Non-Mendelian
Genetics:
Vocabulary Terms…
89. Pedigree
Read 171-180
90. Sex-linked trait
91. Polygenic trait
92. Incomplete dominance
93. Codominance
94. Multiple alleles
95. mutation
Chromosomes and Human
Genetics
I.
Human Chromosomes
A.
Types
1. Sex Chromosomes – 1 pair – carry the
genes that determine male and female
features (also some non-sex traits)
1.
X and Y do not look alike but behave as a
homologous pair at meiosis
2. XX = female, XY = male
2.
Autosomes – non-sex chromosomes (22
pairs) – genes are unrelated to sex
determination
B. Determining Sex…
X
X
MOM
X
X X
X X
X Y
X Y
DAD
Y
II. Gene Location
A. Linked – Linkage Groups – genes located
so close together on a chromosome that the
traits always seem to appear together
Ex. Red hair and freckles
Ex. Colorblindness and Hemophilia
XX
B. Sex-linked Traits – genes on the sex
chromosomes
-
Expression of certain genes often appears more
in one sex than the other
Males require only one copy of a gene since
they only have one X chromosome
See Royal Families of Europe Pedigree
Ex. Eye color in fruit flies, hemophilia, colorblindness
Colorblindness Tests
X-Linked/Sex Linkage – do not
write
• Genes present on the X chromosome
exhibit unique patterns of inheritance
due to the presence of only one X
chromosome in males.
• X-linked disorders show up rarely in
females
• X linked disorders show up in males
whose mothers were carriers
(heterozygotes)
Practice Sex-linked Problems….
• What will the result of mating between a
normal (non-carrier) female and a
hemophiliac male?
• A female carrier who is heterozygous for the
recessive, sex-linked trait causing red-green
colorblindness, marries a normal male. What
proportions of their MALE progeny will have
red-green colorblindness?
• Hemophilia is inherited as an X-linked recessive. A
woman has a brother with this defect and a mother
and father who are phenotypically normal. What is the
probability that this woman will be a carrier if she
herself is phenotypically normal?
• Hemophilia is inherited as an X-linked recessive.
• A man with Hemophilia has several children with a
woman who has a normal phenotype and is NOT a
carrier. What % of the children have hemophilia?
What % are carriers?
C. Gene Interactions
1. Polygenetic trait – many genes influence
a single trait (ex. Height, intelligence)
2. Pleiotropic effect – one gene having
many effects (ex. Gene to make
testosterone)
Pleiotropy
• Expression of a single
gene has multiple
phenotypic effects
• Marfan Syndrome –
abnormal gene that
makes fibrillin (important
in connective tissues)
?
III. Genetic Analysis
A. Karyotype – visualized chromosomes
stained, squashed, and photographed at
metaphase
- They are characteristic of the species or
individual
B. Pedigree – chart showing family
relationships (see worksheet)
Pedigree Analysis
• Method of tracking a
trait through
generations within a
family.
• Good method of
tracking sex-linked
traits as well as
autosomal traits.
Sex-Linked Pedigree
• Shows gender
bias with males
exhibiting the
trait more often
than females
Autosomal Dominant Pedigree
• Autosomal dominant
traits do not skip a
generation
• Autosomal dominant
traits do not show
gender bias
Autosomal Recessive Pedigree
• Autosomal
recessive traits
skip a generation
• Autosomal
recessive traits
do not show
gender bias
IV. Non-Mendelian Genetics
1. Incomplete Dominance – blended
inheritance
-
Neither form of the gene is able to mask the
other
Ex. Snap dragon petal color
R1R1 – RED
R1R2 – PINK
R2R2 - WHITE
Incomplete
Dominance
• Neither allele is
dominant
• Heterozygotes are a
blend of homozygous
phenotypes = no distinct
expression of either
allele
Try these
• In a plant species, if the B1 allele (blue flowers) and
the B2 allele (white flowers) are incompletely
dominant (B1 B2 is light blue), what offspring ratio
is expected in a cross between a blue-flowered
plant and a white-flowered plant?
•What would be the phenotypic ratio of
the flowers produced by a cross between
two light blue flowers?
2. Codominance
• No dominance and both alleles are
completely expressed
• Ex. Cat color
• C1C1 – Tan
• C1C2 – Tabby (black and tan spotted)
• C2C2 - Black
Try These
1.
Cattle can be red (RR = all red hairs), white (WW
= all white hairs), or roan (RW = red & white hairs
together.
a. Predict the phenotypic ratios of offspring when
a homozygous white cow is crossed with a roan
bull.
b. What should the genotypes & phenotypes for
parent cattle be if a farmer wanted only cattle
with red fur?
1.
A cross between a black cat & a tan cat produces a
tabby pattern (black & tan fur together).
a. What pattern of inheritance does this illustrate?
b. What percent of kittens would have tan fur if a
tabby cat is crossed with a black cat?
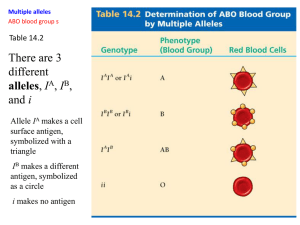
3. Multiple Alleles
• More than 2 alleles for one trait
• Ex. Eye color, hair color, blood type,
guinea pig fur color
• ABO blood groups
–
–
–
–
Each individual is A, B, AB, or O phenotype
Phenotype controlled by marker on RBC
IA and IB alleles are dominant to the i allele
IA and IB alleles are codominant to each
other
Blood Types
Blood Type:
• A
• B
• AB
• O
Genotype
• IAIA , IAi
• IBIB , IBi
• IAIB
• ii
Try These
1. If a male is homozygous for blood type B
and a female is heterozygous for blood type
A, what are the possible blood types in the
offspring?
2) Is it possible for a child with Type O
blood to be born to a mother who is type
AB? Why or why not?
3. A child is type AB. His biological mother
is also type AB. What are the possible
phenotypes of his biological father?
Human hair color follows a similar pattern:
Alleles: HBn = brown HBd = blonde hR = red hbk = black
HBnHBn = dark brown HBdHBd = blonde
HBnHBd = sandy brown HBdhR = strawberry
HBnhR = auburn
blonde
HBnhbk = dark brown HBdhbk = blonde
Dominant does NOT mean frequent!
hRhR = red
hRhbk = red
hbkhbk = black
Recessive can
be common!
V. Genetic Conditions
1. Genetic Abnormality – rare condition
with little or no ill effects
- Ex. Six fingers, albino, colorblindness
2. Genetic Disorders
• Inherited condition that results in a medical
problem
- Ex. Huntington’s Disease, Sickle Cell
Anemia, Hemophilia, Muscular Dystrophy
3. Genetic Disease
• A genetic condition that makes the individual
susceptible to infection (bacterial or viral)
- Ex. Cystic fibrosis, Down syndrome, SCID
(severe combined immunodeficiency disease =
bubble boy)
VI. Mutations
• Definition – any change in the DNA
• Possible outcomes: good, bad, or no effect
• Location:
– Somatic Cell (body cell) – can lead to cancer
– Sex Cell – reproductive organ effecting
gametes
Observed vs. Expected Ratios
• Observed Ratio – what you actually get
from two organisms having offspring – all
girls
• Expected Ratio – based on your punnett
square results – what you would expect to
get – half girls and half boys
• Example – using dice
Human Genetics Test Topics
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Sex-linked Traits
Incomplete Dominance/ Codominance
Multiple Alleles (blood typing problems)
Genetic Conditions
Sex Chromosomes vs. Autosomes
Pedigrees/Karyotypes
Observed vs. Expected Ratios
LOTS OF GENETICS PROBLEMS – SHOW
WORK!!!
Human Genetics Test Review
Questions:
My daughter is type A, my grandson is type B.
What are the blood type(s) that the father
would have to be in order for my grandson to
be type B?
Red-green color blindness is X-linked in humans.
If a male is red-green color blind, and both
parents have normal color vision, which of
the male's grandparents is most likely to be
red-green color blind?
• A. maternal grandmother
• B. maternal grandfather
• C. paternal grandmother
• D. paternal grandfather
• E. either grandfather is
equally likely
1. Suppose a child is of blood type A and the
mother is of type 0. What type or types may
the father belong to?
Suppose a father and mother claim they have
been given the wrong baby at the hospital.
Both parents are blood type A. The baby they
have been given is blood type O. What
evidence bearing on this case does this fact
have?
Hemophilia is a sex-linked recessive trait. Cross a
hemophiliac female with a normal male. Of all
their offspring, what is the probability they will
produce a hemophiliac daughter? (H = normal
blood, h = hemophilia)
A man with Type A blood marries a woman with
Type B blood. They have a type O child.
What is the probability of their 15th child
having type O blood?
A man whose father is type B and whose mother is
type A, has a blood type of A. He marries a
type A woman, whose parents had the same
blood types as his parents. What are the
genotypes of the man and the woman and what
is the probability that their first child will be
blood type A?
Coat color in cats is a codominant trait. Cats can be
black, yellow or calico. A calico cat has black and
yellow splotches. In order to be calico. the cat must
have an allele for the black color and an allele for
the yellow color. Show a cross between a calico cat
and a yellow cat. What are the possible genotypes
and phenotypes of the offspring?
A mother and father with normal color vision produce
six male children, two of whom exhibit red-green
colorblindness. Their five female children exhibit
normal color vision. Ignoring the fact that these
parents ought to seek some family planning advice,
explain the inheritance of red-green colorblindness
in their male children.
A nurse at a hospital removed the wrist tags of three babies in the maternity
ward. She needs to figure out which baby belongs to which parents, so she
checks their blood types. Using the chart below, match the baby to its correct
parents. Show the crosses to prove your choices
Parents
Blood Types
Baby
Blood type
Mr. Hartzel O
Mrs.
Hartzel
A
Jennifer
O
Mr. Simon
AB
Rebecca
A
Holly
B
Mrs. Simon AB
Mr. Peach
O
Mrs. Peach O