Multiple alleles
ABO blood group s
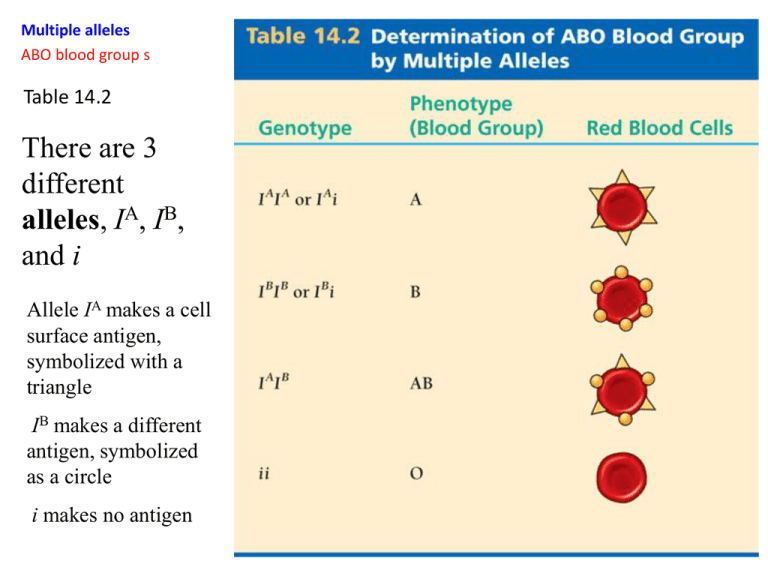
Table 14.2
There are 3
different
alleles, IA, IB,
and i
Allele IA makes a cell
surface antigen,
symbolized with a
triangle
IB makes a different
antigen, symbolized
as a circle
i makes no antigen
Multiple alleles
ABO blood group s
Human ABO Blood Groups
• Gene “I” specifies which sugar is found on the
outside of red blood cells
• 3 alleles are present in the human population:
•IA = N-acetyl-galactosamine
•IB = galactose
•i (also referred to as o) = no sugar present
• 6 possible genotypes
Multiple alleles
ABO blood group s
Immunology 101
•Sugar on the blood cell is an antigen* (A, B, A and B,
or none)
•Your immune system thinks your own antigens are fine
•Your immune system makes antibodies against non-self
antigens
•Antibodies recognize and target cells with antigens for
destruction
*something that elicits an immune response
Multiple alleles
ABO blood group s
The Human ABO Blood Group System
Multiple alleles
ABO blood group s
The Human ABO Blood Group System
multiple alleles
codominance
Multiple alleles
ABO blood group s
Codominance in the Human ABO Blood Group System
Dominance
Dominance
Codominance
Sex linked inheritance
Sex-linked traits are produced by genes only on the X chromosome.
They can be Dominant or Recessive.
A = dominant a = recessive
What would be the genotypes of a male and female that have a Sexlinked Dominant trait and do not express the trait?
Expresses Trait:
Male - XA Y
Female - XA XA or XA Xa
No Expression:
Male - Xa Y
Female - Xa Xa
What would be the genotypes of a male and female that have a Sexlinked Recessive trait and do not express the trait?
Expresses Trait:
Male - Xa Y
Female - Xa Xa
No Expression:
Male - XA Y
Female - XA XA or XA Xa
(Carrier)
Most Sex-linked traits are Recessive!
• Gene located on the X chromosome
• More males than females affected (males inherit X
from mother)
• Females can only inherit if the father is affected and
mother is a carrier (hetero) or affected (homo)
• An affected female will pass the trait to all her sons
– Daughters will be carriers if father is not affected
• Males cannot be carriers (only have 1 X so either
affected or not)
• Can skip generations (hide)
• E.g. color blindness, hemophilia, Duchene muscular
dystrophy
Sex Linked Problems:
• Red-green color blindness in men is caused by the
presence of a sex-linked recessive gene c, whose
normal allele is C.
a) Can two color blind parents produce a normal
son?
b)Can they produce a normal daughter?
c) Can two normal parents produce a colorblind son
or daughter?
d)Can a normal daughter have a colorblind father
or mother?
e) Can a colorblind daughter have a normal father
or mother?
Sex influenced traits
• A phenotypic characteristic or trait that is
expressed differently in males and females
– male pattern baldness
How to Construct a Pedigree
• A Pedigree is a visual showing the pattern of
inheritance for a trait. (Family tree)
•
•
•
•
Symbols and Rules:
Male =
Female =
Affected =
Unaffected =
Carrier =
Link parents together with a line and then make
a vertical line to connect to offspring.
Autosomal Dominant Pedigree
• Draw a Pedigree showing a cross between
Heterozygous parents that have 2 boys and 2
girls. (Show all possibilities)
Genotypes of Affected and Unaffected:
• AA and Aa = Affected aa = Unaffected
Aa
aa
Aa
Aa
Aa
AA
Autosomal Recessive Pedigree
• Draw a Pedigree showing a cross between
Heterozygous parents that have 2 boys and 2
girls. (Show all possibilities)
Genotypes of Affected and Unaffected:
• AA=Unaffected Aa=Carrier, Unaffected
aa=Affected
Aa
aa
Aa
Aa
Aa
AA
Sex-Linked Recessive Pedigree
• Draw a Pedigree showing a cross between a Red
eyed Male fruit fly and a Carrier Female fruit fly
which have 2 males and 2 females. (Show all
possibilities) Red is dominant to white.
• Genotypes of Parents:
• Male = XR Y Female = XR Xr
XRY
XRY
XRXr
XrY
XRXR
XRXr
Characteristics of Autosomal Dominant, Autosomal
Recessive, and Sex-linked Recessive Traits
• In groups, analyze your notes on each type of
disorder and examine the pedigrees.
• Come up with rules/characteristics for each
type of Trait.
Autosomal Dominant Traits
• Heterozygotes are affected
• Affected children usually have affected parents.
• Two affected parents can produce an unaffected
child. (Aa x Aa)
• Two unaffected parents will not produce affected
children. (aa x aa)
• Both males and females are affected with equal
frequency.
• Pedigrees show no Carriers.
Autosomal Recessive Traits
• Heterozygotes are carriers with a normal phenotype.
• Most affected children have normal parents. (Aa x Aa)
• Two affected parents will always produce an affected child.
(aa x aa)
• Two unaffected parents will NOT produce affected children
unless both are carriers. (AA x AA, AA x Aa)
• Affected individuals with homozygous unaffected mates will
have unaffected children. (aa x AA)
• Close relatives who reproduce are more likely to have affected
children.
• Both males and females are affected with equal frequency.
• Pedigrees show both male and female carriers.
Sex-Linked Recessive Traits
• More males than females are affected.
• An affected son can have parents who have the
normal phenotype. (XAY x XAXa)
• For a daughter to have the trait, her father must also
have it. Her mother must have it or be a carrier.
(XaY, XaXa, XAXa)
• The trait often skips a generation from the
grandfather to the grandson.
• If a woman has the trait (XaXa), all of her sons will be
affected.
• Pedigrees show only female carriers but no male
carriers.
Polygeny
Polygenic inheritance: additive effects (essentially,
incomplete dominance) of multiple genes on a single trait
AA = dark
Aa = less dark
aa - light
And similarly for the
other two genes - in all
cases dominance is
incomplete for each
gene.
Think of each “capital”
allele (A, B, C) as adding
a dose of brown paint
to white paint.
Environmental effects
• environment often influences phenotype
• the norm of reaction = phenotypic range due to
environmental effects
• norms of reactions are often broadest for polygenic
characters.
Blue require low pH
Environmental effects
Environmental effects: effect of temperature
on pigment expression in Siamese cats












