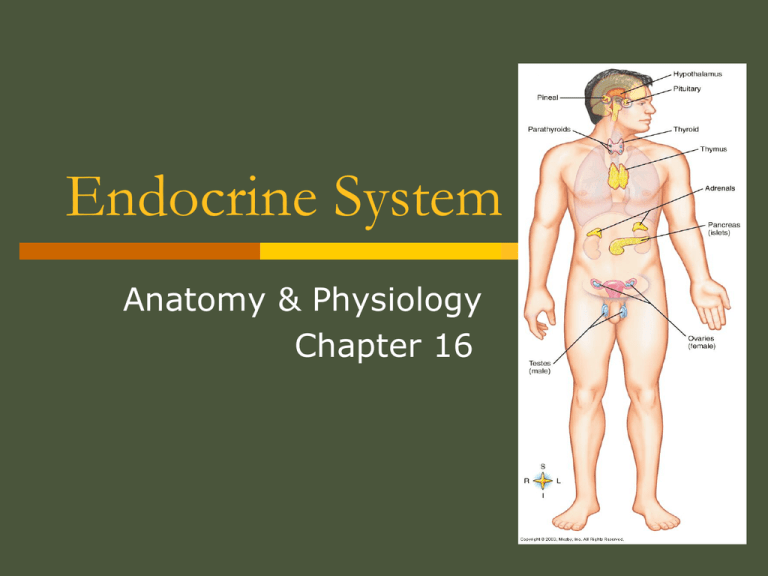
Endocrine System
Anatomy & Physiology
Chapter 16
Endocrine vs. Nervous System
See Table 16-1
Classification of hormones by chemical
structure
Steroid hormones
Derived from
cholesterol
Lipid-soluble
Pass through plasma
membranes easily
Nonsteroid hormones
Synthesized primarily from amino acids
Protein hormones: long chains of amino acids ex:
insulin, PTH
Glycoproteins: protein hormones with a
carbohydrate group attached ex: FSH, LH
Peptide hormones: short chain of amino acids ex:
oxytocin, ADH
Amino acid derivatives: derived from a single
amino acid
Amine hormones: derived from tyrosine ex:epinephrine
Iodine added to tyrosine ex: thyroid hormones
General Principles of Hormone Action
Bind to a specific receptor on cell by “lockand-key” mechanism
Some hormones are attached to plasma
proteins in bloodstream
Since blood carries hormones most
everywhere lots more produced than
makes it to its target
Mechanism of steroid hormone action
(Mobile-receptor hypothesis)
Attach to soluble
plasma proteins in
blood
Receptors usually found
within the cell
Regulate cells by
regulating production of
certain critical proteins
Amount of steroid
hormone present
determines magnitude
of target cell’s response
Response to steroid
hormones often slow
Mechanisms of Nonsteroid Hormones
Second messenger mechanism: also called
fixed-membrane-receptor hypothesis
Nuclear receptor mechanism
Second messenger mechanism
Binds to receptors on
target cell’s plasma
membrane
Then second
messenger within cell
triggers appropriate
cellular changes
Most use cAMP as
second messenger
Operates more quickly
than steroid
mechanism
Nuclear receptor mechanism
Small iodinated amino acids (T3 & T4)
Enter target cell & bind to receptors
associated with DNA which triggers
transcription of mRNA
Regulation of hormone secretion
Usually part of a negative feedback loop
and is called endocrine reflexes
Endocrine cells often sensitive to changes
produced by its target cells
May be regulated by hormone produced
by another gland, esp pituitary gland
May be influenced by nervous system
input
Prostaglandins
Lipid molecules
Tissue hormones: secretion produced in
tissues & diffuse short distance only to
other cells in same tissue
Tissues known to secrete prostaglandins:
kidneys, lungs, iris, brain, thymus
Vocabulary Words
Hormone
Synergism
Permissiveness
Antagonism
Tropic hormones
Sex hormones
Anabolic hormones
Pituitary Gland
Pituitary gland (Hypophysis)
Lies within sella
turcica of skull
Connected to the
hypothalamus by a
stalk, infundibulum
Consists of 2 different
glands
Adenohypohysis or
anterior pituitary
Neurohypophysis or
posterior pituitary
Anterior Pituitary
Two parts
pars anterior: major part
pars intermedia
5 types of secretions
Somatrophs-secrete GH
Corticotrophs-secrete ACTH
Thyrotrophs: secrete TSH
Lactotrophs: secrete prolactin
Gondatrophs: secrete LH and FSH
Growth Hormone (GH)
Promotes
promotes
Promotes
Indirectly
Indirectly
protein anabolism thus
growth of bones, muscles
lipid mobilization & catabolism
inhibits glucose metabolism
increases blood glucose levels
Prolactin (PRL)
During pregnancy promotes breast
development
After birth stimulates mammary gland to
begin milk secretion
Tropic hormones
Have stimulating effect on other endocrine
glands
Thyroid stimulating hormone: TSH
Adrenocorticotropic hormone: ACTH
Follicle stimulating hormone: FSH
Luteinizing hormone: LH
TSH
Maintains growth & development of
thyroid gland & causes it to secrete its
hormones
ACTH
Promotes & maintains normal growth of
cortex of adrenal gland & stimulates it to
secrete some of its hormones
Gonadotropins
Stimulate growth & development of
gonads
FSH: stimulates follicles (with ovum) to
maturity, also stimulates follicle to secrete
estrogen; in male: stimulates
development of seminiferous tubules
LH: stimulates formation of corpus
luteum; in males: stimulates interstitial
cells in testes to develop & secrete
testosterone
Control of secretion of anterior pituitary
Hypophyseal portal
system: complex of
small blood vessels
between hypothalamus
& anterior pituitary
Hypothalamus secretes
releasing hormones
through this system
During times of stress
cerebral cortex can
send impulses to
hypothalamus to
secrete releasing
hormones thus mindbody link
Posterior pituitary
Storage & release site
for:
ADH (antidiuretic
hormone)
Oxytocin
Hormones are not
made within the
pituitary but within
the supraoptic or
paraventricular nuclei
of hypothalamus
Release of these
hormones thus
controlled by nervous
stimulation
Antidiuretic hormone
Prevents formation of a large volume of
urine
Release triggered by osmoreceptors near
supraoptic nucleus
Oxytocin
Stimulates contraction of uterine muslces
Causes ejection of milk from breasts
Regulated by a positive feedback
mechanism
Pineal gland
Located on dorsal surface of brain’s
diencephalon
Member of both nervous system &
endocrine system
Produces melatonin, functions to support
biological clock
Thyroid gland
In neck, on anterior &
lateral surface of
trachea just below the
larynx
Composed of
structural units called
follicles
Hormones:
Thyroid hormones
Calcitonin
Thyroid hormones
T3: principal thyroid hormone
T4: most abundant, precursor of T3
Thyroid gland stores thyroid hormone as
thyroglobulins
Regulate metabolic rate of all cells
Calcitonin
Produced by parafollicular cells of thyroid
Influences processing of calcium by bone
cells by decreasing blood calcium levels
Antagonist to parathyroid hormone
Parathyroid gland
4-5 of them
embedded on
posterior surface of
thryoid’s lateral lobes
Hormone: PTH
(parathryroid
hormone)
PTH
Antagonist to calcitonin
Acts on bones & kidneys to increase blood
calcium
Bones: calcium & phosphate released from
bones
Kidneys: calcium reabsorbed, phosphate
secreted, activates Vitamin D in kidney
which permits Ca to be absorbed in
intestine
Adrenal glands
On top of kidneys
Adrenal cortex: outer
part
Zona glomerulosa:
mineralocorticoids
Zona fasiculata:
glucocorticoids
Zona reticularis:
gonadocorticoids
Adrenal medulla: inner
portion
Mineralocorticoids
Aldosterone: important
mineralocorticoid
Primary function is
maintenance of sodium
homeostasis by
increasing sodium
reabsorption in
kidneys
Increase water
retention & promotes
loss of potassium
Secretion controlled by
renin-angiotensin &
blood potassium
concentration
Glucocorticoids
Cortisol most significant
Affect every cell in body
Protein mobilizing, lipid catabolism as
energy source, secretion increase in times
of stress, essential for maintaining normal
blood pressure, decrease in number of
WBCs
Gonadocorticoids
Secretes small amounts of male hormones
Released from zona fasiculata & zona
glomerulosa
Influences appearance of pubic & axillary
hair
Adrenal medulla
Composed of neurosecretory tissue
Produce epinephrine & norepinephrine
Prolong & enhance effects of sympathetic
stimulation (fight or flight response)
Pancreas
Endocrine portion: pancreatic islets (or
islets of Langerhans)
Alpha cells: secrete glucagon
Beta cells: secrete insulin
Delta cells: secrete somatostatin
Pancreatic polypeptide cells: secrete
pancreatic polypeptide
Glucagon
Increase blood glucose levels by
stimulating conversion of glycogen to
glucose in liver cells
Also stimulates gluconeogenesis in liver
Hyperglycemic effect
Insulin
Promotes movement of glucose, amino
acids, fatty acids into tissue cells
Lowers blood glucose
Somatostatin
Regulates other endocrine cells of
pancreatic islets by inhibiting secretion
Gonads
Primary sex organs
Males: testes
Females: ovaries
Testes
Interstitial cells within testes produce
testosterone
Responsible for growth & maintenance of
male sexual characteristics & for sperm
production
Ovaries
Estrogens: secreted by follicles, promote
development & maintenance of female
sexual characteristics, breast
development, menstrual cycle
Progesterone: secreted by corpus luteum,
maintains lining of uterus necessary for
pregnancy
Placenta
Produces human chorionic gonadotropin
(hCG), serves as a signal to maintain
uterine lining for pregnancy
Temporary endocrine gland
Thymus
Atrophies at puberty
Produces thymosin & thymopoietin
Stimulate production of T cells
Gastric & Intestinal Mucosa
Secretin: reduce acid secretion, triggers
pancreas to produce bicarbonate
CCK: trigger pancreas to release digestive
enzymes, gall bladder contraction
Ghrelin: stimulates hypothalamus to boost
appetite
Heart
Atrial natriuretic hormone (ANH):
promotes loss of sodium in urine thus it
opposes increase in blood volume or blood
pressure
Antagonistic to ADH & aldosterone