Chapter 3 * The Biosphere
advertisement

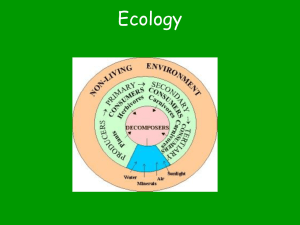
Chapter 3 – The Biosphere interact All organisms __________with the environment to understand these_______________, interactions we study ecology _________= the scientific study of interactions among organisms Ecology and between organisms and their environment (surroundings) organization Ecology is all about ________________ this leads to a better understanding of the interactions that take place _____________ = the combined Biosphere portions of the planet in which all life exists, including land, water, air, or atmosphere There are 5 levels of organization within the biosphere; a species, populations, communities, ecosystems, and biomes 1. Species Species = a group of organisms so similar to one another that they can breed and produce offspring an individual most This levels of organization looks at just _________________ of the time 2. Population Population = a group of individuals that belong to the same species and live in the same area at the same time 3. Communities Communities = assemblages of different populations that live together in the same area at the same time 4. Ecosystem Ecosystem = collection of all the organisms that live in a certain area, together with the nonliving (physical) environment 5. Biome Biome = a group of ecosystems that have the same climate and similar dominant communities Ecologists use a wide range of tools and techniques to study the living world The 3 basic approaches ecologist use are _____________, observing __________________, and ____________ experimenting modeling In order for organisms to interact, they need energy! Sunlight is the main source of energy for life on Earth ____________ Some types of organisms rely on energy stored in ___________ inorganic __________________________ chemical compounds Autotrophs = organisms that can capture energy from the ________________ sun or chemicals to produce food producers They are also called ______________ Includes plants, some algae, since they make their own food and certain bacteria start Producers help _______the flow of energy through the biosphere photosynthesis to use light Most autotrophs we think of use ___________________ energy to power chemical reactions that produce carbs Photosynthesis adds ___________ oxygen to the atmosphere and removes CO _____2 Land plants, as well as algae that remain in the sunlit portion of aquatic environments use photosynthesis chemosynthesis Some autotrophs use ____________________ (chemical reactions) to produce carbs Many ___________ bacteria use chemosynthesis Heterotrophs = organisms that rely on other organisms _________________ for energy and food supply They are also called consumers There are several different types of heterotrophs 1. ______________ Herbivores – only eat plants (cows, caterpillars, deer) 2. Carnivores _____________ – only eat animals (lions, snakes, owls) Omnivores – eat both plants and 3. ______________ animals (humans, bears, crows) Detritivores 4. ________________(scavengers) – feed on animal and plant remains and other dead matter (vultures) 5. _________________– Decomposers break down organic matter (bacteria and fungi) Energy flows through ecosystems in one direction; sun/inorganic compounds autotrophs heterotrophs _____________ Food chain = a series of steps in which organisms transfer energy by eating or being eaten In a food chain, the arrows point in the direction in which energy is _______________ transferred The amount of energy remaining is _______________ only a portion of what was available at the first transfer Ex. Grass antelope coyote ____________ Food web = shows the complex network of interactions within an ecosystem Food webs link the food chains in an ecosystem together Food webs can be ________________ very complex because 1 producer can be food for several consumers and 1 consumer can feed on several types of producers as well as other consumers Trophic level = each step in a food chain or food web ________________ Producers are the 1st trophic level _____________ Consumers make up the 2nd, 3rd, ______________ or higher trophic levels Each consumer depends on the trophic level below for energy pyramids Ecologist have come up with ecological ______________________ to model energy or matter in an ecosystem _______________________ Ecological pyramids = a diagram that shows the relative amounts of energy or matter within each trophic level in a food chain or web There are 3 types of pyramids; energy, biomass, numbers 1. Energy pyramid – shows the amount of energy available at each trophic level 10% of the energy gets passed from one trophic Only about _______ level to the next The transfer amount is small because organisms use much of respiration the energy they obtain for basic processes like ______________, _____________, and ________________ movement reproduction The more trophic levels, the ______ less energy reaches the top 2. Biomass pyramid – shows the total amount of living mass (biomass) in a given trophic level Biomass is usually expressed in grams per unit area It represents the amount of potential ______ food available for each trophic level 3. Pyramid of numbers – shows the number of individuals at each trophic level Sometimes the shape of the numbers and biomass pyramid are the same because ______________________ lots of individuals produce food for a _________________ lesser number of consumers Sometimes a numbers pyramid can be upside down when ____ one producer can be food for ____________________ many consumers (Ex. one trees _____________ feeds many insects) Section 3-3: Cycles of Matter Organisms need more than just energy to survive they need nutrients too! Energy only flows one way, but matter is _________________________ recycled within and between ecosystems ___________ Biogeochemical cycles = connect __________________________ biological geological, and chemical aspects of the biosphere to help recycle matter Matter is never used up, it is transformed that is why it can be recycled The water cycle is very important because all living things require water to live! evaporates (liquid to gas) from lakes and oceans Water _______________ and becomes ________________ water vapor Plants release water vapor through transpiration breathe (also when Animals release water vapor when they __________ they perspire/urinate) As water cools high in the atmosphere, it condenses on dust in the air to form clouds Eventually the water vapor _____________ condenses enough to fall as _________________ precipitation ______________ Nutrients = all chemical substances that an organism needs to sustain life Every living organism needs nutrients to build tissues and carry out essential life functions carbon ____________, nitrogen and _______________ The_________, phosphorus cycles are important nutrient cycles (oxygen is involved in each) The carbon cycle! – we have already learned that carbon is a very important element Carbon takes many forms and is a key ingredient of _______________ living tissue 4 main processes move carbon through its cycle Biological processes like 1. _____________ photosynthesis, respiration, decomposition Geochemical processes like erosion and volcanic activity 2. _________________ 3. ____________________________ Mixed biogeochemical processes like burial and decomposition of dead organisms 4. _____________________ Human activities like mining, cutting/burning forests, and burning fuels The nitrogen cycle! – nitrogen is essential for amino acids and protein building There are many different naturally occurring forms of nitrogen 78% nitrogen, most plants can’t use it – even though the air is _____ Certain bacteria _________ on plant roots can help convert the nitrogen in the air to usable nitrogen in ammonia (_____________________) nitrogen fixation Animals eat plants and use the nitrogen proteins for various form muscles uses (__________________) When animals _________, urinate nitrogen is released back into the soil dies for plant use (the same thing happens when an animal ______) Some soil bacteria convert nitrates into nitrogen gas through denitrification The phosphorus cycle! – phosphorus is important in the formation of DNA and RNA Phosphorus cycles in 2 ways ______________ – when animals die, phosphorus is returned to Short-term the soil to be used again ______________ Long-term – phosphates get incorporated into rock and other insoluble compounds – millions of years later that rock becomes exposed and erodes, releasing the phosphorus back into the local system Since nutrients are so important to ecosystems, they can sometimes be limiting _________________________ Primary productivity of an ecosystem = the rate at which organic matter is created by producers Sometimes an ecosystem is limited by a single nutrient Primary productivity is limited by (_____________________) limiting nutrient available nutrients Oceans are considered __________________ nutrient-poor compared to land An _______________ algal bloom can occur when a large amount of the limiting nutrient is introduced to an aquatic ecosystem These blooms can disrupt the equilibrium of a system ________________ Grand Lake on July 1st, 2011