote and in turn produced energy for the eukaryote (symbiotic relationship) Ribosomes site for protein synthesis – “PROTEIN FACTORY” constructed in nucleolus assemblage of protein & RNA (ribonucleic acid) most numerous not surrounded by membrane (found in prokaryotic cells too) free/loose in cytosol or attached to endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Ribosomes manufacture proteins based on messenger RNA (mRNA) instructions. Each ribosome reads mRNA, recruits transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to fetch amino acids, and assembles the amino acids in the proper order. endoplasmic reticulum(ER) “INTRACELLULAR HIGHWAY” – path along which molecules move w/in the cell rough ER – has ribosomes smooth ER – no ribosomes synthesis of steroids regulate calcium level in muscle cells breakdown toxic substance by liver cells Golgi apparatus – “Post Office” – processing, packaging & secreting organelle - Modifies proteins for export Lysosomes “THE CUSTODIAN” sm hydrolytic enzymes w/in membranes Acidic enviro digest proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, DNA, & RNA, even bacteria Rare in plant cells Remeber that hydrolysis breaks down the water molecule and separates a polymer into monomers, thus hydrolytic means to make eliminate water, then it becomes acidic Cytoskeleton network of lonG protein strands in cytosol to maintain shape Microfilaments – small strands Actin – protein molecules linked to form polymer chain Microtubules – lg tubes Spindle fibers – assist in the movement of chromosomes during cell division Cilia – many short hairlike extensions fr surface assist in movement - Line respiratory tract to trap particles in air e.g. nose hair Flagella – few or single long extension - e.g. sperm Nuclear matrix – gives nucleus its shape Nuclear envelope – double membrane surrounds nucleus Chromatin – combination of DNA & protein Chromosomes – formed when chromatins pack together before cellular division Nuclear pores – sm holes in nuclear envelope that allow RNA to travel to cytosol for protein synthesis Nucleolus – ribosomes are synthesized PLANT CELLS Cell wall – rigid, support & protect plant Cellulose fiber embedded Vacuoles – fluid-filled; store enzymes & metabolic wastes Plastids – contain DNA surrounded by 2 membranes Store starch/fats Absorb visible light – pigments Chloroplast – site where photosynthesis takes place Thylakoids – membranous sacs contains chlorophyll Difference btw animal & plant cells Plants have & we don’t: cell wall Vacuoles Plastids (where photosynthesis takes place) Activities cell biology - http://www.cellsalive.com/cells/cell_model.htm cell biology worksheet needed cell biology quiz http://www.biologycorner.com/bio1/cellquiz.html Multicellular Organization 4.3 Organization Tissues – organized groups of cells that carry out specific functions E.g. skin, muscle Organ – several types of tissues that interatct to perform a specific function E.g. stomach, liver, heart Organ system – group of organs that work together to perform a set of related tasks e.g. digestive system, respiratory system Colonial organisms – collection of genetically identical cells that live close together E.g. volvox Organization review from least to greatest: Cell > tissue > organ > organ system References http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/cells/animals/images/animalcell.jpg http://www.cartage.org.lb/en/themes/sciences/zoology/AnimalPhysiology/Anatomy/AnimalCellStru cture/Mitochondria/mitochondria.jpg http://images.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://publications.nigms.nih.gov/insidethecell/images/ch2 _ribosome_proteinbig.jpg&imgrefurl=http://publications.nigms.nih.gov/insidethecell/chapter2.html&h =274&w=284&sz=35&hl=en&start=10&um=1&tbnid=pGsv2UDZt4F_6M:&tbnh=110&tbnw=114& prev=/images%3Fq%3Dribosome%26svnum%3D10%26um%3D1%26hl%3Den%26rlz%3D1T4GGIC _enUS233US233%26sa%3DN http://images.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://computer.act.ac.th/webproject5_2548/st/m53/divi sion/Endoplasmic%2520reticulum.jpg&imgrefurl=http://computer.act.ac.th/webproject5_2548/st/m 53/division/menu.html&h=286&w=402&sz=44&tbnid=nCYKX9rqWjAVoM:&tbnh=88&tbnw=124& prev=/images%3Fq%3Dendoplasmic%2Breticulum%26um%3D1&start=1&sa=X&oi=images&ct=imag e&cd=1 http://library.thinkquest.org/C004535/endoplasmic_reticulum.html http://library.thinkquest.org/C004535/golgi_apparatus.html http://microscopy.fsu.edu/cells/lysosomes/images/lysosomesfigure1.jpg